Renewable or Green Energy : Types, Forms & Sources
Today, fossil fuels provide 80 percent of global energy. Renewable energy sources are crucial in reducing reliance on fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas.
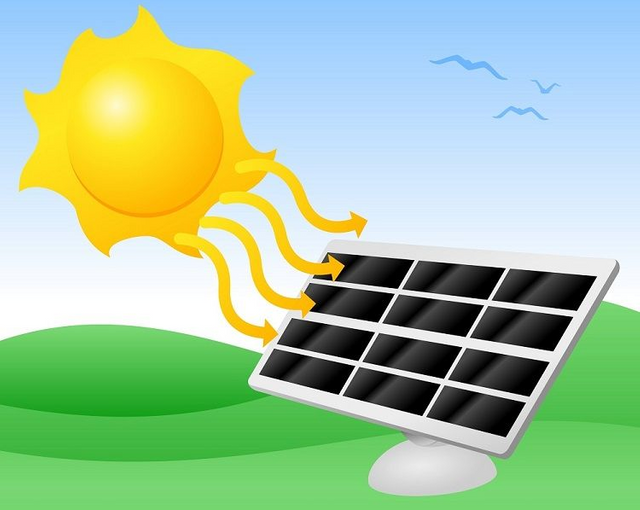
Solar energy systems directly gather the sun's rays and convert them into heat or power. The fusion reactions that occur when the hydrogen on the Sun's surface is transformed to helium are the source of this energy.
Outside the Earth's atmosphere, the intensity of solar energy is essentially constant around 1370 W/m2, but ranges between 0 and 1100 W/m2 on Earth. The most important quality of the energy that the sun sends to the Earth is that it is limitless.
Solar energy is measured in three ways: light, heat, and electricity. Photovoltaic (PV) systems convert solar energy directly into electricity and can be installed on the rooftops of buildings, appliances, and automobiles. Monofocal solar power plants work by reflecting solar energy to a narrow region using mirror and lens components. This concentrated energy can be used to generate electricity or heat via water heating or steam turbines. Water is heated using solar thermal collectors, which are commonly employed in our nation.
Solar energy is a viable energy source in nations that receive a lot of sunlight, such as Turkey. This method is very useful for rural off-grid electricity generation. The most significant disadvantage of this technology is that it cannot be manufactured at night.
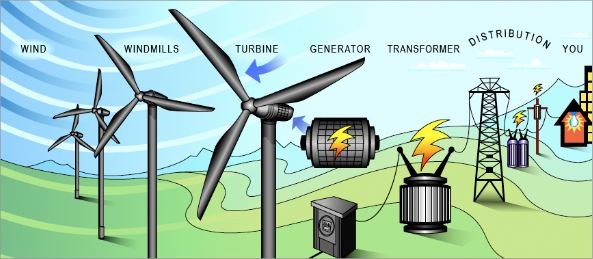
Wind energy is produced as a result of the differential heating of the earth's surfaces caused by solar radiation. Different heating of the earth's surfaces generates differences in the temperature, humidity, and pressure of the air, and this difference in pressure causes the air to move. Wind turbines produce electricity from wind energy, windmills produce mechanical energy, wind pumps for well pumping, and sails drive ships.
Wind energy currently satisfies 2% of the world's electrical demands. Wind turbine technologies have a low environmental impact when compared to other methods of generating electricity. Agriculture and animal husbandry can be carried out in land-based wind power installations. Aside from that, unlike fossil-fuel power plants, wind farms do not require cooling water.
