Steemit Crypto Academy, Season 3: Week 4 BY @pelon53|| ROOT HASH AND MERKLE TREE.
Good day everyone, I am happy to be part of this week cryptoacademy lesson by our dear professor @pelon53. Here is my attempt for all the question.
QUESTION 1.- Explain in detail the hash rate.
In cryptocurrency programming, hashrate is the rate at which a calculation completes an operation. A higher hash rate is preferable for mining since it increases the likelihood of finding the next block and receiving a reward.
Hashrate is also the unit of measurement for a blockchain network's processing power, or how much total individual hashing power is contributed to protect the network.
The speed at which hardware, such as a graphics card or an ASIC, can decrypt hashes is referred to as hashrate. Cryptocurrency mining is built on this foundation.
The greater the Hash Rate, the more people or organizations are trying to secure the network, hence the problem must be more difficult.
To measure Hash Rate: hashes per second [H/s], therefore if a network has a Hash Rate of 6TH/s, it can solve the next block puzzle at a rate of 6 trillion calculations per second.
Hash Rate and Hash Power are both calculated in the same way, with hashes per second H/s. One hash can be viewed as a single computation used to solve the block equation.
The Hash Rate rises as more Hash Power is put into the network, and more individuals desire to protect it and receive rewards, making it difficult to predict the future outcome for each miner.
Hash Power is now measured in terahesh per second (TH/s) when it is supplied to the Blockchain, which signifies how many trillions of calculations per second can be done with the amount of hashing power on the network.

ANSWER TO QUESTION 2.-
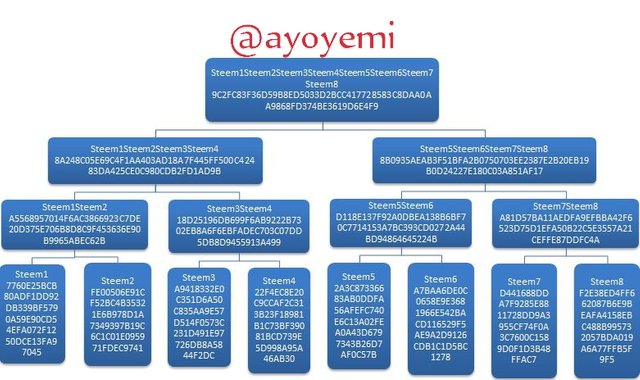
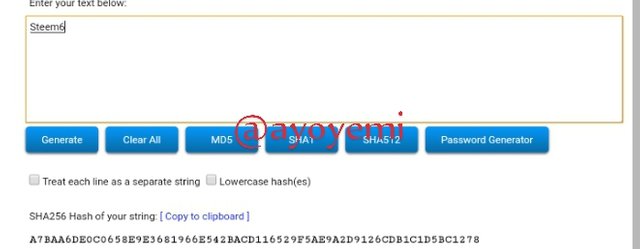
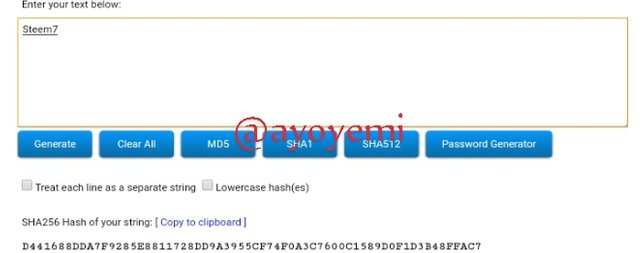
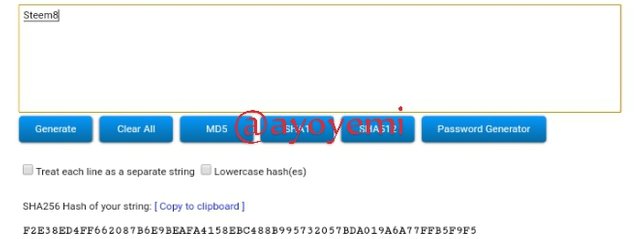
Step 1 We will start with generating the Merkle tree leaves hashes Steem1; Steem2; Steem3; Steem4; Steem5; Steem6; Steem7; Steem8.
