Jellyfish facts: poisonous, glowing, the largest jellyfish in the world
Jellyfish can rightfully be called one of the most mysterious inhabitants of the depths of the sea, arousing interest and a certain concern. Who they are, where did they come from, what species are in the world, what their life cycle is, are they so dangerous, as popular rumor tells - I want to know about all this for sure.
Jellyfish appeared more than 650 million years ago, they can be called one of the oldest organisms on Earth.
About 95% of the body of a jellyfish is water, it is also their habitat. Most jellyfish live in salt water, although there are species that prefer freshwater. Jellyfish - the phase of the life cycle of representatives of the genus Medusozoa, "sea jelly" alternates with a motionless asexual phase of motionless polyps, from which they are formed by budding after maturation.
The name was introduced in the 18th century by Karl Linnaeus, he saw in these strange organisms a certain resemblance to the mythical Medusa the Gorgon, thanks to the presence of tentacles that flutter like hair. With their help, the jellyfish catches small organisms that serve as food for it. The tentacles can be long or short, pointed filaments, but they all have stinging cells that stun prey and make hunting easier.
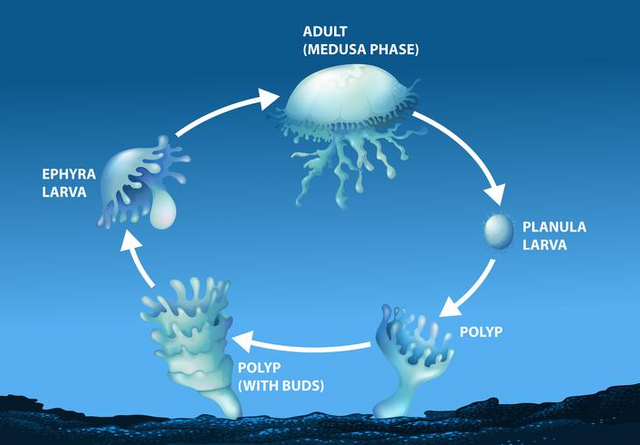
Life cycle of jellyfishSource
Anyone who has seen the sea water shine on a dark night is unlikely to be able to forget this spectacle: myriads of lights illuminate the depth of the sea, shimmer like diamonds. The reason for this amazing phenomenon is the smallest planktonic organisms, including jellyfish. One of the most beautiful is the phosphoric jellyfish. It is not found very often, inhabiting the bottom zone near the shores of Japan, Brazil, Argentina.
The diameter of the umbrella of the luminous jellyfish can reach 15 centimeters. Living in the dark depths, jellyfish are forced to adapt to the conditions, provide themselves with food, so as not to disappear altogether as a species. An interesting fact is that the bodies of jellyfish do not have muscle fibers and cannot resist the flow of water.
Since the slow jellyfish swimming at the behest of the current cannot keep up with the moving crustaceans, small fish or other planktonic inhabitants, you have to go for a trick and force them to swim up themselves, right to the predatory open mouth opening. And the best bait in the darkness of the bottom space is light.
The body of the glowing jellyfish contains a pigment - luciferin, which is oxidized under the influence of a special enzyme - luciferase. The bright light attracts victims like moths - the flame of a candle.
Some types of luminous jellyfish, such as Ratkea, Equorea, Pelagia, live near the surface of the water, and, gathering in large numbers, they literally make the sea burn. The amazing ability to emit light has piqued the interest of scientists. Phosphors have been successfully isolated from the genome of jellyfish and introduced into the genomes of other animals. The results turned out to be quite unusual: for example, mice, whose genotype was changed in this way, began to grow overgrown with green hairs.
Poisonous Jellyfish - Sea Wasp
Nowadays, more than three thousand jellyfish are known, and many of them are far from harmless to humans. Stinging cells, "charged" with poison, have all types of jellyfish. They help to paralyze the victim and deal with it without any problems. Without exaggeration, a mortal danger for divers, swimmers, fishermen is a jellyfish, which is called the Sea Wasp. The main habitat of such jellyfish is warm tropical waters, especially near the shores of Australia and Oceania.
