CIRCULATORY SYSTEM IN ANIMAL
Transport systems are essential for survival. Single-celled organisms depend on simple circulation to maneuver nutrients and eliminate waste. Multicellular organisms have developed more complex circulatory systems.
[image source](
There are two kinds of circulatory systems in animals:
- Open circulatory system
- Closed circulatory systems.
OPEN CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
In open circulation, blood vessels carry all the fluids within the lumen. When the animal is moving, the blood moves into the lumen freely altogether directions of the body. The blood washes the organs directly, providing oxygen and removing waste products from the organs. The blood flows at a very slow rate because of the actual fact that there aren't any smooth muscles responsible for the contraction of the blood vessels. Most invertebrates (crabs, insects, snails, etc.) have an open circulatory system .
CLOSED CIRCULATORY SYSTEMS
Closed circulatory systems differ from open circulatory systems because blood remain
within the vessels. Instead , it's constantly transferred from one vessel to a special without entering a lumen. The blood moves in one direction, because it carries oxygen and nutrients to the cells and removes waste products.
Closed circulation systems can also be divided into;
Single circulation systems and
Double circulation systems.
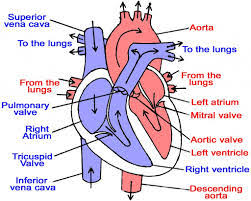
Single and double circulation system could also be a broad term that has the circulatory system , heart, blood vessels, and lymphatic system . The lymphatic system are getting to be discussed later during this section. The cardiovascular system consists of the center (heart) and thus the vessels (blood vessels) needed for a transfusion . Consists The system of arterioles, veins, and capillaries. Vertebrates (animals with backbones like fish, birds, reptiles, etc.) have closed cardiovascular systems that the bulk mammals participate in. the two main pathways of blood circulation in invertebrates are single and double circulation pathways. Single Circulatory Pathways. Single circulatory pathways contains a double-chambered heart containing the atrium and ventricle. Fish have only one because of rotate. the center pumps deoxygenated blood into the gills where it's oxygenated. Then the oxygenated blood is delivered to the whole body of the fish, and thus the deoxygenated blood is returned to the center . Individual circulatory system as in typical fish species. Red represents blood that's rich in oxygen or oxygenated blood, and blue represents blood that's deficient or deoxygenated. Dual circulation systems for birds and mammals have dual circulation pathways. Animals that have this type of circulation have a four-chambered heart. Oxygen is away from the right atrium from the body, and thus the ventricle sends it to the lungs to obtain oxygen. The left atrium of the heart receives oxygenated blood from the lungs, and thus the ventricle sends it to the rest of the body. Most mammals, including humans, have this type of circulation. These circulatory systems are mentioned as 'dual' circulatory systems because they contains two circuits called the pulmonary and systemic circulatory systems. Humans, birds and mammals have a four-chambered heart. Fish have a two-chamber heart, an ear, and a ventricle. Amphibians have a three-chambered heart with two atria and one ventricle, and thus the guts is that the absence of a mixture of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood.
The human circulatory system includes the pulmonary and systemic circulatory system.PULMONARY CIRCULATION
The pulmonary circulatory system consists of blood vessels that carry deoxygenated blood from the center to the lungs and return oxygenated blood from the lungs to the center . within the circulation , blood vessels transport oxygenated blood from the center to varied organs of the body and return deoxygenated blood to the center . Pulmonary Circulatory System: Deoxygenated blood within the circulation exits the center through the right ventricle and travels to the lungs viaPulmonary artery. The pulmonary artery is that the sole artery that carries oxygen-poor blood. The blood is transported to the capillaries where CO2 is released from the blood into the alveoli (lung cells) then to the lungs, where it's exhaled. At the same time, oxygen diffuses into the alveoli then enters the blood and returns to the the guts |atrium sinistrum|atrium cordis|atrium of the heart"> left atrium of the heart of the heart through the vena pulmonalis .
circulation
SYSTEMIC CIRCULATION
Systemic circulation refers to the type of circulation that carries oxygenated blood to the cells of the body and returns deoxygenated blood back to the center . Blood passes from the ventricle into the aorta, the foremost important artery within the body. The aorta leads to smaller arteries that provide all of the body's organs. These arterioles eventually divide into capillaries. within the capillaries, oxygen diffuses from the blood into the cells, and waste and CO2 diffuses from the cells into the blood. Then the blood is transfused deoxygenated blood into capillaries that merge with the veins. These veins fuse into two main veins, the superior vein and therefore the inferior vein. Deoxygenated blood enters the upper atrium through the superior vein . Major arteries supply blood to the brain, intestine , liver, and kidneys. However, the circulation also reaches other organs including muscles and skin.
Please, can we see your introduction post:-P
Yes ma/sir @churchangel