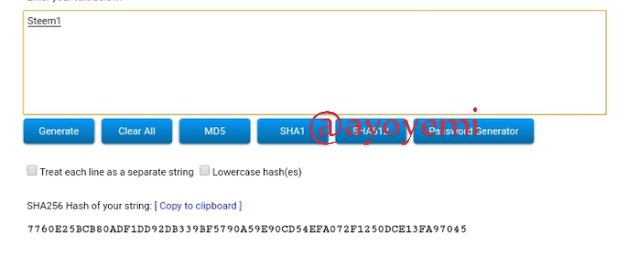
Steem1 7760E25BCB80ADF1DD92DB339BF5790A59E90CD54EFA072F1250DCE13FA97045
Steem2 FE00506E91CF52BC4B35321E6B978D1A7349397B19C6C1C01E095971FDEC9741
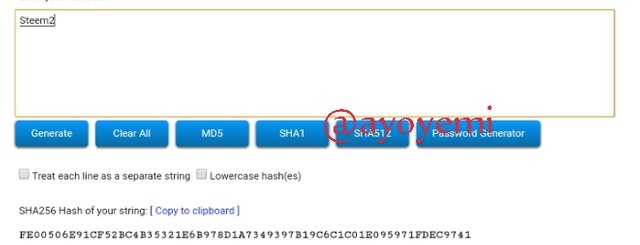
Steem3 A9418332E0C351D6A50C835AA9E57D514F0573C231D491E97726DB8A5844F2DC
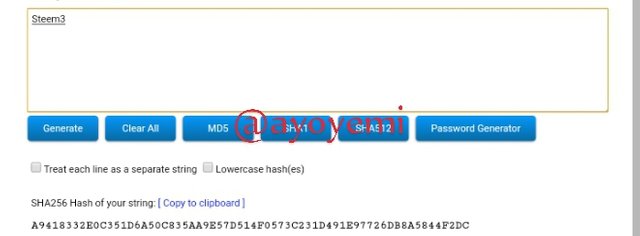
Steem4 22F4EC8E20C9CCAF2C313B23F18981B1C73BF39081BCD739E5D998A95A46AB30
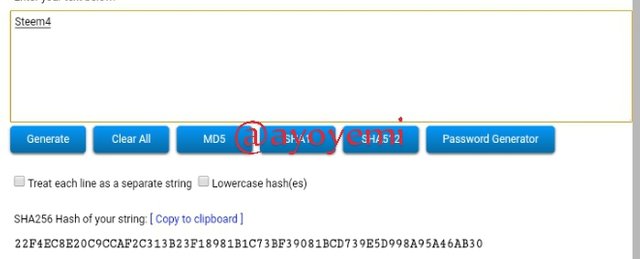
Steem5 2A3C87336683AB0DDFA56AFEFC740E6C13A02FEA0A43D6797343B26D7AF0C57B
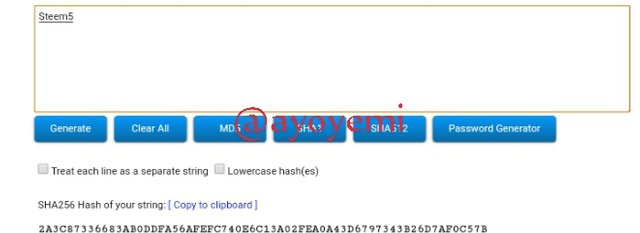
Steem6 A7BAA6DE0C0658E9E3681966E542BACD116529F5AE9A2D9126CDB1C1D5BC1278
Steem7 D441688DDA7F9285E8811728DD9A3955CF74F0A3C7600C1589D0F1D3B48FFAC7
Steem8 F2E38ED4FF662087B6E9BEAFA4158EBC488B995732057BDA019A6A77FFB5F9F5
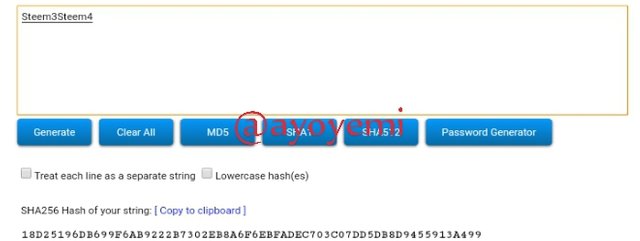
Step 2: The next step is to generate the ashes for merkle tree branch
Steem1Steem2 A5568957014F6AC3866923C7DE20D375E706B8D8C9F453636E90B9965ABEC62B

Steem3Steem4 18D25196DB699F6AB9222B7302EB8A6F6EBFADEC703C07DD5DB8D9455913A499