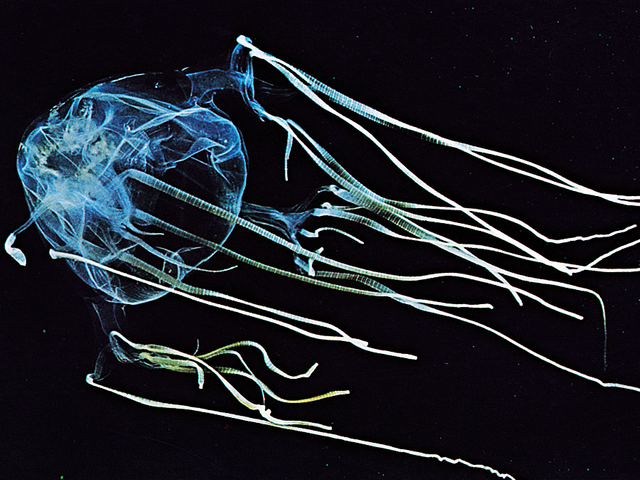
Chironex fleckeri - sea waspSource
Transparent bodies of light blue color are invisible in the warm water of quiet sandy bays. The small size, namely, up to forty centimeters in diameter, also does not attract much attention. Meanwhile, the poison of one individual is enough to send about fifty people to heaven. Unlike their phosphorescent cousins, sea wasps can change direction, easily finding careless bathers. The poison that has entered the victim's body causes paralysis of smooth muscles, including the respiratory tract. Being in shallow water, a person has a small chance to escape, but even if medical assistance was provided in a timely manner and the person did not die from suffocation, deep ulcers form in the places of "bites", causing severe pain and not healing for many days.
The tiny jellyfish Irukandji, described by Australian Jack Barnes in 1964, have a similar effect on the human body, with the only difference that the degree of damage is not so deep. He, like a true scientist advocating for science, experienced the effect of the poison not only on himself, but also on his own son. Symptoms of poisoning - severe headache and muscle pain, cramps, nausea, drowsiness, loss of consciousness - are not fatal in themselves, but the main risk is a sharp increase in blood pressure in a person who personally met Irukandji. If the victim has problems with the cardiovascular system, then the likelihood of death is quite high. The size of this baby is about 4 centimeters in diameter, but thin spindle-shaped tentacles reach 30-35 centimeters in length.
Another very dangerous inhabitant of tropical waters for humans is Physalia - Sea boat. Her umbrella is painted in bright colors: blue, violet, purple and floats on the surface of the water, so it is visible from afar. Whole colonies of attractive sea "flowers" attract gullible tourists, beckoning to pick them up as soon as possible. This is where the main danger lurks: long, up to several meters, tentacles, equipped with a huge number of stinging cells, hide under the water. The poison acts very quickly, causing severe burns, paralysis and disturbances in the work of the cardiovascular, respiratory and central nervous systems. If the meeting took place at great depths or just far from the coast, then its outcome can be the most sad.
The real giant is the Bell Nomura, which is also called the Lion's Mane for some external resemblance to the king of beasts. The diameter of the dome can reach two meters, and the weight of such a "baby" reaches two hundred kilos. It lives in the Far East, in the coastal waters of Japan, off the coast of Korea and China.
A huge hairy ball, falling into fishing nets, damages them, causing damage to the fishermen and escaping them themselves when trying to free them. Even if their poison is not fatal to humans, meetings with the "Lion's Mane" rarely take place in a friendly atmosphere.
