Crypto Academy Week 15 - Homework Post for @alphafx
INTRODUCTION
Effectiveness is the goal of any system ever invented. A system is meant to perform its operations optimally with upgrades being made to bridge any flaw. Blockchain systems have always aimed to be better than older ones as they come. Since the advent of bitcoin, following blockchains have always aspired to be better in different ways.
I’m going to delve into the scalability topic as I complete the tasks given by @alphafx.
Make a transaction on the Binance Smart Chain and the Tron Blockchain
Binance smart chain:
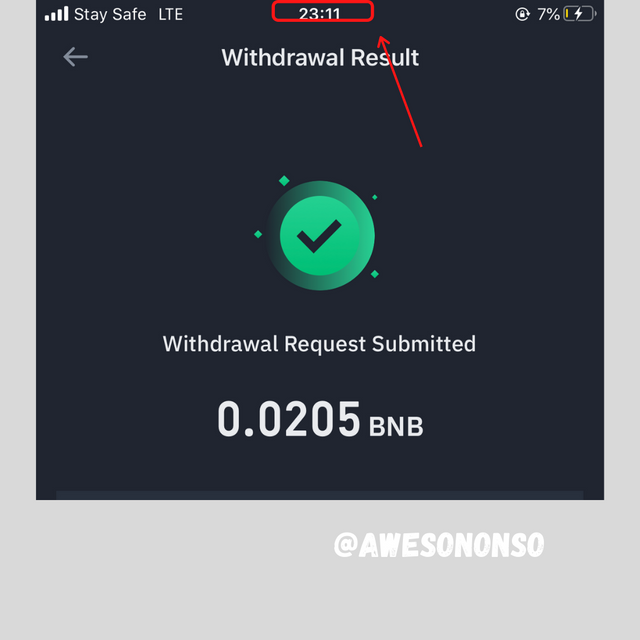
For this part of the task, I sent 0.02 BNB from my binance account to a different binance account.
The transaction was sent at 23:11 local Nigerian time which is equivalent to 22:11 UTC.
Tron blockchain:
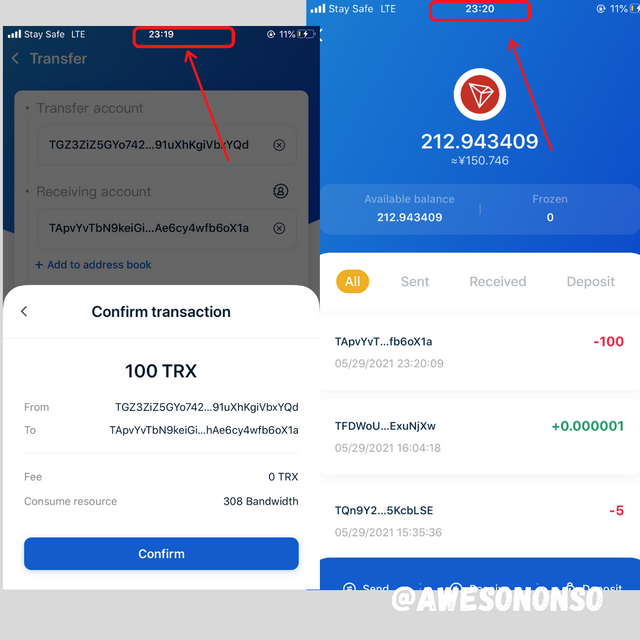
For this task, I transferred 100 TRX from my TronLing wallet to binance trx wallet.
