Steemit Crypto Academy – Season 3 - Week 8 - Post for @stream4u: Lets Open the CryptoGraphy.
Homework: Let's Open The CryptoGraphy.
Professor: @stream4u
Written by @chinma

Picture from source

1. Explain the Blockchain CryptoGraphy and mention few names which are the Blockchain Platforms
Breaking the term "Crypto-graphy" into two words,:
- Crypto
- Graphy
Can be individually defined as Crypto: "secret" from greek origin: kryptos meaning ‘hidden’.
Then Graphy, from greek origin "-graphia" meaning ‘writing’.
Adding these two words, we have Crypto-graphy meaning: Secret Writing.
So Cryptography is simply the making information shared between two or more parties secret and away from the reach of malicious and/or unintended third parties.
The applications of cryptography range from simple mail messages to blockchain networks and even data on websites and databases. Block Chain Cryptography is the application of this art to communication between parties in a blockchain network such that the information between them remains private through the use of "encryption", "decryption" and "public and private" keys.
Encryption is the process of transcribing the message or data to a non readable format such that it becomes only a computer language, while decryption refers to the reverse process back to plain text.
Two major keys are known in asymmetric (as we shall be treating in this article) blockchain cryptography, they are the public key and private keys, I will be explaining below;
Examples of Blockchain Networks are:
- Ethereum blockchain
- NEO blockchain
- Steem blockchain
- Monero blockchain
- Tron blockchain

2. Explain the Public Key CryptoGraphy.
The public key is a message decryption key, it also creates the address for sending of information through cryptography. The public key is known to both the sender and the recipient as to be able to encrypt and decrypt the message respectively. Blockchain public keys are usually formed from their unique private key in a near non reversible process. This helps to avert malicious third parties from acquiring private keys from user public keys.
Public Key example, Picture from source

3. Explain the Private Key CryptoGraphy.
The private key as its name sounds is a very personal key, only to be known to its owner. The private key is used in encrypting messages and signing digital signatures. The private key is to be known to only its owner and to be stored securely.
Like on our Steemit account, with different keys for different purposes which are to be kept secretly, so also is our private key. More like our Master key which can be used for both transfer of Steem and other account purposes under the Steem platform.
Private Key example, Picture from source

4. Explain the Digital Signatures CryptoGraphy and what is Singing Of Transaction/Message?
Just as everyday post letters have stamps are further proof to the receiver of where the letters are coming from, Cryptography has digital signatures.
I will call a Digital signature a trust stamp, one that removes cases of malicious messages and more a verification of trust that the sender is aware and did perform that transaction(send that message). the receiver on getting the message is able to decode the sender using the digital signature, then uses public key to decrypt the message.
Signing of transactions are basically a process of verifying a transaction before it is sent to the pool for miners to validate the transaction, and then confirmed on a block. This makes that transaction immutable and validated.
Signing a transaction is done by the sender, who uses his private key for this action. the receiver can then verify the transaction from the blockchain using his public key.

5. Explain what is Symmetric and Asymmetric cryptography?
With the encryption and decryption of information in cryptography, there needs to be a form of access to the information in question. Cryptography has in place two methods of encrypting and accessing its private information, they are;
Symmetric Cryptography:
Symmetric meaning equal sides, or identical sides, in cryptography it is a case where both the sender and receiver share a key for encrypting and decrypting the information.
This method of encryption key eases CPU memory usage since it is the same key, and also saves time, but it suffers the problem of scalability. This is exemplified by simple encryption of mail messages between users who intend to keep the message private.
Asymmetric cryptography:
Asymmetric cryptography is a method of private information sharing through cryptography where both parties have different private and public keys. Here information sharing now involves the receiver sharing his public key with the sender, then the sender encrypting the information with his private key to that public key.
The receiver may now be able to decrypt the information with his public key creating a tighter security system and better scalability. This is exemplified in Blockchain networks like the Bitcoin network.

6. How Blockchain Wallets CryptoGraphy works and explains the available types of Crypto Wallets.
Similar to our everyday wallets which contain our assets and private information, assets on Blockchain networks are available to users on their wallets. These wallets also contain the private key, which is the unique and personal identifier of each user on the network, and as explained earlier, is used in signing off on transactions. Wallets as we have established contain sensitive information that must be kept safe. The safety of wallets that are constantly in the glare of the internet, which are referred to as hot wallets, are usually called into question as they're available to hackers. This has given birth to cold wallets which are an offline way of storing sensitive private keys. In this method, signatures are taken offline to be signed before taken back to the network and broadcasted. Examples of cold wallets could be USB drives or paper wallets that can be scanned to sign.