Hairy Cyanea is the largest jellyfish in the ocean
Cyanea is considered one of the largest jellyfish. Living in cold waters, it reaches its largest size. The most gigantic specimen was discovered and described by scientists at the end of the 19th century in North America: its dome was 230 centimeters in diameter, and the length of the tentacles was 36.5 meters. There are a lot of tentacles, they are collected in eight groups, each of which contains from 60 to 150 pieces. It is characteristic that the dome of the jellyfish is also divided into eight segments, representing a kind of octagonal star. Fortunately, it does not live in the Azov and Black seas, so you can not be afraid of them when going to the sea to relax.
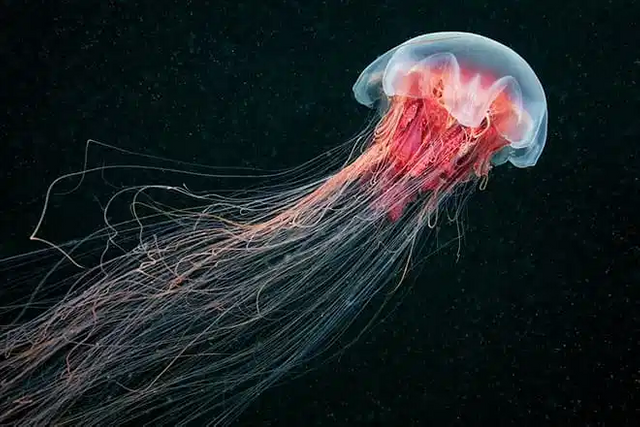

Hairy Cyanea is the largest jellyfish in the oceanSource
Depending on the size, the color also changes: large specimens are painted in bright purple or violet, smaller ones - in orange, pink or beige. Cyanei live in surface waters, rarely descending into the depths. The poison is not dangerous to humans, causing only an unpleasant burning sensation and blisters on the skin.
The use of jellyfish in cooking
The number of jellyfish living in the seas and oceans of the Earth is truly enormous, and none of the species is threatened with extinction. Their use is limited by the possibilities of extraction, but people have long used the beneficial properties of jellyfish for medicinal purposes and enjoy their taste in cooking. In Japan, Korea, China, Indonesia, Malaysia and other countries, jellyfish have long been eaten, calling them "crystal meat". Its benefits are due to the high content of protein, albumin, vitamins and amino acids, trace elements. And with proper preparation, it tastes very exquisite.
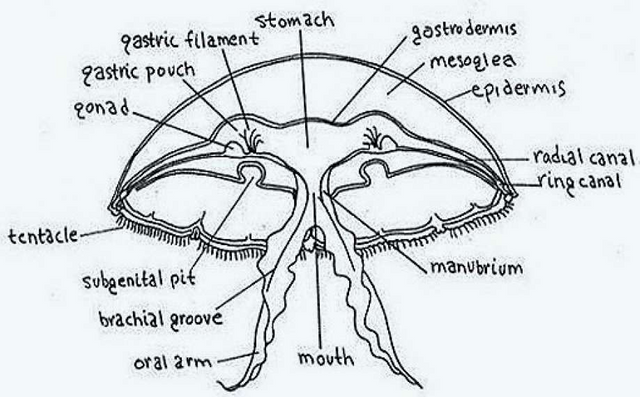
Diagram of the structure of the jellyfishSource
Jellyfish "meat" is added to salads and desserts, sushi and rolls, soups and main courses. In a world where population growth is steadily threatening the onset of hunger, especially in underdeveloped countries, jellyfish protein can be a good help in solving this issue.
Jellyfish in medicine
The use of jellyfish for the manufacture of medicines is characteristic, to a greater extent, in those countries where their use in food has long ceased to be a subject of surprise. For the most part, these are coastal countries where jellyfish are directly harvested.
In medicine, preparations containing processed jellyfish bodies are used to treat infertility, obesity, baldness and gray hair. The poison extracted from stinging cells helps to cope with diseases of the ENT organs and normalize blood pressure.



This post was resteemed by @steemvote and received a 3.49% Upvote. Send 0.5 SBD or STEEM to @steemvote