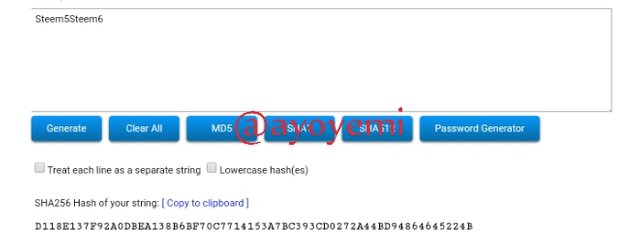
Steem5Steem6 D118E137F92A0DBEA138B6BF70C7714153A7BC393CD0272A44BD94864645224B
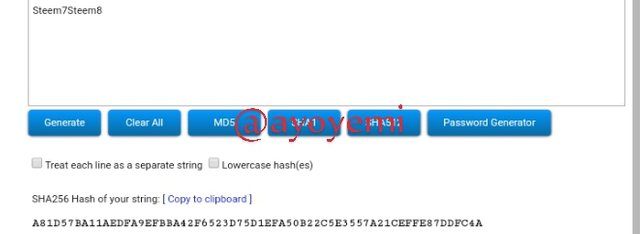
Steem7Steem8 A81D57BA11AEDFA9EFBBA42F6523D75D1EFA50B22C5E3557A21CEFFE87DDFC4A
Step 3: In this step, we will be generating the second branches hashes
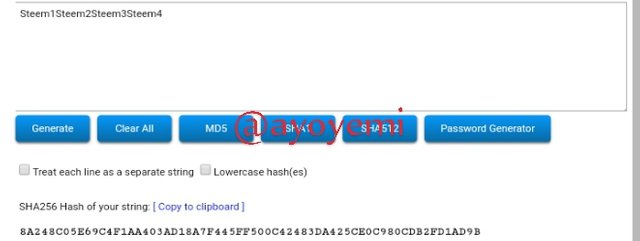
Steem1Steem2Steem3Steem4 8A248C05E69C4F1AA403AD18A7F445FF500C42483DA425CE0C980CDB2FD1AD9B
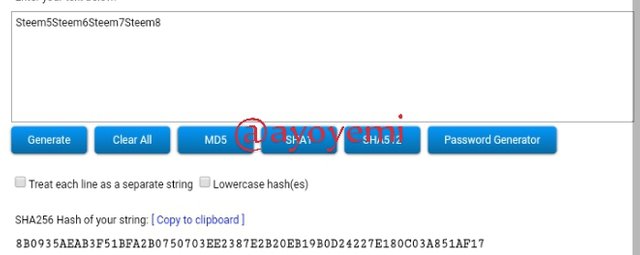
Steem5Steem6Steem7Steem8 8B0935AEAB3F51BFA2B0750703EE2387E2B20EB19B0D24227E180C03A851AF17
Step 4: In the step, we will be generating the Merkle Tree Root hash as show below
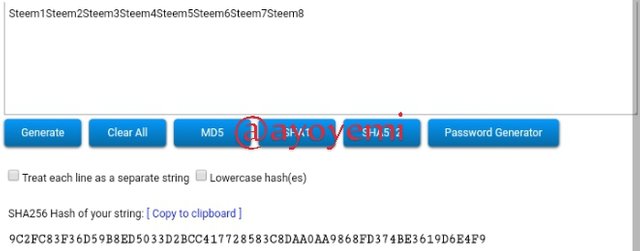
Steem1Steem2Steem3Steem4Steem5Steem6Steem7Steem8 9C2FC83F36D59B8ED5033D2BCC417728583C8DAA0AA9868FD374BE3619D6E4F9
Step 5: We will draw the merkel tree for all the hashes we have generated as shown below

QUESTION 3A
Using the SHA-256; you must place each complete hash in the Merkle Tree.