7. What is the Merkle trees and What its importance in blockchain?
With the fast expanding use of blockchain technology and the bitcoin network, there is a need for a scalable algorithms for verifications of transactions, one that simplifies transactions to a single block saving processing time, CPU energy , data and more making it easy to confirm transactions just by going through a single block.
What am I trying to explain.
The Merkle tree algorithm makes different transactions within the blockchain come together under a single block by concatenating them forming an even number of pyramidal downline blocks that join together after their transactions have been hashed.
This method of information storing uses the Merkle root and Merkle leafs pyramid structure, where data is read from "down-up". From the leafs which are individual blocks to the root which is like the "Mother block". Here leaf blocks are coupled together such that if an odd number of blocks are formed, a block is doubled and then coupled together.
This couples are linked to one block ontop as a pyramid form, and the process continues till it gets to the mother block.
This way the mother block (Root Block) contains all the information of the subsidiary blocks under it.
Importance of Merkle Tree in Blockchain
The Merkle tree saves users a lot of time to crosscheck transactions in a single block in the very voluminous Block chain network.

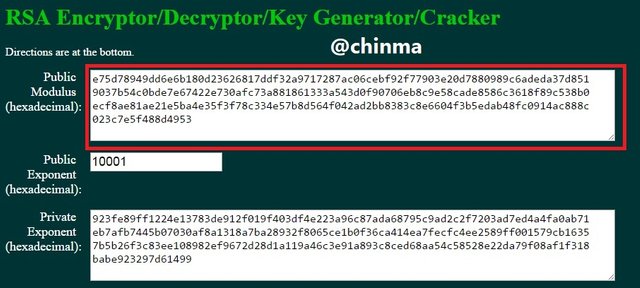
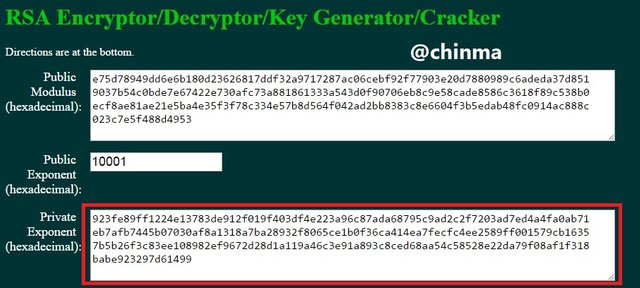
8. Practical + Theory, do some practical research, study on Blockchain Demo: Public / Private Keys & Signing and then explain the functionality of Key, Signature, Transaction, Blockchain with proper screenshots of yours practical.