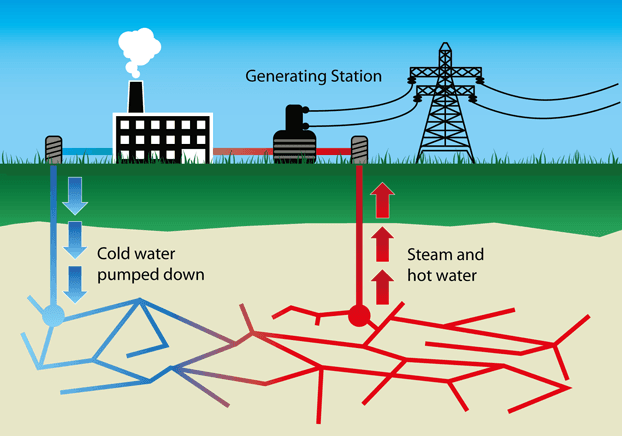
Geothermal energy has been used since ancient times in human history. The ancient Romans and the Chinese Natural geothermal resources were used for bathing, heating, and cooking in the 1500s. This energy source's enormous potential is only now being realised.
The thermal energy stored in the earth's crust is referred to as geothermal energy. Heat stored at various depths underground, as well as hot water containing chemicals, steam, and gases, are used to generate heat or electricity. When the heat level is high enough, geothermal energy may be employed to generate electricity and provide high-quality water for industries. Unlike solar and wind energy, geothermal energy can supply continuous power.
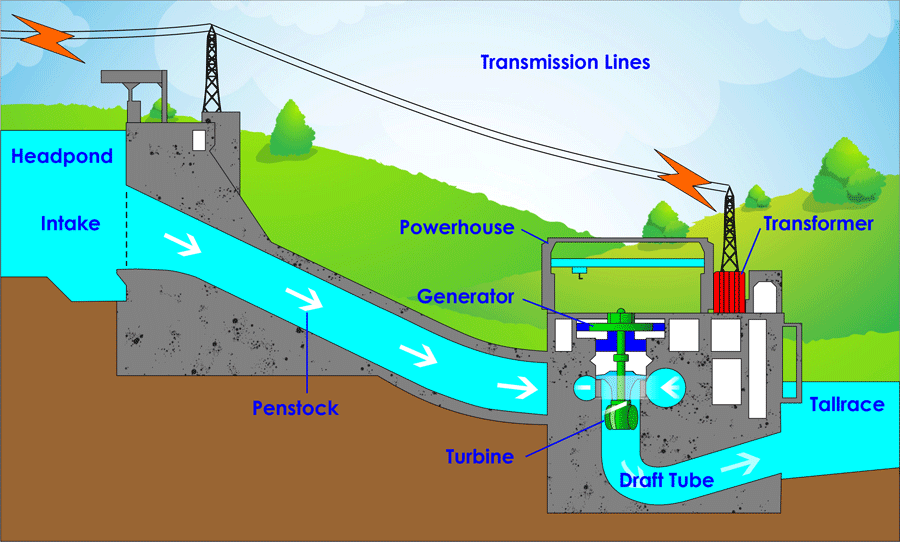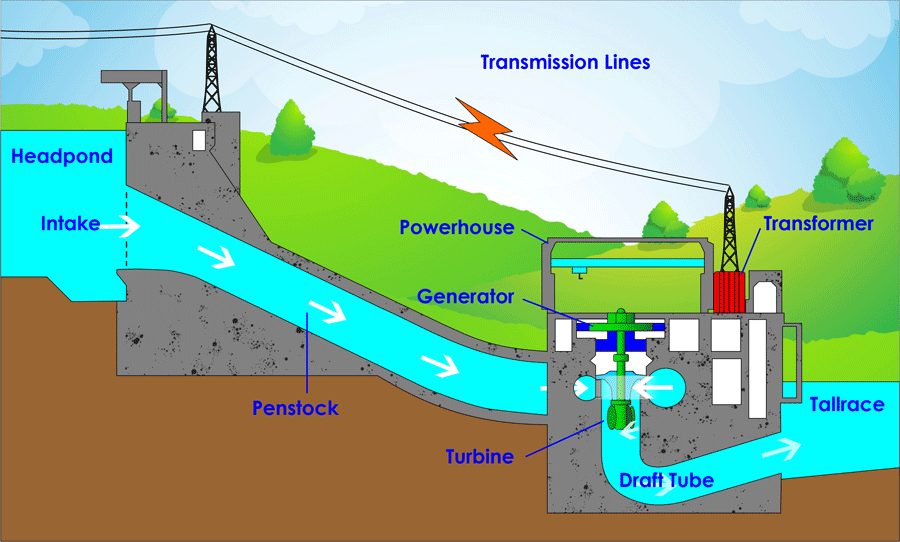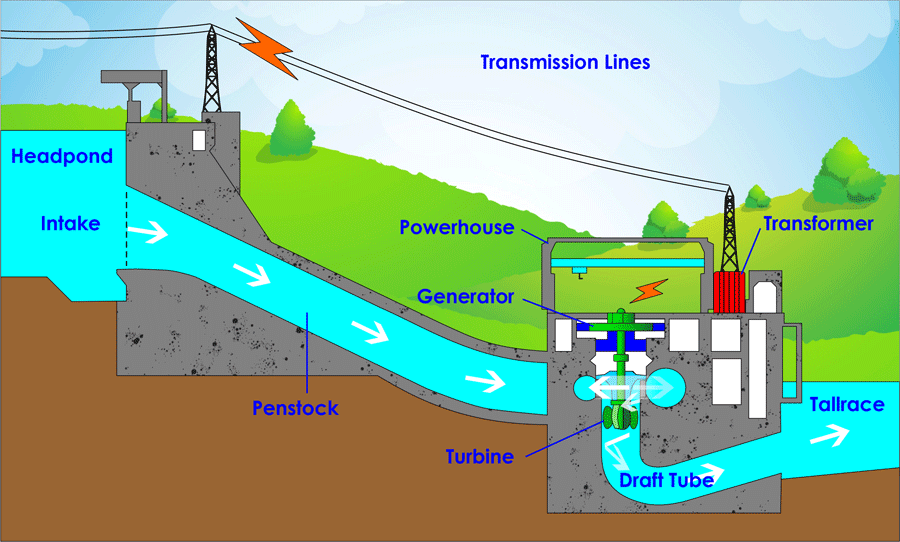
Hydroelectric power plants generate electricity by utilising the potential energy difference between two sites containing water. The dam's stored water is dropped from a specific height and converted into mechanical energy. This mechanical energy is converted into electrical energy by the generator motor and used to turn the tribune wheels. Hydropower is currently the world's greatest renewable energy source, accounting for over one-fifth of global electricity demand.
Dams and rivers are the two types of hydroelectric power plants. River-type power plants exploit the kinetic energy of flowing water, whereas dam-type power plants conserve it.
Dams modify the volume, water quality, and flow time of rivers; they degrade river systems by restricting the flow of nutrients and sediment in the natural life cycle via geomorphological processes. Dams have huge societal consequences; dams have influenced the living regions of 40-80 million people, forcing