Transaction (tree leaves): SCA1; SCA2; SCA3; SCA4; SCA5; SCA6; SCA7; SCA8. Explain each step, show screenshots.
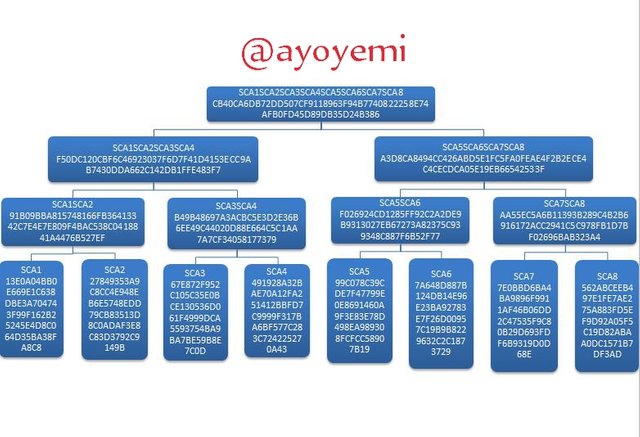
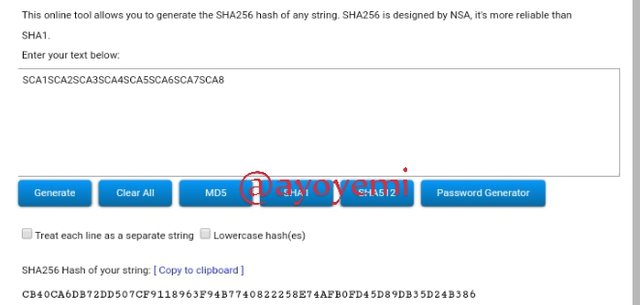
Step 1 We will start with generating the Merkle tree leaves hashes (tree leaves): SCA1; SCA2; SCA3; SCA4; SCA5; SCA6; SCA7; SCA8.
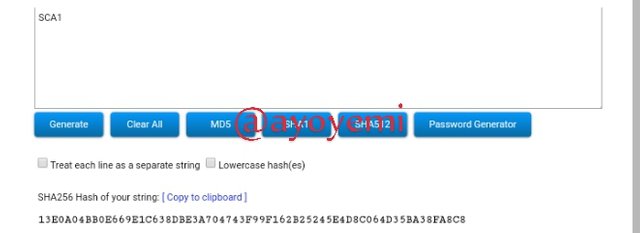
SCA1 13E0A04BB0E669E1C638DBE3A704743F99F162B25245E4D8C064D35BA38FA8C8
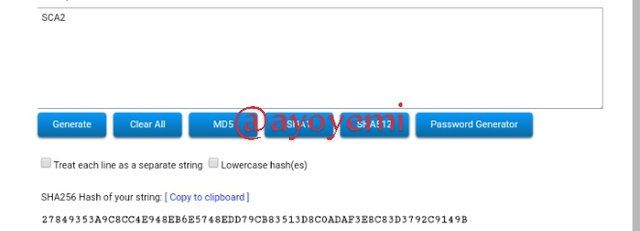
SCA2 27849353A9C8CC4E948EB6E5748EDD79CB83513D8C0ADAF3E8C83D3792C9149B
SCA3 67E872F952C105C35E0BCE130536D061F4999DCA5593754BA9BA7BE59B8E7C0D

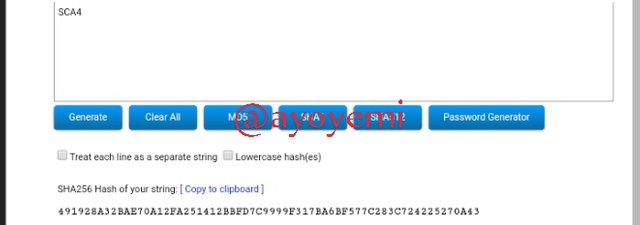
SCA4 491928A32BAE70A12FA251412BBFD7C9999F317BA6BF577C283C724225270A43
SCA5 99C078C39CDE7F47799E0E8691460A9F3E83E78D498EA989308FCFCC58907B19
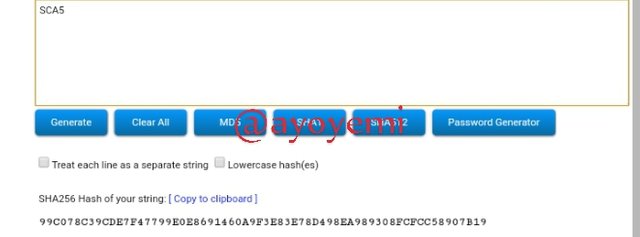
SCA6 7A648D887B124DB14E96E23BA92783E7F26D00957C19B9B8229632C2C1873729
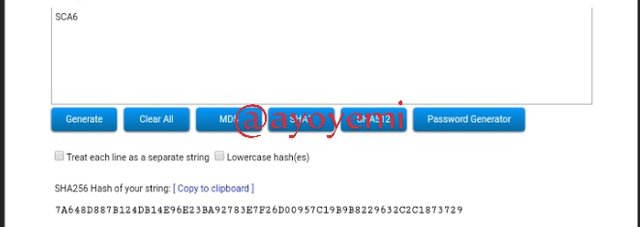
SCA7 7E0BBD6BA4BA9896F9911AF46B06DD2C47535F9C80B29D693FDF6B9319D0D68E
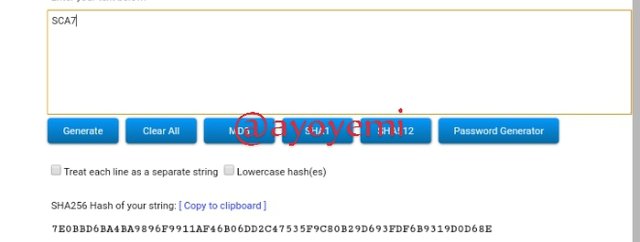
