The use of electrostatic induction in technology
During electrostatic induction, an electric charge appears on the surface of a conductor introduced into an external electrostatic field. This charge, which accumulates on the surface of the said conductor, is called induced or induced charge. Moreover, on opposite sides of such a conductor, the induced charges will be of the opposite sign - on the one hand there will be positive, on the other - negative.
The accumulation of charge on the surface of a body during electrostatic induction will continue until the body's own electrostatic field almost completely compensates for the external electrostatic field in which this body is placed. This happens with bodies with high conductivity, that is, with metals that are characterized by low resistivity.
The phenomenon of electrostatic induction finds application in technology. It is used, for example, to protect various sensitive circuits from external electromagnetic and electrostatic fields.
These circuits primarily include: measuring, receiving, high-frequency and transmitting circuits. To protect them, special metal screens are made in the form of nets or casings, which are grounded or galvanically connected to the negative electrode of the protected circuit.
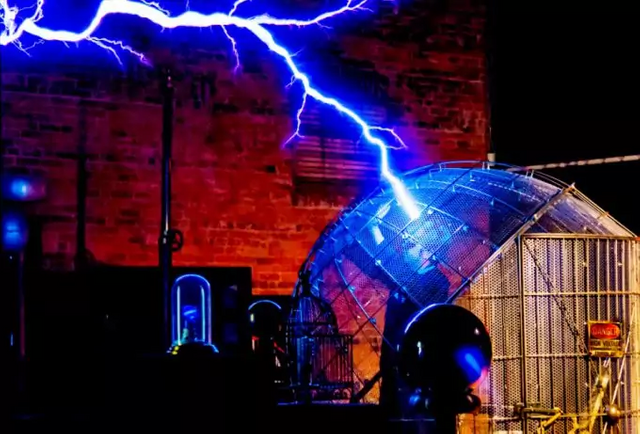

Electrostatic protection, Faraday cageSource
The use of electrostatic induction in technology
The electrostatic protection device is called a Faraday cage after its inventor Michael Faraday. English physicist Michael Faraday, the father of the law of electromagnetic induction, created this device in 1836.
In one form or another, the Faraday cage is used in technology to this day to protect (shield) electronic equipment and technology from external electromagnetic fields. Usually it is a cage made of a material with low resistivity or a hollow, well-conducting, well-shaped structure.
Electrostatic protection based on a Faraday cage works according to the following principle. When a closed conducting shell enters an electric field, free electrons in it come into motion under the action of this field. As a result, as described above, the opposite sides of the cell acquire opposite charges, which compensate for the external electric field with their fields.
This type of protection is only applicable for shielding against an electric field, while a constant magnetic field of course penetrates into the containment.
An alternating electric field generates an alternating magnetic field, which again creates an alternating electric field. Therefore, if the alternating electric field is blocked with the help of electrostatic protection based on the Faraday cage, then the alternating magnetic field will not fall on the protected elements inside either, since it simply will not be generated in that area.
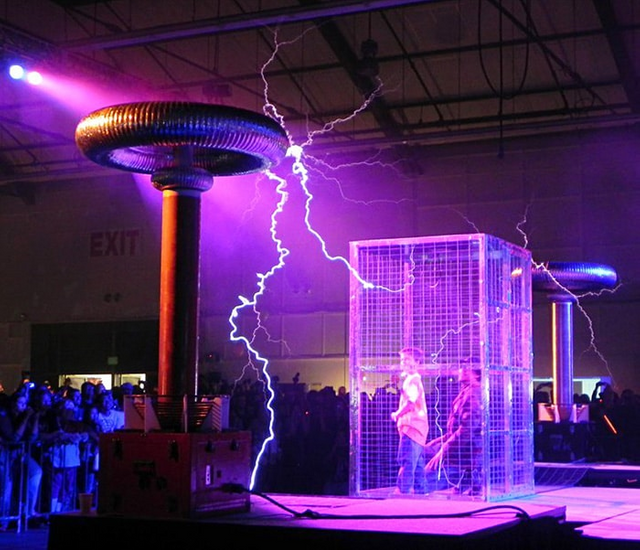

Demonstration of a Faraday cageSource
Electrostatic induction is of great importance for the field of the latest alternative energy. Electrostatic action on atmospheric air allows the charged particles in it to be directed towards technical devices collecting electric charge.
In the normal state, charged particles rush chaotically in the air, simply due to the phenomenon of thermal motion. At the same time, they rub against each other, charging each other positively and negatively - this is how positive and negative ions are formed.
Technical devices, due to the phenomenon of electrostatic induction, are able to interact with these ions and use their charges as if in the electrolyte of a charged battery. This direction has been actively explored in recent years by fans of alternative energy and electrostatics.
This post was resteemed by @steemvote and received a 5.12% Upvote. Send 0.5 SBD or STEEM to @steemvote