Steemit Crypto Academy [Beginners’ Level] | Season 3 Week 4 | Blockchain Forks by @amritraj
QUESTION 1
What is Fork ?
Answer 1
A blockchain fork is basically cut up by means of a blockchain network. The network is open source software, and the code is free to use.Blockchain depends on a team of dispensed computer systems that work together. Individual computers, oftentimes referred to as "all nodes," check the public books on the blockchain and run the software needed to hold the community secure. The greater nodes that run the software at the identical time, the greater secure your network. This capability every person can suggest enhancements and make modifications to the code. Experimental choices in open supply software are a integral section of cryptocurrencies, facilitating updates to blockchain software. Forks happen when the software program of different miners is proper tuned. Deciding which blockchain to use is up to trivial. In the absence of a unanimous decision, it is likely that there will be two variations of this blockchain. There might also be periods of high price fluctuations around these events.However, the nodes of the network may not unanimously agree on the future state of the blockchain. This event leads to a tuning fork-like fork used in experimental science. This means that the ideal "single" blockchain is split into multiple valid chains.
Question 2
Explain in details what a Hard Fork is with examples (Can be of any blockchain).
Answer 2
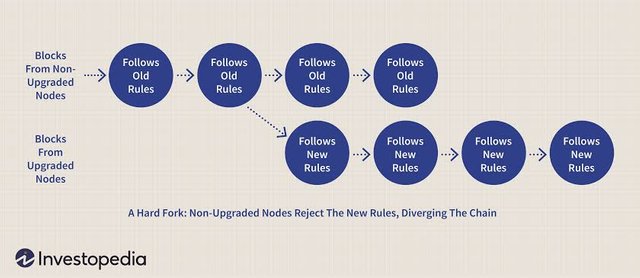
A hard fork is a fundamental change to a network protocol that enables so far bad blocks and transactions, or vice versa, as it relates to blockchain technology. A tough fork requires every node or customer to improve to an ultra-modern version of the protocol software. Forks are sometimes initiated by developing crypto community builders or individuals who are attracted to the features offered by current blockchain implementations. It is also likely to emerge as a way to crowdsource funds for new professional obligations and cryptocurrencies offerings.Hard fork refers to a fundamental change in the protocol of a blockchain network that efficiently produces two that comply with the old protocol and follow the new version. The owner of the original blockchain token on the hard fork will also be granted the token on the new fork, but the miner must choose a blockchain for continuous verification. Hard forks can occur on all blockchains, not just Bitcoin.
Example-Casper is a new update on the Liam blockchain, in which the consensus protocol will be changed from a Proof of Work (PoS) type to a Proof of Stake (PoS) type. Nodes that install Casper updates will use the new consensus protocol. Even if Furuno is installed, choosing to install the Casper update is not compatible with Furuno.
QUESTION 3
Explain in details what a Soft Fork is with examples (Can be of any blockchain).
Answer 3
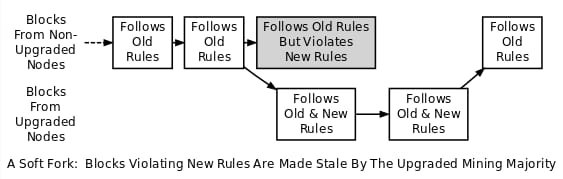
A soft fork is a software protocol change that has previously disabled only valid transaction blocks. The soft fork is compatible with the previous version because the previous node recognizes the new block as valid. These types of forks only upgrade most miners to apply the new rules, instead of requiring all nodes to upgrade and accept newer versions of hard forks.Also, if a miner node using a non-upgraded node violates a new consensus rule that it does not know, a soft fork can occur due to the temporary divergence of the blockchain.All blocks with rules that are new soft forks In order to comply with old rules, soft forks do not need to upgrade nodes to maintain consensus. So older clients accept them. A soft fork cannot cancel a soft fork without a hard fork in order to ensure that only a set of blocks valid by definition are an appropriate subset of a valid free fork. Users upgrade to the postsoft fork client If for some reason the majority of miners return to the presoft fork client, the postsoft fork client user will immediately break the consensus when encountering a block that does not follow the client's new rules.