SCA8 562ABCEEB497E1FE7AE275A883FD5EF9D92A05F5C19D82ABAA0DC1571B7DF3AD
Step 2: The next step is to generate the ashes for merkle tree branch
SCA1SCA2 91B09BBA815748166FB36413342C7E4E7E809F4BAC538C0418841A4476B527EF
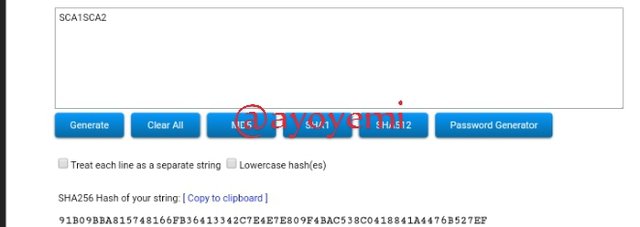
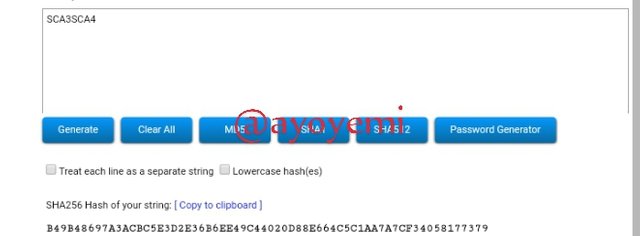
SCA3SCA4 B49B48697A3ACBC5E3D2E36B6EE49C44020D88E664C5C1AA7A7CF34058177379
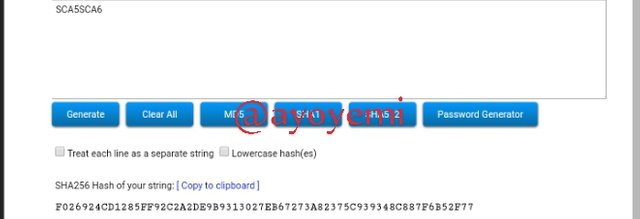
SCA5SCA6 F026924CD1285FF92C2A2DE9B9313027EB67273A82375C939348C887F6B52F77
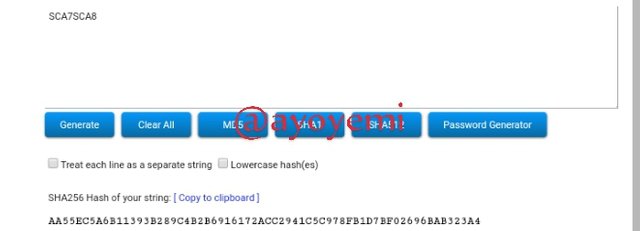
SCA7SCA8 AA55EC5A6B11393B289C4B2B6916172ACC2941C5C978FB1D7BF02696BAB323A4
Step 3: In this step, we will be generating the second branches hashes
SCA1SCA2SCA3SCA4 F50DC120CBF6C46923037F6D7F41D4153ECC9AB7430DDA662C142DB1FFE483F7
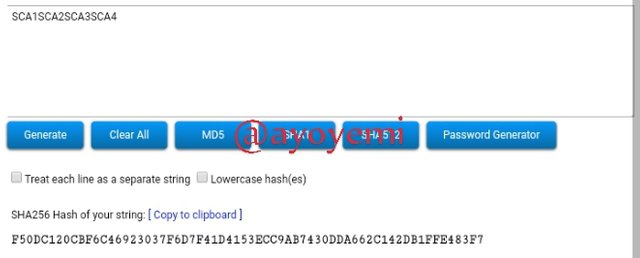
SCA5SCA6SCA7SCA8 A3D8CA8494CC426ABD5E1FC5FA0FEAE4F2B2ECE4C4CECDCA05E19EB66542533F
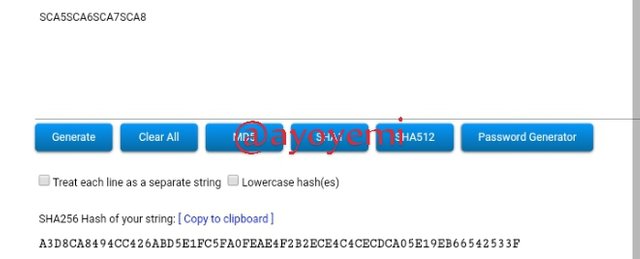
Step 4: In the step, we will be generating the Merkle Tree Root hash as show below