Keys, asymmetric as we are treating in this article are of the public and private keys. In the page shown below, we see that the public key is tagged to the private key.
Screenshot from andersbrownworth.com
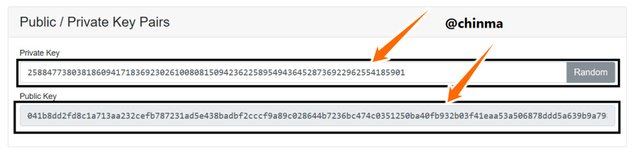
Now I try to check if really each public key is unique to a private key by changing the private key to a number (randomly)
Screenshot from andersbrownworth.com
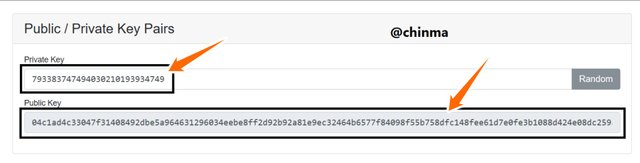
This which shows a change in the public key, and so verifies the fact that public keys are linked to private keys can be checked again by clicking on the random button to generate a totally random private key.
A new public key is generated.
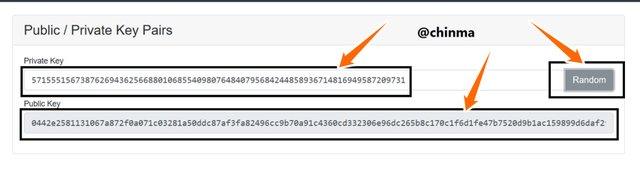
Screenshot from andersbrownworth.com
Signatures
Signature which are like stamps, or bank signatures on cheques but on a cryptographic message as form of verification of sender to receiver of the crypto message. Can be seen on the page below where we have the Message, the Private key and the Message signature boxes:
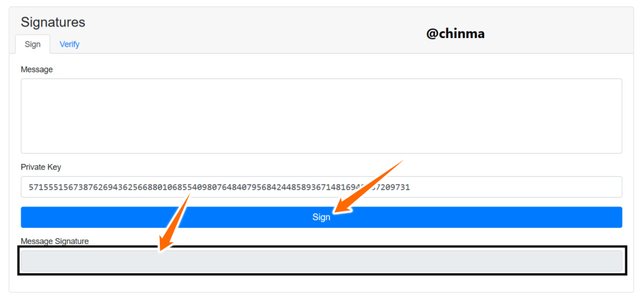
Screenshot from andersbrownworth.com
The message signature box is left empty and cant be manually filled because there is no message and it hasn’t been signed.
Screenshot from andersbrownworth.com
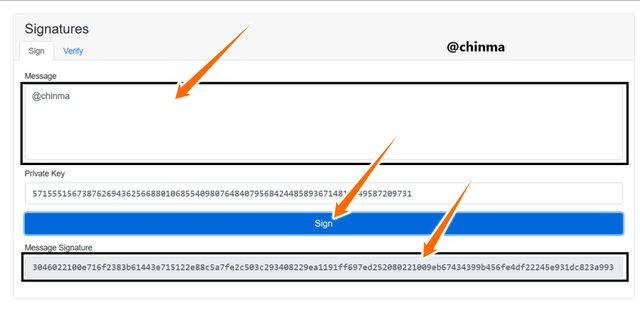
Now filling the message box with @chinma, we still find that the message signature is still empty because it still hasn’t been signed.
Screenshot from andersbrownworth.com