Example-Bitcoin community SegWit update provides a new class of addresses (Bech32). However, this does no longer invalidate current P2SH addresses. Furunodo with P2SH type addresses can execute valid transactions with nodes with Bech32 type addresses.
Question 4
4.What are the differences between Hard Forks and Soft Forks?
Answer 4
Hard forks and soft forks are the same from the experience that when the current code of the password currency platform actually changes, the previous version remains on the network while the new model is generated. With a soft fork, only one blockchain is valid, even if the user adopts the update. For hard forks, each historic blockchain and new blockchain exist side by side, and this feature must be up-to-date for software programs to work through new rules. It produces both splits of both forks, but the tough fork produces two block chains and the soft fork is for producing one result. Given the difference in protection between difficult and soft forks, almost every customer and developer names a difficult fork even when the soft fork seems to be working properly. A scrutiny of blocks on a blockchain requires a huge amount of computing power, but the personal life gained with a challenging fork gives it a greater feel than using a soft fork.Soft and hard forks are imperative for the long-term success of blockchain networks. You can upgrade on a distributed utility other than a central authority. Generate each fork for both forks, but for auction forks there is only one valid blockchain. On the other hand, a hard fork results in the presence of two consecutive blockchains.Soft fork Works at the network level Requires 51% of mining hash power. No nodes, replacements, or users need to upgrade.
Hard fork Works at protocol level Hash power doesn't matter Both nodes, exchanges and users need to be upgraded.
Question 5
Explain the following Bitcoin Forks and explore the blockchain where necessary. Indicate if they are hard forks or soft forks;
Bitcoin Cash
Segregated Witnesses
Answer 5
Bitcoin Cash ( Hard fork)
Bitcoin Cash used to be created by means of challenging forking Bitcoin in 2017. While explaining Bitcoin-based soft forks earlier, he stated that some Bitcoin users disagree with the ideas on the segment. They say that lowering the block dimension can substantially reduce the range of transactions carried out on the blockchain per second, and this is not a right thought about password currency, which is the predominant password foreign money in the world. did. Therefore, most developers have begun to alternate the blockchain protocol. Opponents of the SegWit concept have challenging forked Bitcoin and barely modified the Bitcoin source code to create a new version of Bitcoin. This difficult fork resulted in the Bitcoin blockchain being break up into Bitcoin and Bitcoin Cash.
Here are some minor changes that make the new blockchain distinctive from the basic blockchain:
The Bitcoin Cash blockchain switch price is cheaper than the Bitcoin blockchain switch fee. This capacity that Bitcoin Cash transactions are less pricey than Bitcoin transactions.
The switch velocity of Bitcoin Cash is quicker than Bitcoin transactions. As with Bitcoin transactions, you don't have to wait up to 10 minutes for the transaction to be confirmed. Bitcoin Cash techniques greater transactions per 2d than Bitcoin.
