Crypto Academy / Season 3 / Week 4 - Homework Post for Professor @awesononso

Introduction
The increasing adoption and use of blockchains in the crypto world create a varying opinion of users in search of ways to enhance the wonderful technology. Some problems associated with scalability, type of consensus protocols adopted, etc. creates a level of disagreement between developers and miners of blockchains, this leads to the various need for modifications and enhancement.
Blockchain technology was developed based on a decentralized model that allows users full access control. it allows for modification of its technology to suit the need of users within the ecosystems if approved and agreed upon by the majority of developers and miners.

Question 1
What is a Fork? (In your own Words)
Source
Blockchain Fork
A Blockchain fork occurs when there is a separation within a Blockchain network resulting from a change in the software and different needs for improvement of the network. This is evident as there are different opinions on the uses and method of adoption of a particular Blockchain between miners and developers.
Forking in Blockchain is achieved because of its decentralized nature, where the developer's code is open source and allows interested developers and miners the luxury of modifying the technology to suit the need of their community.
The aftereffect of the Blockchain fork creates a destabilized network resulting from the new changes made to the blockchain, this can create increased volatility in the pricing of the native token of the Blockchain. This is evident as investors plan for the uncertain effect of the new upgrades made to the blockchain.
When miners decide to unanimously adopt the new fork, this maintains a single version of the Blockchain, but in an event of varying opinion, where some miners prefer the previous version to the new, this creates two versions of the Blockchain that can function and coexist simultaneously.
There are two categories of Blockchain fork hard fork (backward incompatible) and soft fork (backward compatible).

Question 2
Explain in detail what a Hard Fork is with examples
Source
Hard fork (backward incompatible)
The hard fork is a type of Blockchain fork that effects major changes on a Blockchain, causing separation within the blockchain network leading to two different versions of the blockchain coexisting. One of the versions will be a continuation of the old Blockchain, maintaining the previous rules, protocols, etc. And the other version will develop new rules and protocols.
After a Blockchain hard fork is done, the new version of the blockchain treats blocks from the previous chains as invalid as it now runs on a new protocol, similarly, the old blockchain will treat the new connecting blocks as an invalid block as the protocol is different. This effects the backward incompatibility of a hard fork on blockchains, irrespective of the simultaneous coexistence.
The common history shared between the old and versions of a blockchain after a hard fork is done, allows the new connection nodes of the new chain to maintain token balances from the old upgraded account. Although the new Blockchain will create a new native token as the protocol is different now. The old version blockchain users can buy shares of the newly created token but cannot earn them from activities like mining.
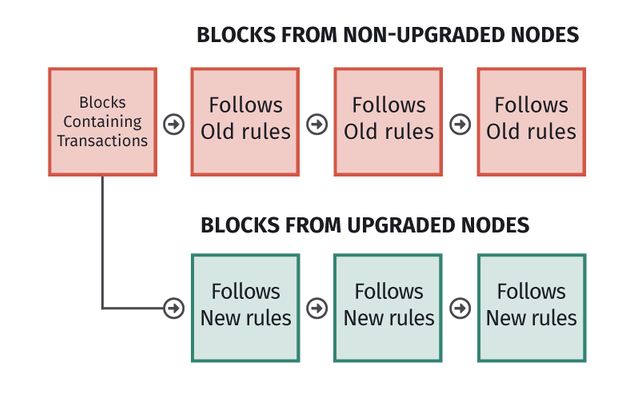
Image Source
Example of Blockchain hard fork
A recent example of a would hard fork is the proposed "Ethereum London Hard Fork" based on ethereum blockchain technology slated to happen on, August 4th 2021.
The developers of the ethereum blockchain have proposed a change in consensus protocol, moving from a Proof-of-Work based protocol to a Proof-of-Stake based protocol. This change in protocol resulted from high energy consumption associated with the proof of work protocol, which causes high gas fees for processing transactions.
The new protocol proposes to improve on keys areas in their released Ethereum Improvement proposal (EIP). A major area mentioned is:
Improving value of Ethereum
Unlike other cryptocurrencies, ethereum has no fixed max supply cap( the total number of ethereum tokens that will be created), and this can cause inflation of the value of the token in the long run. Ethereum miners are paid with a new token for verifying transactions and also get some fractions for the transactions fees charged.
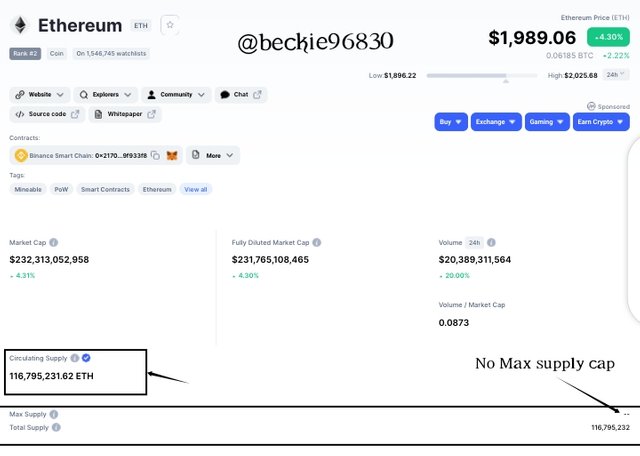
The London hard fork has a new rule that will stop rewarding miners the fractions of transaction fees paid to them, rather the percentage will be infused into the network to get burnt, doing this, in turn, will reduce the circulating supply of ethereum and further boost the value of the coin in long run.
Other benefits of the proposed hard fork are possible reduction of transactions fees and an increase in the number of ethereum based transactions that can be handled within a second.
There had been mixed reactions between miners of the ethereum blockchain on whether the transaction fees should be removed or not. But after the hard fork, a consensus will be reached on which protocol should be adopted.