I confirmed the transaction
Time taken for each transaction to be verified
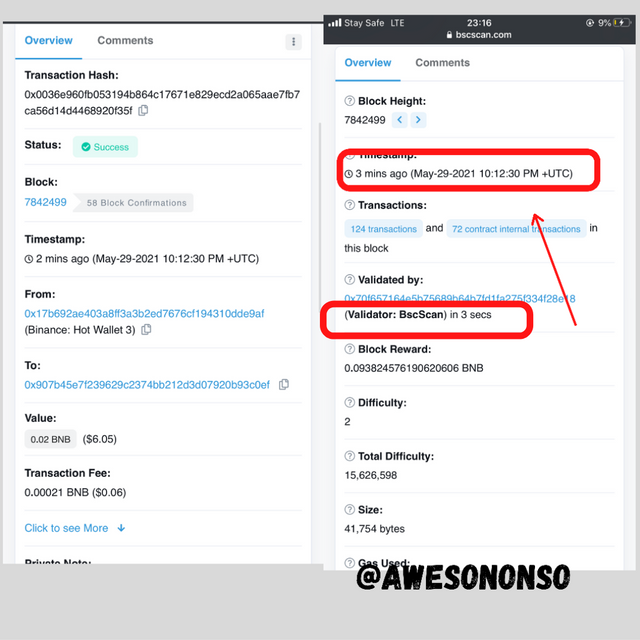
Starting with the BSC, the transaction was really fast.
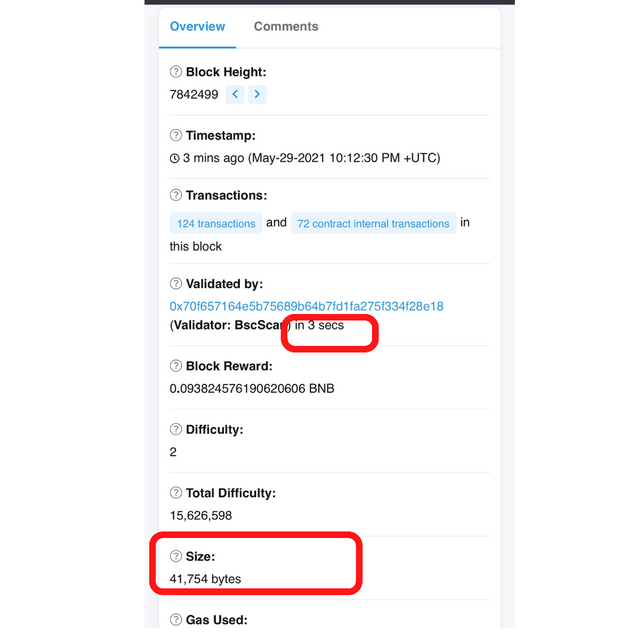
The picture above shows that the transaction was confirmed in 3 seconds.
The TRX transaction was probably the faster between the two. The transaction was filled as soon as I put it.

The average block creation time is 3 seconds just like with BSC.
Comparing with BTC
Scalability in blockchain is simply the ability of the network to handle a huge number of transactions within a small period of time. Scalability has proven to be a serious problem for bitcoin’s blockchain. I’m going to talk about the different Consensus algorithms, block size, block time and transaction speed.
Consensus algorithm
Bitcoin uses the archaic Proof of Work consensus which has proven to have a lot of issues. In this type of consensus algorithm, miners have to solve mathematical problems in order to validate a transaction.
Tron uses the special Delegated proof of stake consensus which is kind of a democratic consensus simulate. Holders of TRX can freeze the TRX to obtain Tron power and use that power to vote for Super Representatives. Super representatives are charged with making blocks and book keeping. Super representatives are re-elected periodically (every 6 hours). Unlike PoW and PoS, this system allows for quick validation of transactions because the number of decision makers is greatly reduced. The Tron blockchain has been known to be able to process about 2000 transactions per second. That is really far from bitcoin which handles 5 transactions per second. But we’ll come to that.
BSC employs a combination of proof of stake and proof of authority (PoA) giving rise to the special Proof of Staked Authority(PoSA). Now this isn’t just any common consensus system. In the PoSA system, staking of coins is not just enough. Validators stake something much more valuable which is their reputation. Trustworthy nodes with enough stakes get to become validators.
Block size and block time
Block size is really important when it comes to scalability. A bigger tank always holds more water. Let’s say that block sizes are tanks and the transaction is the water in them. A 1000 liter tank would take more time to pump a reasonable amount of water. Now let’s say you have to hurry to work but you have a small tank you share with the rest of the tenants. The flow rate would be slow and that might Make you go really late to work. What’s the solution? A bigger tank! That’s it. More water and a higher flow rate.