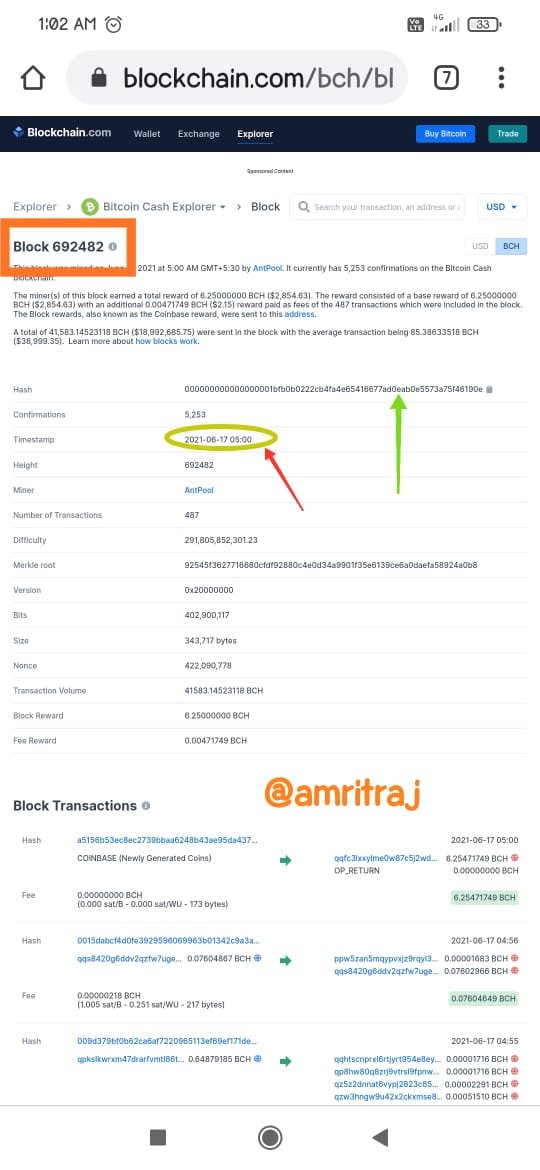
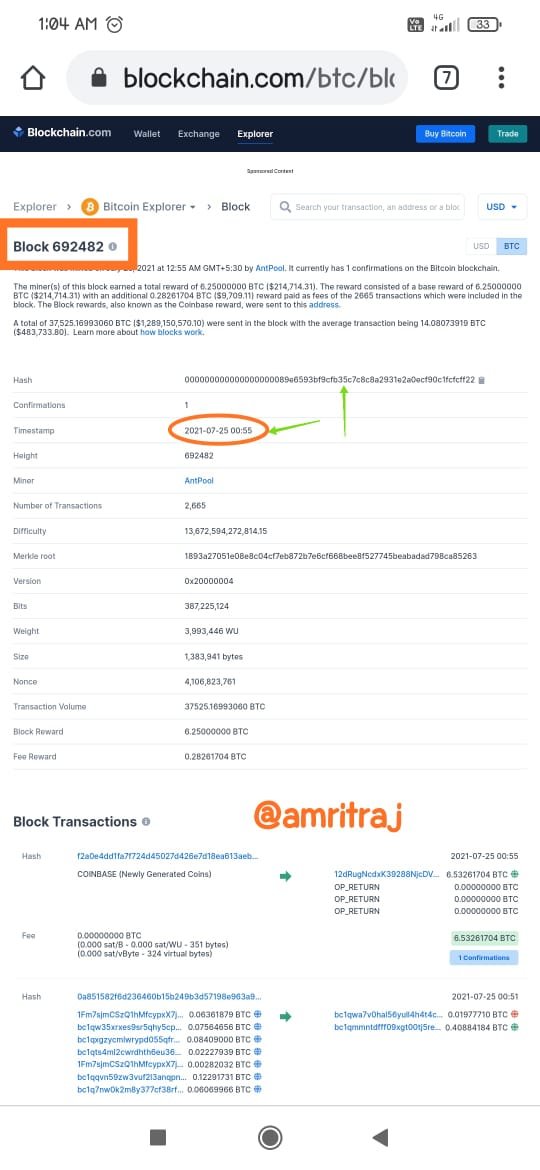
Segregated Witness (Soft fork)
The concept Segregated Witness or \ u201cSegWit \ u201d is associated with a branch of the Bitcoin blockchain. The person who proposed "SegWit" stated that it was unwise to increase Bitcoin's block metric in the past. This is because each time it is added, more hardware is required to run the node. They believe that blocking the block size at 1MB per block is quality.The concept of SegWit is not to create new blockchains and cryptocurrencies, but rather to make minor changes to the Bitcoin blockchain protocol. A high-quality strategy to achieve this goal is a "soft fork".Since the fork bidding will not require individual participant approval instead of majority approval, however, the majority in favor of Segwit has gone ahead to regulate the blockchain protocol.