Question 3
Explain in detail what a Soft Fork is with examples
Source
Soft Fork (Backward compatible)
The soft fork is a type of blockchain fork that maintains the same Blockchain after an upgrade in the software of the blockchain. These changes effected on the blockchain do not cause splitting of the blockchain, previous history, protocols, and rules are maintained in the blockchain after the upgrade.
Since all previous history and protocols are maintained, no network upgrade is required to be done by the users. Connecting nodes (before and after upgrade) treat each block as valid blocks within the blockchain, thus confirming the backward compatibility of the soft fork applied on the Blockchain.
The miners and developers of a Blockchain unanimously agree on the proposed change within the blockchain, thus resulting in wide adoption of the new changes without needing separation from the previous Blockchain.
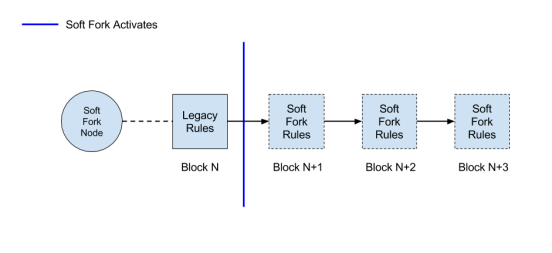
Image Source
Example of Blockchain Soft Fork
A popular referenced soft fork is the segregated witness (segwit) upgraded done on Bitcoin Blockchain. It was developed in 2015 by Pieter Wiulle. The need for the upgrade resulted from the increasing scalability of the Bitcoin Blockchain network, where the number of transactions queues was increasing.
To improve the situation, the developer proposed a transaction block model that has no witness signature included to increase the number of transactions that can be loaded in a block at once, by leaving the witness signature blank. The standard Bitcoin block had a capacity of 1 MB which can contain about 2700 transaction details.
By removing the witness signature contained in the transactions, the block can now contain more transaction details this reducing the queuing problem experienced within the Blockchain.
The segwit upgrade was implemented in the Bitcoin Blockchain in 2017, which was not so welcomed by some of the members of the Blockchain. This led to the hard fork of Bitcoin technology creating the Bitcoin Cash Blockchain. This turned out not to be the ideal soft fork planned.

