Crypto Academy Week 16 - Homework Post for [@Pelon53]... Hashgraph Technology

HASHGRAPH TECHNOLOGY
Hashgraph technology is a compelling successor to blockchain and has earned the nickname 'Blockchain-Killer'. It is a decentralized and public distributed ledger that seeks to surpass blockchain by providing solutions to faster transaction speed, lower transaction fees, organized governance, and higher security among others.
Hashgraph technology is employed on the Hedera blockchain and its consensus algorithm is based on the following key concepts: Transactions, Fairness, Gossip, Hashgraph, Virtual voting, and Famous witnesses.
These concepts have proven efficient against Proof of Work(PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus algorithms.
Hashgraph Gossip Protocol
To provide the fastest and most resilient medium to validates transactions, the common and most effective human means which is gossip was adopted. Indeed, gossip spreads as fast as wildfire, and Hashgraph Gossip Protocol is no different. With gossip as a blueprint, Hashgraph created the gossip protocol using a history ledger known as gossip-about-gossip.
Gossip about gossip - the hashgraph is spread through the gossip protocol. The information being gossiped is the history of the gossip itself, so it is “gossip about gossip”. This uses very little bandwidth overhead beyond simply gossiping about the transactions alone.
source
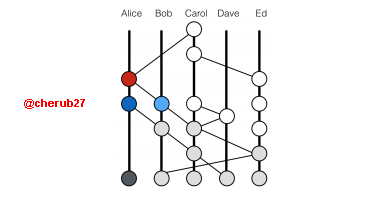
From, the screenshot, let's assume Alice, Bob, Carol, Dave, and Ed are separate nodes on the system. Alice gets wind of information and tells Bobs all she knows and in return, Bobs also shares his information with Alice. They both move on to share their information along with the newly acquired information to the other members and the cycle continues randomly. In the end, everyone will know everything each member knows and every new information spreads quickly to all participants.
The information which is spread is known as an Event which is a bundle of transaction data with its own unique properties. Each event carries a timestamp, signature, and two hashes. This is how data history is captured across the system.
The Gossip Protocol allows about 10,000 transactions to be carried out per second, making it faster and more efficient than PoW and PoS of Bitcoin and Etheruem respectively
Tolerance to Byzantine Faults in Hashgraph.
Byzantine Faults has got to do with the lack of distribution nodes to detect and respond to distribution failure in one of the nodes. This phenomenon is common in deterministic systems as the system often fails to recognize delayed messages and unresponsive nodes.
Hashgraph consensus algorithm has proven to be nondeterministic. Transactions are randomly distributed between nodes which eradicate the option of being predictive. Hashgraph applies Asynchronous Byzantine Fault Tolerance. I mentioned earlier that an event(transaction) has two cryptographic hashes unique to it.
With the use of a gossip system in place, one Carol(node) would already have obtained information on an event from Alice(node), thus have the access to both hashes. Once Bob jumps into gossip, the hashes presented by Bob are verified to check their uniqueness to the already obtained event from Alice. Carol will not accept the event from Bob if the hashes don't match.
In short, nodes will not sync with other malicious nodes if the cryptographic hashes are not consistent with each other. A consensus has to be agreed on for a transaction to be validated. Hashgraph ensures that out of 'n' number of nodes, 2/3 nodes are in consensus.
Hashgraph Vs Blockchain
Hashgraph was purposely designed to address the setbacks in blockchain technology in terms of scalability, transaction speed and fees, fairness, and less energy consumption among others. Let us take a look at some comparison with blockchain
Speed
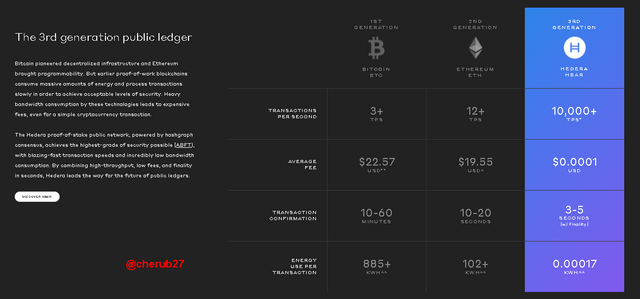
Hashgraph boosts faster transaction speed and time as compared to blockchain which experiences delays when transactions are overboard. The gossip protocol allows about 10,000 transactions to be carried out per second which are validated within 3-5 seconds. For voting purposes, the large populace can all vote in a short time frame and assured to receive results of votes without delay.Cost
A lot of energy is consumed by blockchains in an attempt to validate the transaction. Bitcoin's PoW requires miners to acquire expensive rigs and utilizes 885KWH for validating a block. These transactions also attract heavy bandwidth consumption which results in high transaction fees. Hashgraph provides a greener solution, consuming only 0.00017 KWH with a transaction fee of about $0.0001. This makes it cost-effective for governments hoping to cut down cost on election processesSecurity
Hashgraph's randomness of nodes interaction prevents coordinated attacks from hackers since they cannot predict the order of event distribution. The Gossip protocol combined with its Byzantine Faults Tolerancemakese sure that transactions are of consensus before validation. Since nodes can predict the events of another, malicious is not synchronized with, thus providing high security. Voting results are thereby safer with Hashgraph technology as governments are offered high security during the voting processVirtual Voting
Hashgraph promotes transparency as each member's vote is synced on the system. Every member has access to the hashgraph and can already predict which vote would be cast by another user. This way, the incidence of vote manipulation and deceit is checked during an election period. Blockchain platforms like Bitcoin with PoW algorithm rely on miners to validate blocks. Miners can leave transactions unvalidated or even delayed in favor of certain parties.
Hashgraph technology is a better choice to adopt for elections. Election results are processed with the shortest time for every citizen to see the outcome of the election. The government will tend to save a lot more money which would have been channeled into paying transaction fees on blockchain networks.
Election results are certified to be without biased or subjected to hacking due to the high-security service offered by Hashgraph. Elections are assured to be fast, transparent, and fair.
My country's governance is yet to accept the existence of blockchain technology so it would take some time to get to known the hashgraph. Regardless, I would recommend Hashgraph for election purposes to eradicate the incidence of violence and court sues over elections results which are often ambiguous.
Hedera Hashgraph
Hedera Hashgraph is the only decentralized public network privileged to run on the Hashgraph technology. It provides a fast, fair, and efficient platform for business with high security. Dr. Leemon Baird, the creator of Hashgraph, is a co-founder of Hedera Hashgraph.
The main menus of the Hedera Hashgraph homepage are Network, Dev, Use Cases, Governance, and About
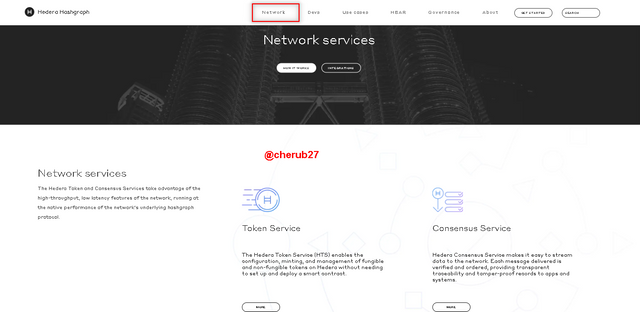
- Network menu
This menu provides two main functionalities which are Token Service and Consensus Service.
Token service allows users to create and manage their own tokens on the network.
Consensus service acts as a trust layer for any application or permission network and allows for the creation of an immutable and verifiable log of messages
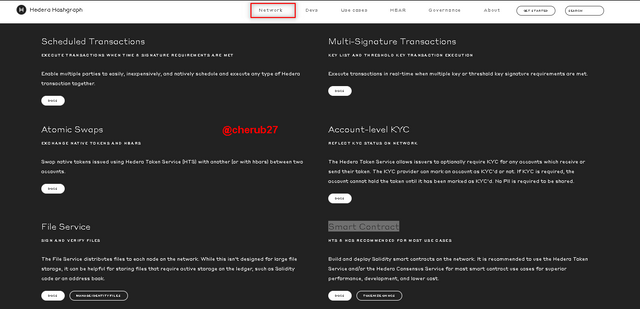
There are other functionalities such as Scheduled Transactions, Multi-Signature Transactions, Atomic Swaps, Account-level KYC, File Service, and Smart Contract also available in the Network section.
Users can always find help in the How it works section
- Dev
This menu houses information on all tools and resources available on the network.
DOCS provides info on the core concepts of the network. Hedera SDK provides an avenue to choose any language of preference. Integration lists all plugins and microservices for the network. Fees help users to estimate costs for preferred transactions. Open Source section allows developers to make contributions to the Hedera source code and Learning Center provides info on the organizations governing the network.
- Use Cases
Just as the name suggests, this menu lists all services the network provides. These use cases are Payments, Tokenized assets, Fraud mitigation, Identity, Data Compliance, Permissioned blockchain. Users can choose from this list, the kind of service they wish to seek on the network. There is also information on the network use cases in various productivity sectors.

