The Greatest and Greatest Muslim Scientist in the world
Scientists and inventors of Muslims (Arabs, Persians and Turks) have managed to make some remarkable discoveries hundreds of years earlier than their counterparts in Europe.
They drew influences from the philosophies of Aristotle and the Neo-Platonists, including Euclid, Archimedes, Ptolemy and others. The Muslims at that time had succeeded in making innumerable discoveries in the fields of medicine, surgery, mathematics, physics, chemistry, philosophy, astrology, geometry and other countless fields and wrote his works in various books.

- Logic
- Mathematical Sciences
- Natural Science
- Theology
- Political Science and State
- Potpourri (Pole Munawwa'ah).
His most famous work is Al-Madinah Al-Fadhilah (City or Main State) which discusses the achievement of happiness through political life and the relationship between the best regimes in Plato's understanding with the Divine Law of Islam.
- AL-BATANI

Al Battani (ca. 858-929) also known as Albatenius was an astronomer and mathematician from Arabia. Al Battani full name: Abū Abdullāh Muhammad ibn Jābir ibn Sinān ar-Raqqī al-Harrani as-Sabi al-Battānī), was born in Harran near Urfa.
One of his famous achievements in astronomy is about the determination of the Sun Year as 365 days, 5 hours, 46 minutes and 24 seconds.
Al Battani also found a number of trigonometric equations:

It also solves the equation sin x = a cos x and finds the formula:
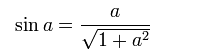
and using al-Marwazi's notion of tangent in developing equations for calculating tangent, cotangen and compiling tangent count tables.
Al Battani works in Syria, precisely in ar-Raqqah and in Damascus, which is also the place of his death.
- IBNU SINA

Ibnu Sina (980-1037) also known as Avicenna in the Western World was a philosopher, scientist, and also a Persian-born physician (now part of Uzbekistan). He is also a prolific writer where much of his work is about philosophy and medicine.
For many, he is the Father of Modern Medicine and there are many more titles to him that are mostly concerned with his works in the field of medicine. His most famous work Qanun fi Thib is a medical reference for centuries
Ibn Sina's full name Abū 'Alī al-Husayn bin' Abdullāh bin Sīnā was born in 980 in Afsyahnah area near Bukhara, now Uzbekistan (then Persia), and died in June 1037 in Hamadan, Persia (Iran).
He is the author of 450 books on several major subjects, many of which focus on philosophy and medicine. He is regarded by many as the father of modern medicine, George Sarton calls Ibn Sina "The most famous scholar of Islam and one of the most famous in all areas, places, and times." His most famous works are The Book of Healing and The Canon of Medicine, also known as Qanun (full title: Al-Qanun fi At Tibb).
Creation
- Qanun fi Thib (Canon of Medicine / Rules of Medicine)
- Asy Syifa (consisting of 18 volumes containing about various sciences)
- An Najat
- IBNU BATUTAH

Abu Abdullah Muhammad bin Battutah or also spelled Ibn Battuta is a Berber traveler (explorers) of Morocco.
At the instigation of the Sultan of Morocco, Ibn Battuta dictated some of his important journeys to a scholar named Ibn Juzay, whom he met while in Iberia. Although it contains several fictional stories, Rihlah is the world's most complete travel record dating from the 14th century.
Born in Tangier, Morocco between 1304 and 1307, at the age of about twenty years Ibn Batuta went to pilgrimage - a pilgrimage to Mecca. After completion, he continued his journey through 120,000 kilometers throughout the Muslim world (about 44 modern countries).
- IBNU RUSYD

Ibn Rushd (Ibn Rushdi, Ibn Rusyid, born in 1126 in Marrakech, Morocco, died December 10, 1198) also known as Averroes, was a Spanish philosopher (Andalusia).
Overview
Abu Walid Muhammad bin Rusyd was born in Cordoba (Spain) in 520 Hijri (1128 AD). Ibn Rushd's father and grandfather were the famous judges of his day. Little Ibn Rushd himself was a child with many interests and talents. He studied many sciences, such as medicine, law, mathematics, and philosophy. Ibn Rushd studied the philosophy of Abu Ja'far Aaron and Ibn Baja.
Ibn Rushd is a genius who came from Andalusia with encyclopedic knowledge. His lifetime was mostly given to serve as "Kadi" (judge) and physicist. In the western world, Ibn Rushd is known as Averroes and the greatest commentator on Aristotelian philosophy that influenced medieval Christian philosophy, including such thinkers as St. Thomas Aquinas. Many people came to Ibn Rushd to consult medical and legal issues.
The thought of Ibn Rushd
Ibn Rushd's works cover the fields of philosophy, medicine and Jurisprudence in the form of essays, reviews, essays and resumes. Almost all of Ibn Rushd's works are translated into Latin and Hebrew (Jews) so that the original works are unlikely to exist.
Ibn Rushd's philosophy is two, Ibn Rushd's philosophy as understood by the medieval Europeans; and Ibn Rushd's philosophy of faith and his religious attitudes.
Creation
- Bidayat Al-Mujtahid
- Kulliyaat fi At-Tib (Medical Lecture)
- Fasl Al-Maqal fi Ma Bain Al-Hikmat Wa Ash-Shari'at
- MUHAMMAD BIN MUSA AL-KHAWARIZMI