them to relocate to new towns. Large dam projects are currently being contested by local residents in numerous areas. Furthermore, dam lakes generated by huge dams can upset the biological equilibrium and promote undesirable methane generation due to organic material accumulation on the lake bottom.
The flow characteristics of the river limit electricity generation in river-type power plants, thus they are modest and medium-sized. If the water flow route is not changed, the environmental impact of these power plants is minimal. However, if a river-type hydroelectric power plant is built on a stream with a capacity significantly greater than the capacity of the stream, there will be no water in the bottom layers of the river, disrupting the ecological balance. The biological parameters of the river basin should be thoroughly studied while developing river-type power facilities.
The amount of plants that employ carbon dioxide, water, and solar energy to form organic matter on Earth and in the biosphere is referred to as biomass. Bioenergy is produced from biomass in the form of liquid biofuel (often obtained from energy-rich products), garbage (including domestic waste), solid biomass (wood, charcoal, and other biomass materials), or gas (derived from biomass decomposition). It is theoretically feasible to re-grow plants used in energy generation. As a result, biomass is a source of renewable energy.
Currently, biomass provides around 46 EJs of bioenergy globally. It is estimated that conventional biomass accounts for more than 10% of worldwide primary energy production, however the proportion consumed in underdeveloped nations is unknown.” In poor countries, biomass applications range from conventional biomass (such as open fire cooking) to highly efficient electricity, heat, and transportation fuels.