Question 6
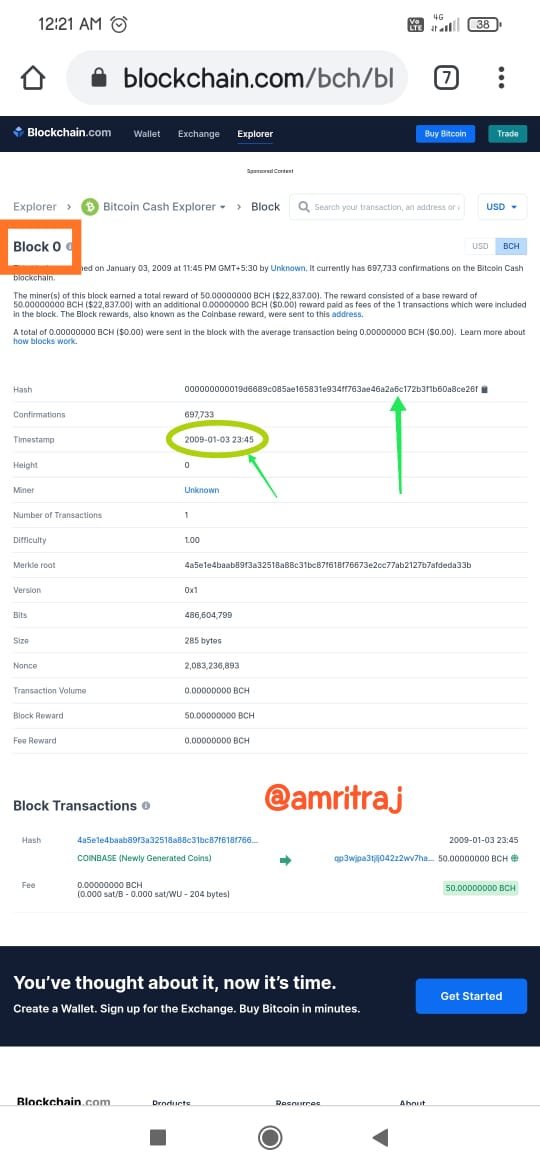
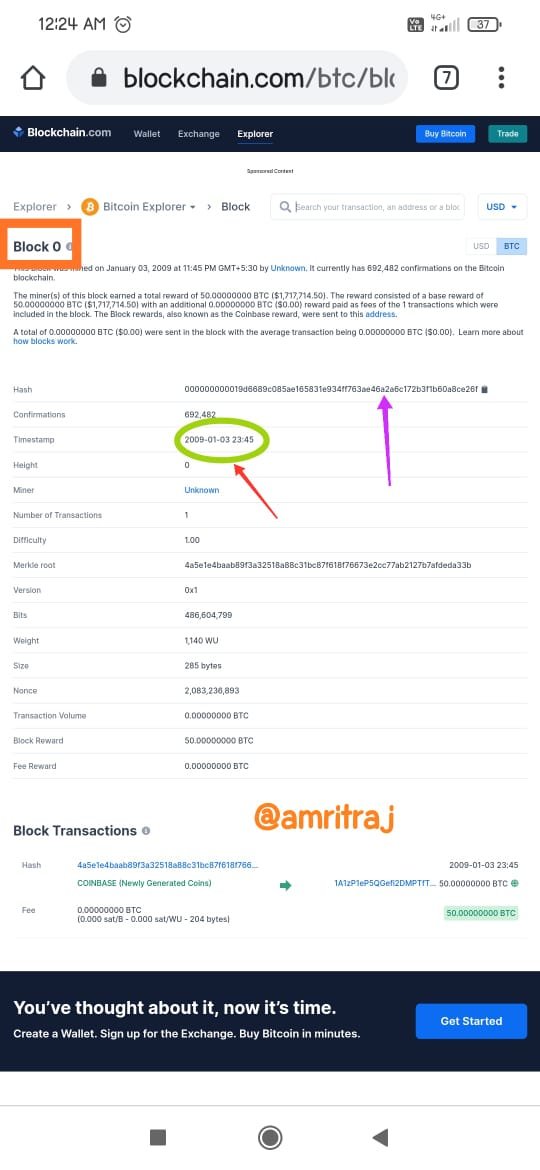
Write on the Steem and Hive Hard fork and show similarities in their Genesis Blocks(Provide screenshots).