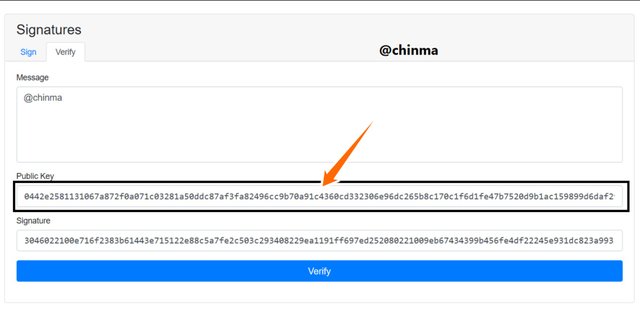
On signing the message, we see that it gives us a message signature, we can now head for verification.
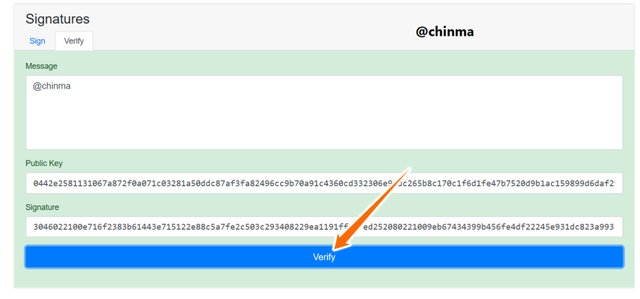
Screenshot from andersbrownworth.com
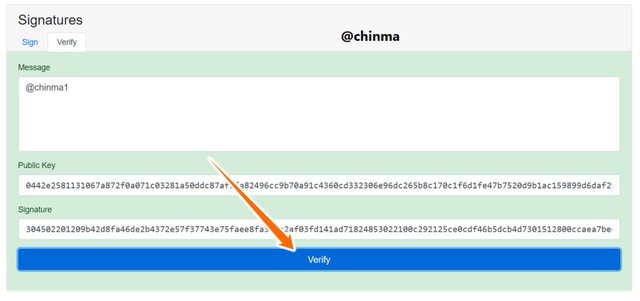
We can now see that the verification is menu is showing that it is verified
Screenshot from andersbrownworth.com
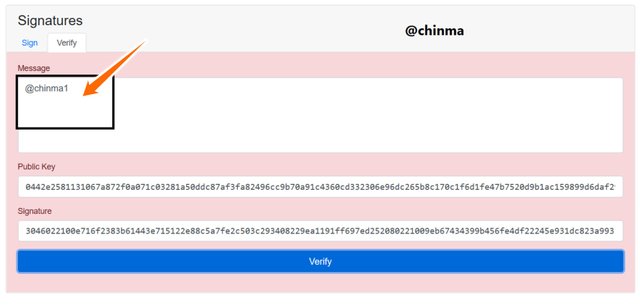
On changing message by only adding a 1 to the @chinma, we see that the verification becomes void and we need to go back again to resign the message for reverification.
Screenshot from andersbrownworth.com
Transactions:
The transaction page on the website gives a better understanding of how blockchain cryptography works. Here we have the Message, From, To and Message Signature boxes, with the Sign button.
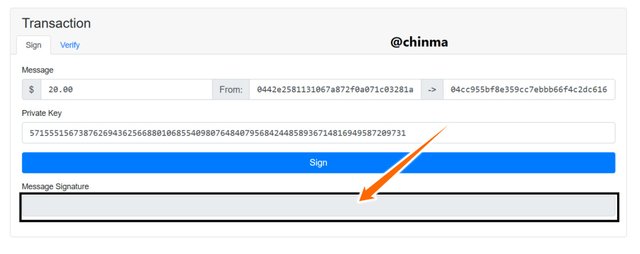
Screenshot from andersbrownworth.com
On our transaction page we are going to make a transaction from:
Public key:0442e2581131067a872f0a071c03281a50ddc87af3fa82496cc9b70a91c4360cd332306e96dc265b8c170c1f6d1fe47b7520d9b1ac159899d6daf29357e7f1c0f3
to Public key:0442e2581131067a872f0a071c03281a50ddc87af3fa82496cc9b70a91c4360cd332306e96dc265b8c170c1f6d1fe47b7520d9b1ac159899d6daf29357e7f1c0f3
of $20 with Private key:57155515673876269436256688010685540980764840795684244858936714816949587209731
And with Signed Message address:3046022100b4cb06fd2c089b2ba97cea12040ff73d7be67f3e47db67b9e1e4f294dd2a71e9022100b78e815eaf4c7a68a4409d15735f8700a8c1bff1eae37f39fcc7bfd57911d8d8
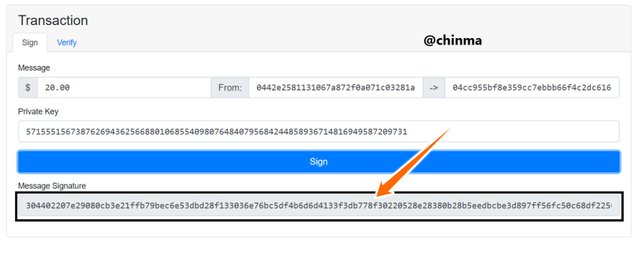
Screenshot from andersbrownworth.com
To verify, we go to the verify page and click on verify:
