Why do some people faint after having their blood drawn?
Hello fellows Steemians!
I would like to open today's topic with a story from my personal life when I was back in high school. We were having one of those mandatory group medical exams, and my whole class had to go together with a teacher to one of the medical facilities, where they would perform standard medical tests and blood analyses, to make sure we're just one healthy bunch of adolescents, with only ''diagnosis'' of not behaving properly in class :)
After having my blood drawn, I went outside to join my classmates, where we were all standing in front of the entrance waiting for everyone to finish with tests. All of the sudden, I started to feel nausea, dizziness and loss of vision. Next thing I remember is me lying on the ground with bunch of worried faces above me, one of which was a nurse asking me: ''Why didn't you tell us that you're afraid of needles?'' Luckily, one of my classmates caught me just before I was going to hit the ground, so thanks to him I didn't bump my head on the concrete (that wouldn't help me in becoming a scientist!), but still I was having difficulties remembering what happened.
I was never afraid of needles, neither of having blood drawn/seeing blood. How could I be, when I had so many injections during my childhood, that my dad use to joke with me all the time that I'm like the Tom Cat (explanation in the image below) :)
Since that medical exam, each time I was having blood drawn, the same would happen. That meant only one thing - a serious research had to be conducted! So today I will talk about this problem many of us have encountered (including myself!) after having blood drawn or after experiencing some other form of physiological stress - syncope, also known as “fainting,” “passing out,” or “blackout.”
Physiological stress and syncope
Let's start by defining the physiological (or biological) stress. It represents any external or internal condition that challenges the homeostasis of a cell or an organism, and can be divided in three different aspects: environmental stress, intrinsic developmental stress, and aging. Environmental stress can be further described by environmental variations exceeding certain levels [1].
Syncope is defined as a transient loss of consciousness, with loss of posture (that is, falling). Since syncope is considered to be a symptom, not a disease, it is classified according to the underlying cause and it can be neurological, metabolic, psychiatric, and cardiac [2].
Vasovagal (neurocardiogenic) syncope
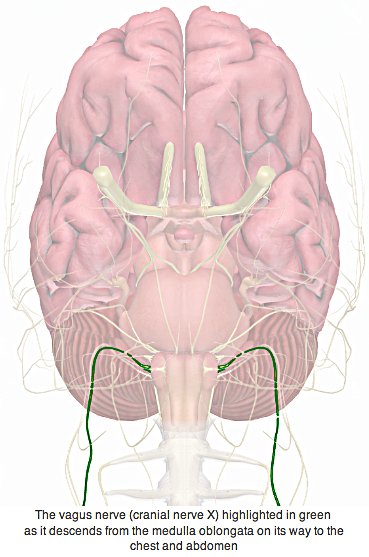
The vagus nerve is the tenth cranial nerve with both sensory and motor nerves, which include both voluntary and involuntary branches. Although normally referred to in the singular, the vagus nerves are paired, with two large nerves in charge of control of the heartbeat, breathing, blood pressure, and other involuntary processes [3].
When vagus nerves are activated due to an environmental stress, it triggers slowing of the heart rate, sudden dropping of blood pressure, and dilatation of the peripheral blood vessels. This causes blood flow to the lower portion of the body, leaving brain with insufficient blood flow. This sequence of events is called the vasovagal response. When vasovagal response causes fainting, it is called vasovagal syncope.
Symptoms of vasovagal syncope may include nausea, pale skin, tunnel and/or blurry vision, cold sweat, dilatation of pupils and feeling hot.
Vasovagal syncope can be caused by physical or emotional distress, such as:
- Prolonged standing
- Standing up quickly after sitting for a long time
- Spending time in a hot, crowded or poorly ventilated place
- Seeing blood and/or having blood drawn
- Intense emotions, including shock, anger, pain, or anxiety
- Straining, when lifting something heavy or having a difficult bowel movement [4, 5].
Vasovagal syncope can actually be avoided by lying on back with the legs elevated on the first sign of symptoms. Another option is to sit down and lean the head between the knees. For example I always put myself in lying position before having blood drawn, and avoid fainting in that way.
Vasovagal syncope is considered to be harmless and requires no treatment, unless you hit your head really bad and waste your chance of becoming a scientist for example - treatment will help your injury/wound heal, but you would definitely need to consider alternative carrier! ;)
As we can see from above, if we faint after having blood drawn, it does not necessarily means that we are afraid of needles/seeing blood. So next time somebody calls you a coward for fainting, you can respond to them - it's not me who is the coward, it's my vagus nerve!
References:
- Kagias, K., Nehammer, C. and Pocock, R., 2012. Neuronal responses to physiological stress. Frontiers in genetics, 3.
- Chen-Scarabelli, C. and Scarabelli, T.M., 2004. Neurocardiogenic syncope. BMJ: British Medical Journal, 329(7461), p.336.
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vagus_nerve
- http://www.innerbody.com/diseases-conditions/vasovagal-syncope
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/vasovagal-syncope/symptoms-causes/syc-20350527


Nice clear explanation. The one time I had this occur is while watching my wife (girlfriend at the time) get her wisdom teeth pulled. Luckily the nurse saw me turning white as a sheet and got me to sit on the ground before I passed out :)
Thank you very much! Then you probably know it's not the nicest experience when it happens :)
That's actually something I was wondering for quite some time, even though I never fainted myself (but I experience the weird feeling when standing up quickly after a long time of sitting pretty often, so it's nice to know that it probably won't kill me anytime soon). Also, it's pretty good to have a list with references, so you can keep reading when you're interested in the topic.