The example might be oversimplified but it’s relatable in the blockchain sense. Bitcoin has a very small block size. The block size used to be about 1 megabyte but recent improvements have increased that to 4 megabyte (which is still overly optimistic). In reality the block size is 2mb. Now the average block creation time for bitcoin is 10 minutes (600 seconds). That means we expect an average of 2mb every 600 seconds.
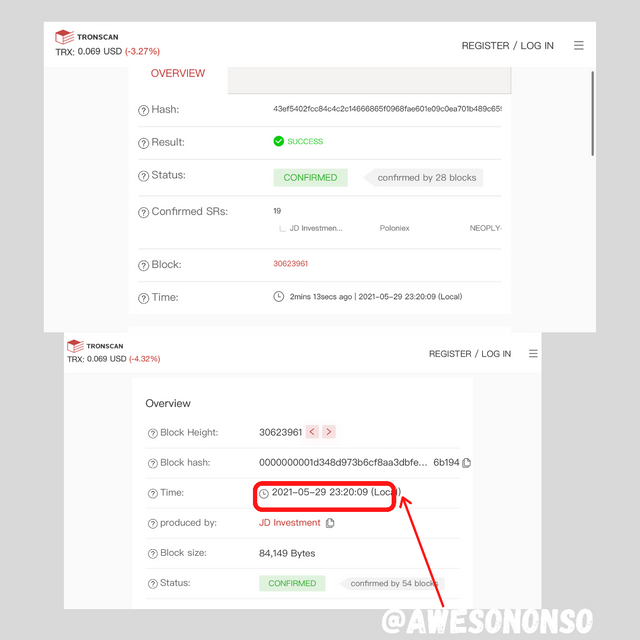
Let’s compare this to Tron.
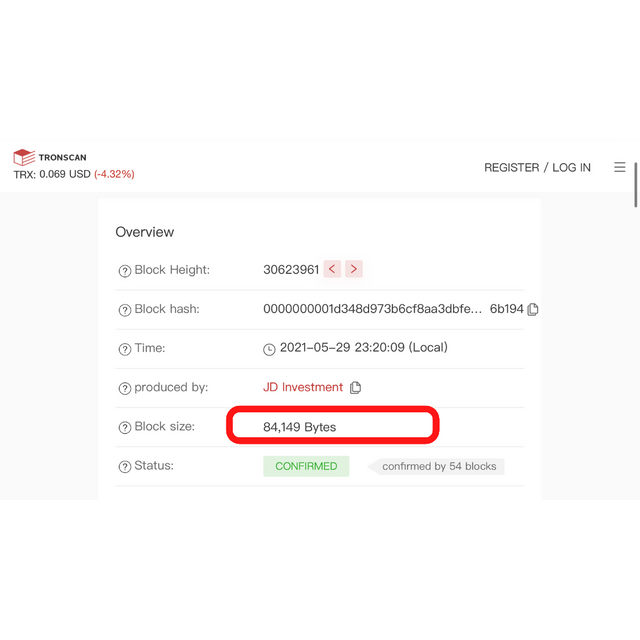
The screenshot above shows a Tron block size of 84, 149 bytes. Let’s see the block creation time.
Taking the difference from the block times above, the block creation time for Tron is 3 seconds in average.
Now if we were to create blocks for 10 minutes on the Tron blockchain, the overall block size would be:
84, 149 * (600/3)
84, 149 * 200
= 16,829,800Bytes
= 16 Mega bytes on average.
Those figures beat bitcoin easily.
Now let’s look at BSC
The block size above is 41, 754 bytes with a creation time of 3 seconds.
Applying the same formula as with Tron above for, the binance smart chain would produce 8,350,800 bytes. This is about 8.351 Mega bytes.