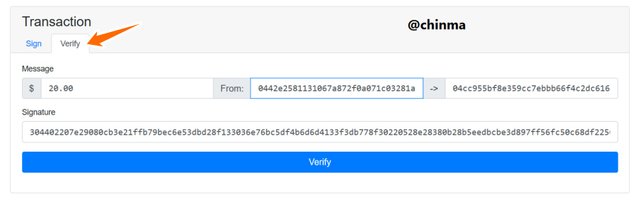
Screenshot from andersbrownworth.com
if we change the amount transferred and try re-verifying it, we see that it shows us a wrong verification.
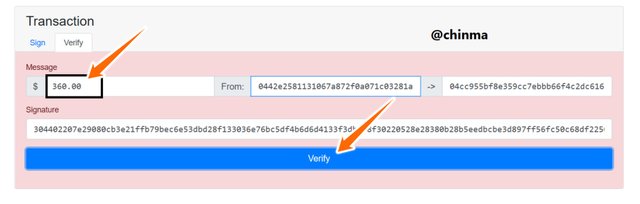
Screenshot from andersbrownworth.com
We have to now go back and resign the message for a new message - signature then re-verify.
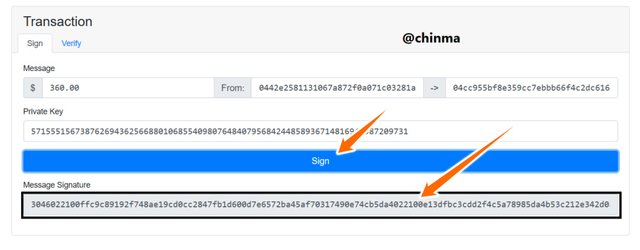
Screenshot from andersbrownworth.com
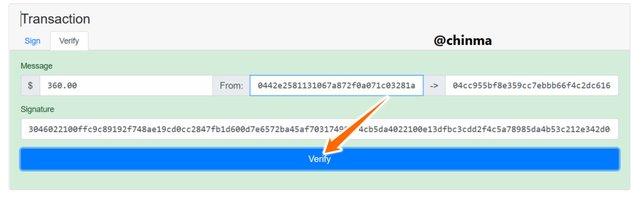
Screenshot from andersbrownworth.com
Blockchain
For the blockchain demonstration, we have the page below which gives us a good analysis of how blockchain works.
We have for every blockchain:
Block:, Nonce, Transaction(coinbase), Previous, Hash.
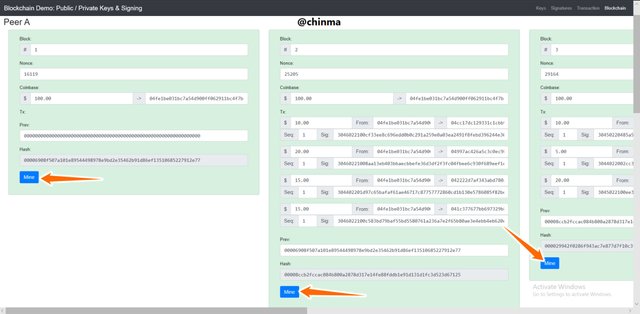
Screenshot from andersbrownworth.com
Above we see all the blocks have been mined successfully.
Screenshot from andersbrownworth.com
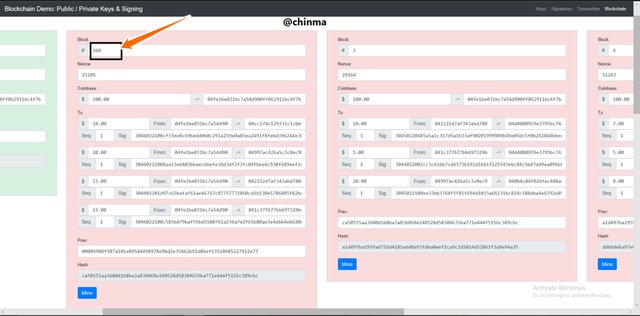
Making a new transaction on a previous block affects it and other blocks following.
Screenshot from andersbrownworth.com
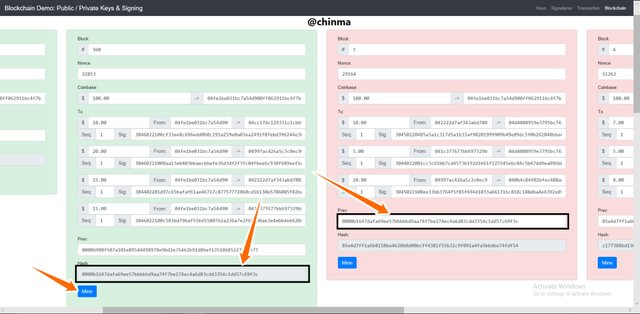
We now have to re-mine the block and blocks following it.
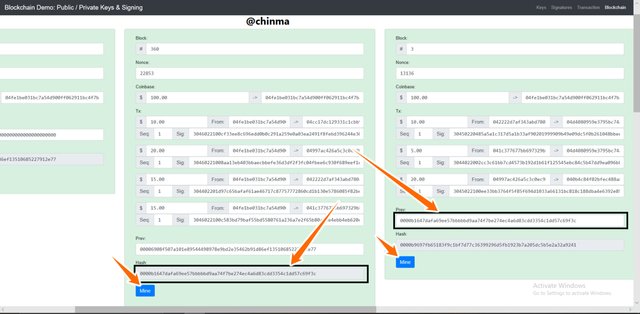
Screenshot from andersbrownworth.com

Cryptography is a wonderful technology, just like the example in the lecture, likes of Warren Buffet no longer have to be scared of privacy infringement in their messages.
Merkle tree, makes crypto data accessibility very easy and saves alot of time and energy. Private and public keys are the aysmmetric method of encrypting and decrypting messages.
Thanks @stream4u