Question 4
What are the differences between Hard Forks and Soft Forks?
Source
There is some notable difference between Hard fork and soft fork of blockchains. They include:
| Hard Fork | Soft Fork |
|---|---|
| 1- A new Blockchain is created after the changes are made. | 1-The old Blockchain is maintained including previous rules and protocol. |
| 2- Treats old connecting block as invalid | 2- Treat both old and new block as valid. |
| 3- Disapproval of some user members on the changes made considered | 3- Almost every connecting member approves the changes |
| 4- New native token is formed for the new Blockchain | 4- No new native token is formed. |

Question 5
Explain the following Bitcoin Forks and explore the blockchain where necessary. Indicate if they are hard forks or soft forks;
Bitcoin Cash
Segregated Witnesses
Source
Bitcoin Cash
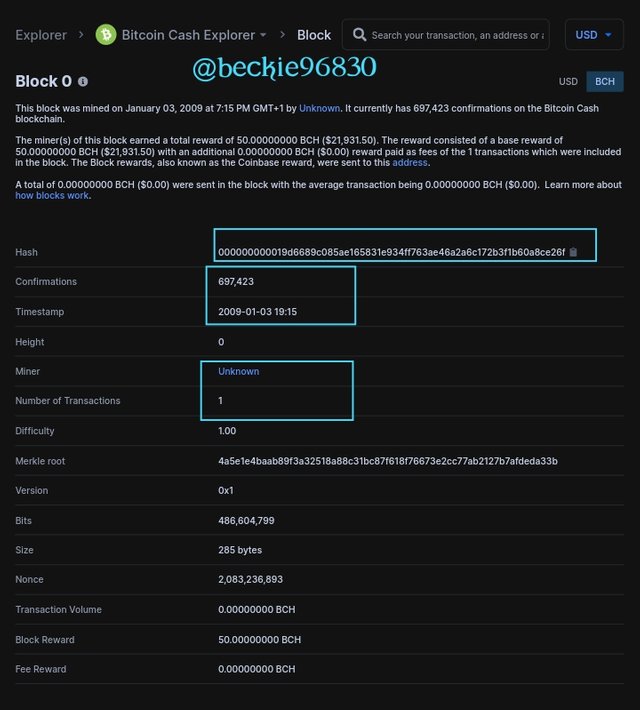
Bitcoin cash is a hard fork Blockchain from the Bitcoin Blockchain, created in 2017 after part members of the Bitcoin developers community disagreed on the implemented segregation witness (segwit) upgrade done on the Bitcoin Blockchain source code.
The Bitcoin cash created a new native token called Bitcoin Cash (BCH). The Bitcoin cash blockchain created treated Bitcoin blocks as invalid as it created new protocols to validated transactions within its network.
The new Bitcoin cash also improved on other slacks associated with the Bitcoin blockchain, which include, improved mining speed, the number of transactions contained in a block, and transaction fees.
Segregated witness
The segregated witness is a soft fork upgrade implemented on the Bitcoin blockchain to reduce the queuing problem experienced within the network.
The upgrade proposed to improve the situation by creating a type of transaction that has no witness signature included to increase the number of transactions that can be loaded in a block at once, by leaving the witness signature blank. The standard Bitcoin block had a capacity of 1 MB which can contain about 2700 transaction details.
The implementation of this upgrade stirred unhappy reactions from some developers and miners, who opted to create a hard fork of the Bitcoin blockchain called Bitcoin cash.
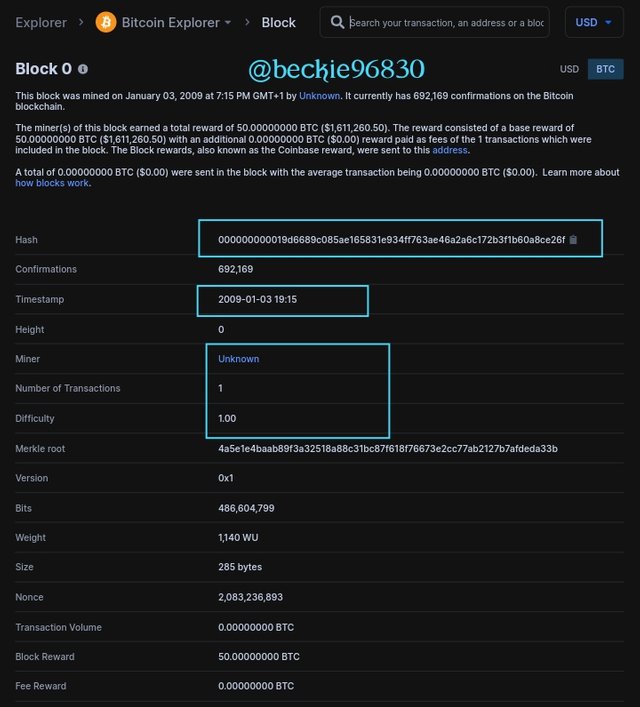
Bitcoin and Bitcoin cash share the same common history, since Bitcoin cash was hard forked from Bitcoin blockchain the genesis block of both blockchains are the same transaction details.
Reference Link
Reference Link