Transactions per second
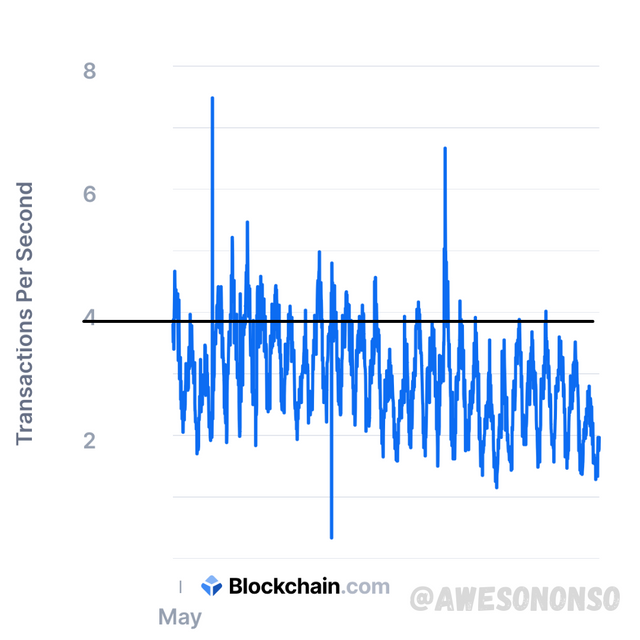
Let’s just go straight to the point with this. The image below shows a chart of the TPS of bitcoin
The average is about 4TPS for bitcoin.
Let’s look at the TPS of Tron.
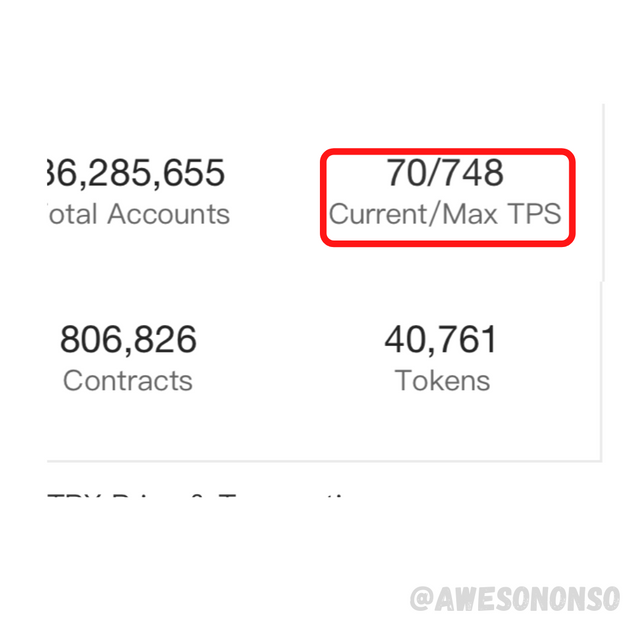
Tron is known for reaching TPS levels of 2000TPS. As of the time of this assignment, the figures shown in the image are valid.
For BSC now,
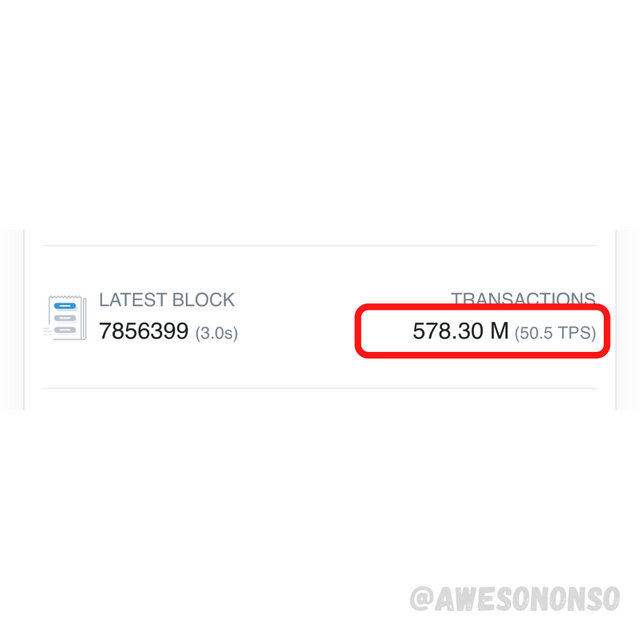
The current TPS for BSC is 50.5 TPS as shown above
These figures show how superior in transaction speed Tron and BSC are to bitcoin.