Answer 6
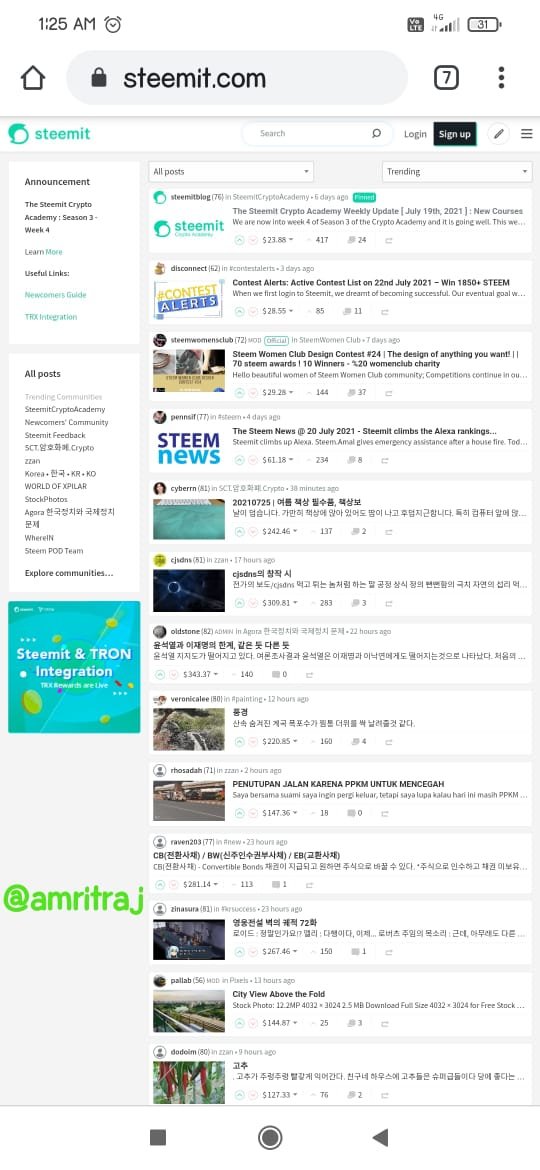
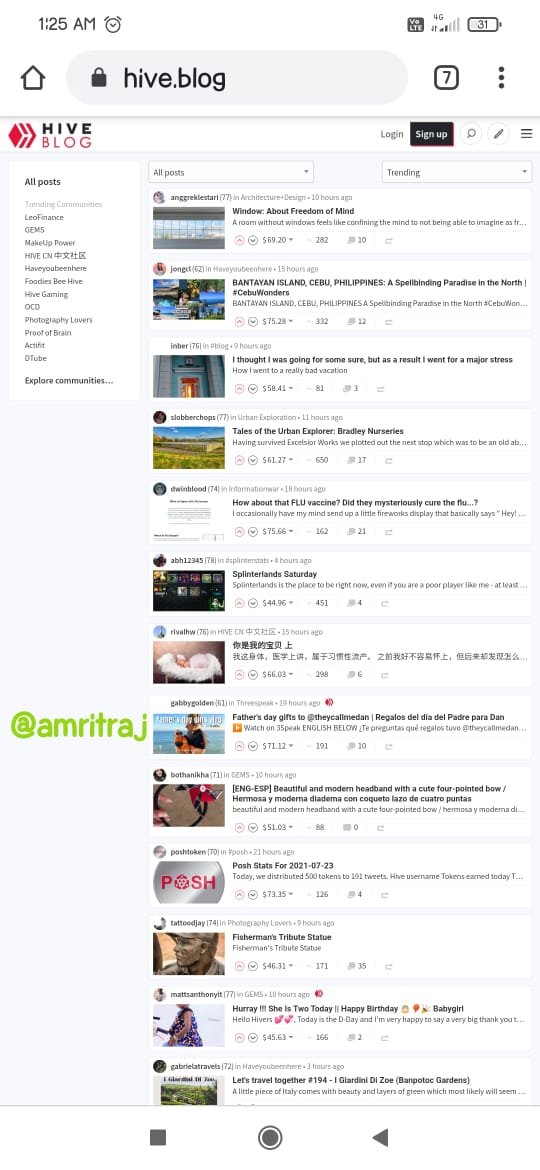
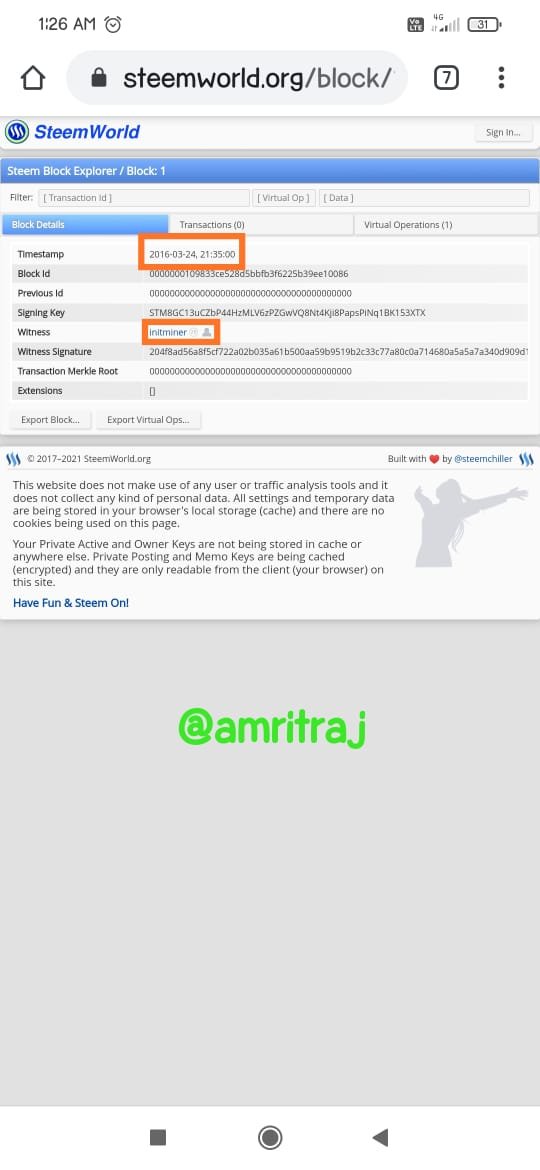
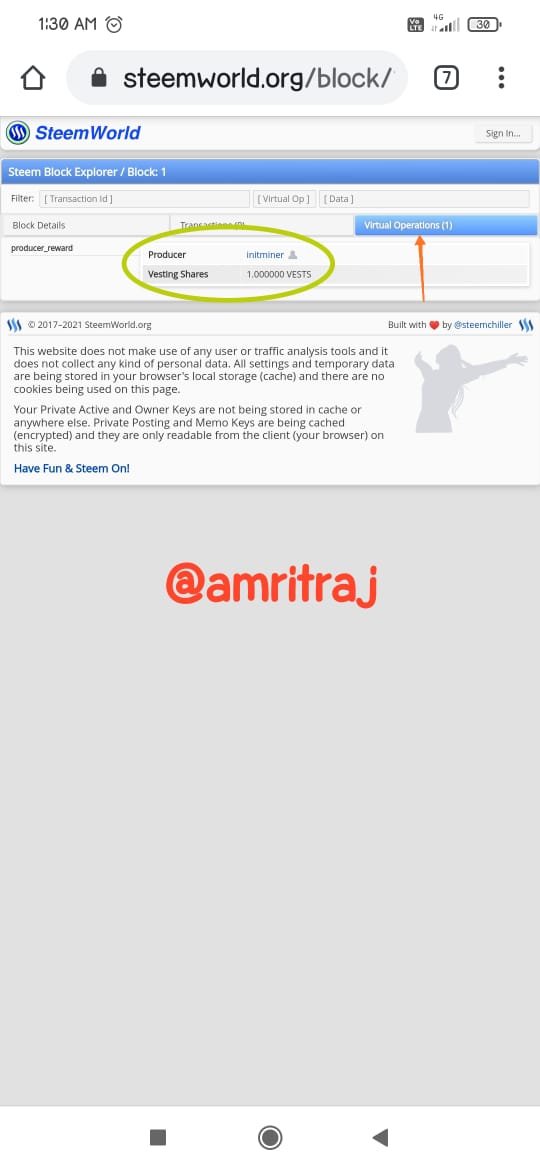
Hive genenis block data
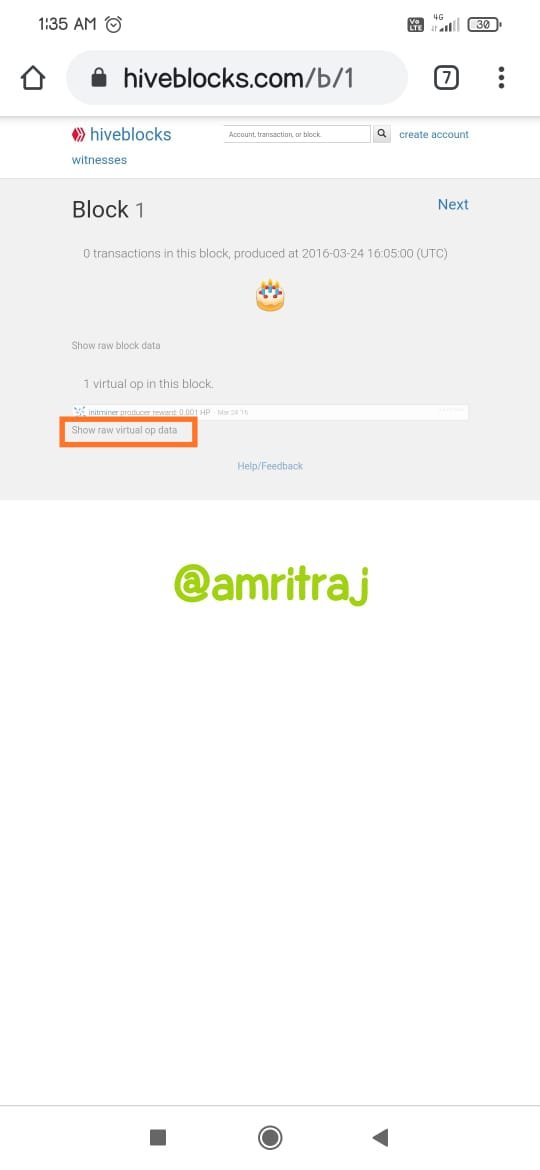
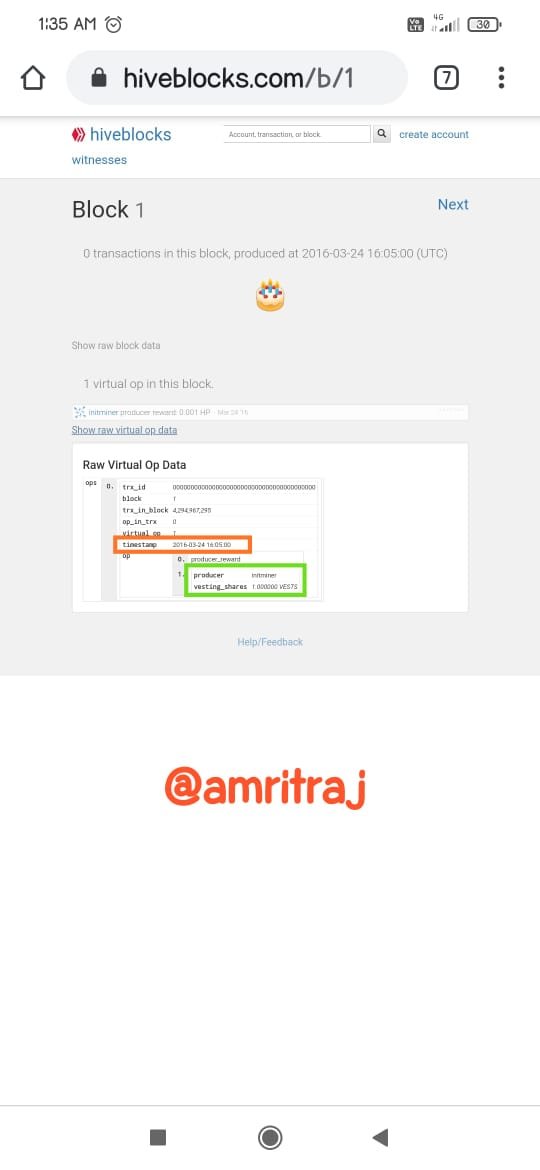
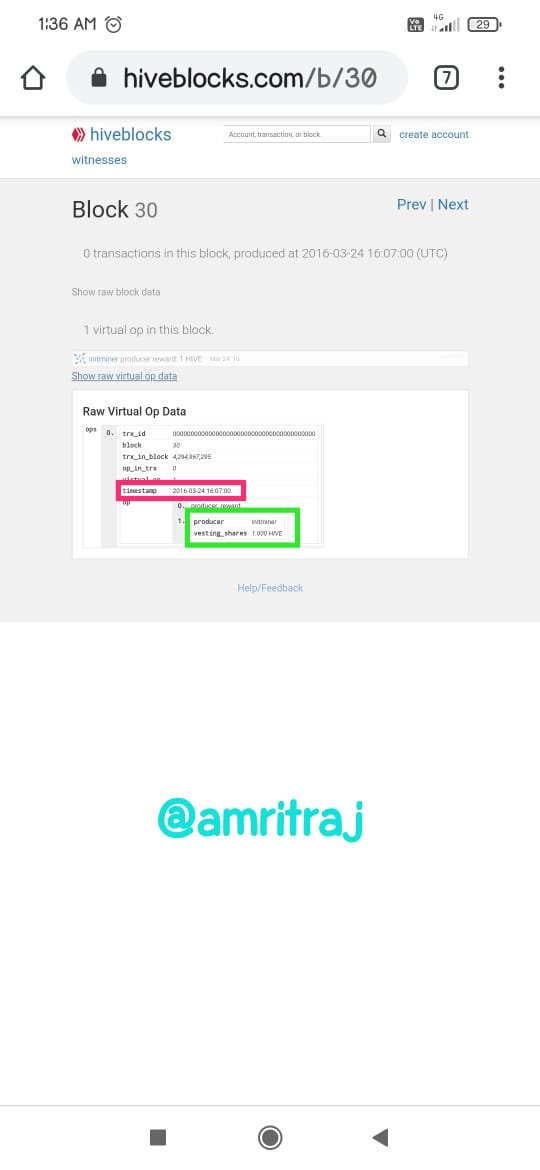

Hive is a fork of Steem, the end result of a series of positive witnesses reaching an agreement on specific leadership agreements and conflicts. As a blockchain, it is decentralized and anyone can leave the chain. The witnesses branched out from Steem to form Hive (DPoS blockchain).Steem is also a very well-known cryptocurrency blockchain. Steem is activated in the Steemit platform. The Steem token is recognized as SBD. Steem is a decentralized blockchain. Like many other crypto blockchains, Steem also has short passes and requires some tweaking. A hard fork of Steem appeared to be a solution to all of Steem's shortcomings. Hive is a separate blockchain operated in "Hive.blog". I'll show you the similarities of each blockchain using screenshots.
CONCLUSION
Blockchain is an expression event that can improve the performance of the network by performing the final result of the community modification result. Customer workers and construction work must be agreed before upgrading the upgrade to Blockchain. This is due to decentralization. That's all we manage the network. The plates have two types of hard forks and soft forks. Folk Hard will usually share the blocks of these blocks in general when you need a title to execute the main update of the community. When a new block is formed, create a new instruction designed. Examples of this amount of BTCoin were present as a final result of difficult intersections that have experienced Btcoin. Flexible fork is only completed to improve the network. Do not divide the blocks of the softfolk. Therefore, it should be noted that the plate is necessary to maintain the stability and operation of the network.
Thank you
Hello @amritraj,
Thank you for taking interest in this class. Your grades are as follows:
Feedback and Suggestions
Your work is really unclear. Try to properly understand a topic before your edit your homework.
You need to improve on your arrangement and paragraph use too.
Thanks again as we anticipate your participation in the next class.