Muhammad bin Mūsā al-Khawārizmī was a mathematician, astronomer, astrology, and geographer from Persia. Born around 780 in Khwārizm (now Khiva, Uzbekistan) and died about 850 in Baghdad. For most of his life, he worked as a lecturer at the Honorary School in Baghdad.
His first book, al-Jabar, is the first book to discuss systematic solutions of linear and quadratic notation. So he is referred to as Mr. Algebra. The Latin translation of his Arithmetic, which introduced the Indian numerals, was then introduced as the Decimal Declining Numbering System in the Western world in the 12th century. He revised and adapted the Ptolemaic Geography as well as working on writings on astronomy and astrology.
His contribution not only had a major impact on mathematics, but also in language. The word Algebra is derived from the word al-Jabr, one of two operations in mathematics to complete the quadratic notation, which is contained in his book. The word logarism and logarithm is taken from the word Algorismi, the Latinization of his name. His name is also absorbed in Spanish Guarismo and in Portuguese, Algarismo which means digit.
Biography
Little can be known from his life, even the location of the birthplace though. His name may have come from Khwarizm (Khiva) residing in Khurasan Province during the reign of the Abbasids (now Xorazm, one of Uzbekistan's provinces). His title is Abū 'Abdu llāh or Abū Ja'far.
The historian al-Tabari named him Muhammad ibn Musa al-Khwārizmī al-Majousi al-Katarbali. The name al-Qutrubbulli indicated he was from Qutrubbull, a small town near Baghdad
In Kitāb al-Fihrist Ibn al-Nadim, we find his brief history, together with his writings. Al-Khawarizmi occupied almost all of his work between 813-833. after Islam entered Persia, Baghdad became a center of science and commerce, and many traders and scientists from China and India ventured into this city, which he also did. He worked in Baghdad at the School of Honor founded by Caliph Bani Abbasid Al-Ma'mun, where he studied natural sciences and mathematics, including studying translations of Sanskrit and Greek manuscripts
Creation
His greatest work in mathematics, astronomy, astrology, geography, cartography, as a foundation and then more innovative in algebra, trigonometry, and in other fields he employs. His logical and systematic approach to linear settlement and quadratic notation provides accuracy in algebraic disciplines, named after one of his books in 830 AD, Summary Book for Calculations by Completing and Balancing ", his first book which was later translated into Latin in the 12th century.
In his book, Calculations with Hindu numerals, written in 825, prescribe the diffusion of Indian numerals into the Middle East and then of Europe. His book was translated into Latin, Algoritmi de numero Indorum, showing the word algorithm being Latin.
- UMAR KHAYYAM

The Mathematician
In his lifetime, he is renowned as a mathematician and astronomer who takes into account how to correct the Persian calendar. On March 15, 1079, Sultan Jalaluddin Malikshah Saljuqi (1072-1092) imposed a calendar that Umar had repaired, as Julius Caesar did in Europe in 46 BC with correction of Sosigenes, and by Pope Gregory XIII in February 1552 with a calendar which Aloysius Lilius had repaired (although the United Kingdom had just switched from the Julian Calendar to the Gregorian calendar in 1751, and Russia just did it in 1918).
He is also famous for finding the method of solving cubic equations by cutting a parabola with a circle
- TSABIT BIN QURRAH

Abu'l Hasan Thabit bin Qurra 'bin Marwan al-Sabi al-Harrani, (826-18 February 901) was an astronomer and mathematician from Arabia, and also known as Thebit in Latin.
Thabit was born in the city of Harran, Turkey. Thabit was educated at Baitul Hikmah in Baghdad at the invitation of Muhammad ibn Musa ibn Shakir. Thabit translated Euclid's book Elements and Ptolemy's Geograpia
Al-Sabi' Thabit bin Qurra al-Ḥarrānī, Latin: Thebit / Thebith / Tebit, 826 - February 18, 901) was a mathematician, physician, astronomer and translator of the Golden Age Islam who lived in Baghdad in the second half of the ninth century.
Ibn Qurra makes an important discovery in algebra, geometry, and astronomy. In astronomy, Thabit is regarded as one of the first reformers of the Ptolemaic system, and in mechanics he is the founder of statics
- MUHAMMAD BIN ZAKARIYA AL-RAZI

Abu Bakr Muhammad bin Zakaria ar-Razi or known as Rhazes in the western world is one of the Iranian scientists who lived between 864-930. He was born in Rayy, Tehran in 251/865 and died in 313 H / 925 .
Ar-Razi has since studied philosophy, chemistry, mathematics and literature. In medicine, he studied with Hunayn bin Ishaq in Baghdad. Upon his return to Tehran, he is believed to lead a hospital in Rayy. He also led the Muqtadari Hospital in Baghdad.
Biography
Ar-Razi was born on 28 August 865 Hijirah and died on 9 October 925 Hijriah. His Razi name comes from the name of Rayy city. The city is located in the southern valley of the Alborz Highlands near Tehran, Iran. In this city too, Ibn Sina completed almost all of his work.
As a child, ar-Razi is interested in becoming a singer or musician but he is then more interested in the field of alchemy. At the age of 30, ar-Razi decided to stop the field of alchemy due to various experiments that caused his eyes to become disabled. Then he seeks a doctor who can heal his eyes, and from here ar-Razi begins to study medicine.
- ABU MUSA JABIR BIN HAYYAN

Abu Musa Jabir bin Hayyan, otherwise known as Geber in the Western world, was thought to have been born in Kuffah, Iraq in 722 and died in 804. Jabir's greatest contribution was in chemistry. This expertise he got with he studied at Barmaki Vizier, during the reign of Harun Ar-Rashid in Baghdad. He developed a systematic experimentation technique in chemical research, so that every experiment can be reproduced. Jabir emphasizes that the quantity of matter is related to the chemical reaction that occurs, so it can be considered that Jabir has pioneered the discovery of fixed comparison law.
Other contributions include improvements in the crystallization, distillation, calcination, sublimation and evaporation processes and the development of instruments to perform.