A summary
| Parameter | Bitcoin | Tron | BSC |
| Consensus | Proof of Work | Delegated Proof of Stake | Proof of Staked Authority |
| Block size | 1 MB | 84,149 bytes | 41,754 |
| Block creation time | 600 seconds | 3 seconds | 3 seconds | Transaction speed | 4 TPS | 70 TPS | 50.5 TPS |
What can be done to develop scalability of the three
People all around the world have sought ways to solve bitcoin’s scalability problems. Of course, solving bitcoin’s scapability problem will boost every other cryptocurrency. Some ways to improve Bitcoin’s scalability are as follows:
1. Introducing batch payments: Batch payments has proven to be a smart way of increasing Transaction speed in a blockchain. Instead of having a single payment in a transaction, different payments can be grouped from the same wallet and completed on different wallets. Batch payment will solve the problem of multiple transaction fees and also reduce the size that would have been the case in multiple transactions. Less data size means that the overall block size of bitcoin will not have to be compromised to improve its scalability.
2. Sharding: Each node in a blockchain network contains all the information of the blockchain. As more nodes join the network, the general speed and latency is reduced because the workload becomes a lot to handle. This is where sharding comes in.
Sharding makes a blockchain more of a blockchain. It is a process of dividing a database network into different segments called shards. It is a kind of division of labor where one network segment does not have to bear the whole network burden. Each shard in a network is concerned with the activities of its own “mini network”.
Shard A, for example, is concerned with transactions of its nodes. The validators of this shard are only Responsible for transactions on their shard. However, data on shard B can still be accessed by shard A maintaining the distributed ledger nature of the blockchain.
3. The Lightning network solution: The Idea of the lightning network was first brought up by Joseph Poon and Thaddeus Dryja back in 2015. This type of technology is an innovative proposal to bitcoin’s scalability issue through off-ledger transactions facilitated by smart contracts and multisignature scripts. Now, the lightning network works by creating an off-chain layer on the bitcoin main chain. User nodes in the network simply have to put funds in a reserve which they use to make payments to connected nodes. Individual nodes, known as lightning nodes, can conduct a number of transactions through channels without the need for consensus. These channels can combine when they have common lightning nodes to facilitate a greater payment network called the Lightning network. Any number of transactions, exchanges or atomic swaps can be done once a channel is open and is only recorded in the blockchain when the channel is closed.
For example, let’s say Nonso has an open channel of 2BTC reserve with Ojo’s perfume store. He can make payments directly and swiftly to the store in real time for perfumes anytime. Now, Kamara has an open channel with a beauty salon and Ojo’s perfume store. Automatically there is a connection between Nonso, the perfume store, Kamara and the beauty salon (The lightning network).
Now, if Nonso wants to pay for his girlfriend’s makeup at the beauty salon he can do so through Kamara’s channel. Similarly, Kamara can make payments to Ojo’s perfume store through Nonso’s channel. Once Kamara’s channel is closed, that connection is lost and Nonso has to open a different channel with the beauty salon.
A downside
Trying to Improve bitcoin’s scalability will generally compromise Satoshi Nakamoto’s intent of decentralization. Blockchains generally want to attain “Visa-like” speed. Visa has a jealous transaction speed of about 1,700 TPS and for blockchains to attain that, they had to somehow sacrifice the general decentralized nature. BSC and Tron blockchain should not be compared to BTC because, well, they are not fully decentralized. The BSC and BNB supply are controlled by Binance while Tron blockchain and TRX are controlled by Tron Foundation. Also, the DPoS and PoSA forgo decentralization to obtain scalability.
For bitcoin to improve in scalability, some form of centralization has to take place.
CONCLUSION
The problem of scalability is something that a lot of people have tried to solve. Blockchain technology is very attractive to people everywhere but this scalability problem has hindered a lot of progress in different spaces of life.
Special thanks to @alphafx



Well done, well done.
Thanks for participating
Yes!
Thanks for the review professor