- HBAR
HBAR is the native token on Hedera Hashgraph and is used as payment for services on the network. At the time of this post, HBAR is ranked #57 based on market capitalization on CoinGecko. It has a price $0.245607 with a 24-hour trading volume of $91,842,251, a circulating supply of 8.6 Billion HBAR coins, and a max supply of 50 Billion.
It can be found on exchanges such as Binance, eToroX, Crypto.com, Bitcoin.com, and HitBTC which is currently the most active exchange for HBAR
HBAR menu offers an overview of HBAR as a cryptocurrency, account creation avenue, and also provides a list of wallets and exchanges the support HBAR token.

- Governance menu
This menu provides details on the world-leading organizations that own and govern the Hedera network.
The governing council consists of a total of 39 organizations from 11 diverse sectors of productivity.

- About menu
This menu provides details on the Team, Journey, Roadmap, User Group, Careers, Media, Press, News, Blog, and Papers regarding the network.
All information on the Hedera Hashgraph Leadership team, investors, partners, system integrators, incubators, and accelerators can be found under the Team sub menu

Comparison of Hedera(HBAR) as a 3rd Generation public ledger to Bitcoin(BTC) and Etheruem(ETH) as 1st and 2nd generation blockcain networks respectively. HBAR can boost of fastest transaction speed, lowest transaction fees, shortest transaction confirmation and lowest energy consumption to BTC and ETH.
Conclusion
This lecture has enlightened me on the various possibilities of Hashgraph technology becoming the successor to blockchain technology. Despite criticism on the technicalities of the Gossip protocol, Hashgraph has proven to provide fast, free, and secured services to its users and should definitely be watched out for.
Thanks to professor @pelon53 for this lecture
Gracias por participar en Steemit Crypto Academy:
Has tu propia investigación no te apoyes en fuentes, en caso de protocolo Gossip.
Debes justificar el texto.
Espero seguir leyendo tus publicaciones.
Calificación: 8.2
Thank you for the review.