SCA1SCA2SCA3SCA4SCA5SCA6SCA7SCA8 CB40CA6DB72DD507CF9118963F94B7740822258E74AFB0FD45D89DB35D24B386
Step 5: We will now draw the Merkle Tree for all the hashes.

Question 3b: If the number of leaves on the tree is odd, what should you do? Explain.
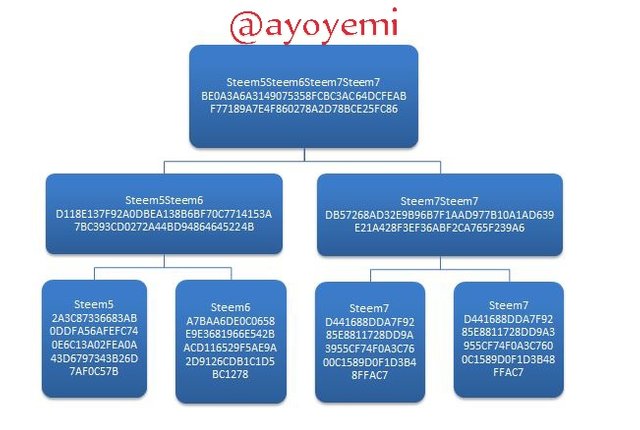
If there is a odd number of transaction, duplication will be done at calculation time with the last odd data. This happens and It is simply part of the merkle root computation algorithm that the duplication is done if number of the data that ought to be calculated happened to be odd.
Calculation of merkle tree algorithm uses only even number
The markle tree will then be like this:

CONCLUSION:
A Merkle tree saves all of the transactions in a block by creating a digital fingerprint of every one of them. It enables the user to check whether or not a transaction is eligible for inclusion in a block.
Merkle trees are made by hashing pairs of nodes over and over until just one hash remains. Merkle Root, or Root Hash, is the name given to this hash. Merkle Trees are made from the ground up.