Question 6
Write on the Steem and Hive Hard fork and show similarities in their Genesis Blocks
Source
Similar to other instances of a hard fork, the steem blockchain experienced a hard fork after a major upgrade was made on its source code. The hard fork created a new blockchain called Hive. Hive and Steem share the same common history blocks but treat transactions blocks from each blockchain as invalid.
The then Steem blockchain integrated a cryptocurrency called Tron into its system, this stirred reactions between witnesses and users of the blockchain. A fraction of the community developed a new Blockchain called Hive.
Similar to steem, Hive has native tokens called Hive Backed Dollar (HBD), Hive, and Hive power. The similarities grow deep to even the blog website layout with differences in color scheme and logo design.
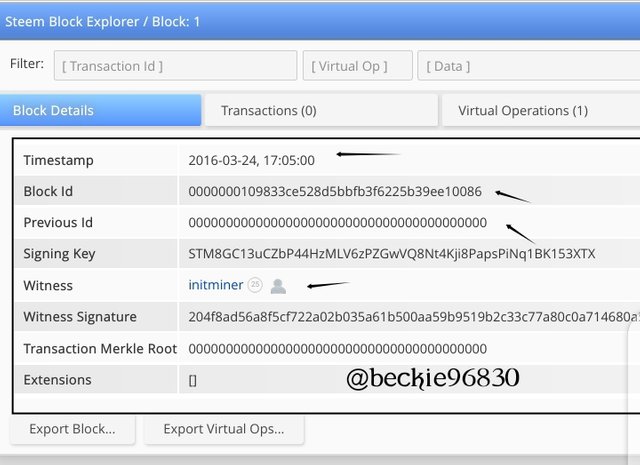
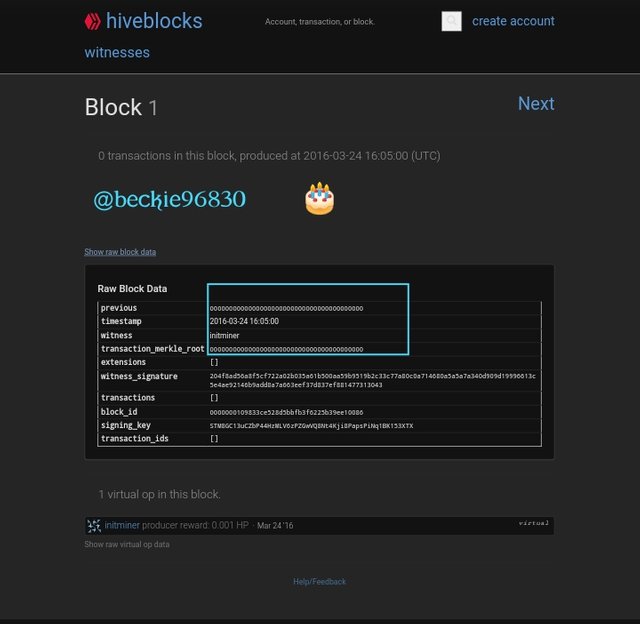
Steem and Hive share the same previous history and this can be verified from their Genesis Blocks.
Reference Link
Reference Link
The block details of Steem genesis block and Hive genesis block show the common history both blockchains share, having the same witness, hash, and the same time of transaction.

Conclusion
The decentralized nature of blockchain allows the creation of new blockchains from an existing Blockchain since the code is open source. This results from various enhancements that might be agreed upon by some members of the blockchain community and rejected by other members.
In all, Blockchain modifications and upgrades serve the interest of users and the sustainability of the Blockchain in the long run.
Thank you professor @awesononso for this insightful lesson.
Hello @beckie96830,
Thank you for taking interest in this class. Your grades are as follows:
Feedback and Suggestions
You have shown a clear understanding of the topic. Good Job!
You still need to work on your expression. Some statements were not so clear.
Thanks again as we anticipate your participation in the next class.
Thank you professor @awesononso I will improve on your next assignment