CELLS
CELL STRUCTURE AND ORGANIZATION:
The cell is the fundamental and structural unit of life. Every living things on earth, including animal,plant,bacteria,yeast, and mould are made of cell. Some living things, such as animal and plant, are multicellular; their bodies are made of many cells. Other living things, such as bacteria and yeast, are unicellular-made of just one cell. two scientists are instrumental in unveiling the microscopic world to humanity.
1.Robert Hooke who discoverd the plant cells in 1665. While observing a cork through his microscope, Hooke saw tiny boxlike cavities, which he illustrated and described as cells
2.in 1676, antonie van Leeuwenhoek used his microscope to look into a drop of lake water-water that appeared clear to his eyes - and was astound to see tiny creature swimming around in it. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek was the first to see bacteria, blood cells, and sperm cells fertilizing an egg.
THE CELL THEORY:
- All living organisms are composed of one or more cells.
- The cell is the most basic unit of life.
- All cells arise only from pre-existing cells.
The first two were proposed by Theodor Schwann and Mathias schleiden in 1838 while the third was proposed by Rudolf Virchow in 1858
MOBERN CELL THEORY:
- All known living things are made up of one or more cells.
- All living cells arise from pre-existing cells by division.
- The cells is the fundamental unit of structure and function in all living argenisms.
- The activity of an organism depends on the total activity of independent cells.
- Energy flow (metabolism and biochemistry) occur within cells.
- Cells contain DNA which is found specifically in the chromosomes and RNA found In the cell nucleus and cytoplasm.
- All cells are basically the same in chemical composition in organism of similar species.
CELLS ARE DIVIDED INTO:
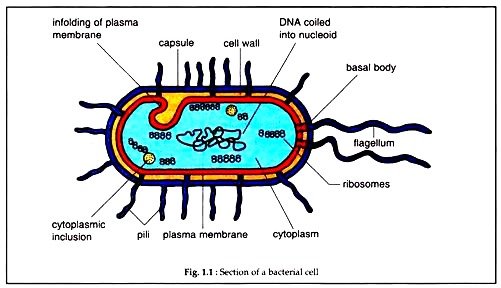
( A) prokaryotic cells: organism without membrane bound nucleus e.g Bacteria and archaea.
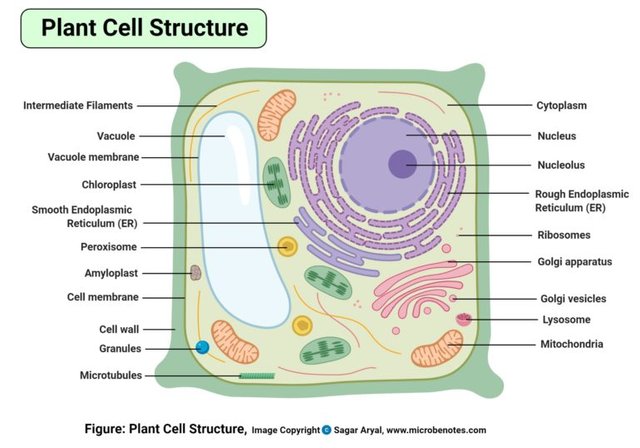
(B) Eukaryotic cells: organisms with membrane bound nucleus e.g unicellular and multi-cellular organisms.
Viruses are neither prokaryotic nor eukaryotic cells. The are perticles that cannot survive outside the host cell and must infect other organism to produce.
Differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
PROKARYOTIC CELLS:
1 Nucleus absent .
2 DNA is found within the cytoplasm.
3 They do not have membrane-bound organelles.
4 The are smaller than eukaryotic cells.
EUKARYOTIC CELLS:
1 Membrane bound nucleus present.
2 DNA is enclosed within the nucleus.
3 The have membrane bound organelles within the cells.
4 The are larger than prokaryotic cells.
SIMILARITIES BETWEEN PROKARYOTIC EUKARYOTIC CELLS.
1 The cells have a boundary that separate them from their environment. The boundary of a cell is called the plasma membrane (or cytoplasmic membrane).
2 The area inside all cells is called the cytoplasm and in all cells.
3 All cells contain deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), which contain the plans for how the cells is built and how it founctions.
4 All cells have ribosomes that make proteins. Proteins after built on structures called ribosomes.
All body organ, tissue is made up of cell and cell is the smallest unit of life.