eukaryotic cell(main organells)(animal cell)
hello my friends. doctor steemit is here again now 21000sp power more 2$ upvote makes the profitable post for you and you can get the information about the eukaryotic cell(main organells).
A cell is defined as eukaryotic if it has a membrane-bound nucleus. Any organism composed of eukaryotic cells is also considered a eukaryotic organism.
any cell or organism that possesses a clearly defined nucleus. The eukaryotic cell has a nuclear membrane that surrounds the nucleus, in which the well-defined chromosomes (bodies containing the hereditary material) are located.
Eukaryotes (also spelled eucaryotes) comprise animals, plants, and fungi—which are mostly multicellular - as well as various other groups that are collectively classified as protists (many of which are unicellular).
Eukaryotic membranes are highly modified. In addition to the protein and phospholipid layer that acts as a selective barrier, single celled animals, for example, have special proteins embedded in their plasma (cell) membrane that interact with molecules outside and allow the cell to react to changing external circumstances.
Organelles:
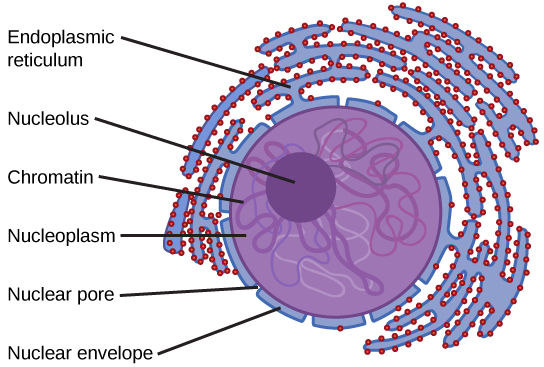
1.Nucleus:
The brains of the cell, the nucleus directs cell activities and contains genetic material called chromosomes made of DNA.
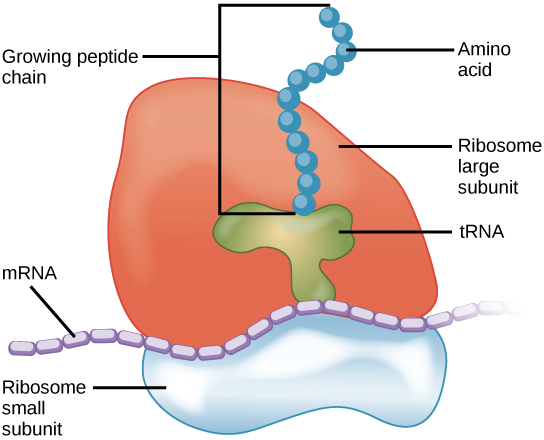
2.Ribosomes:
Ribosomes are the cellular structures responsible for protein synthesis. When viewed through an electron microscope, ribosomes appear either as clusters (polyribosomes) or single, tiny dots that float freely in the cytoplasm. They may be attached to the cytoplasmic side of the plasma membrane or the cytoplasmic side of the endoplasmic reticulum and the outer membrane of the nuclear envelope (cartoon of cell above).
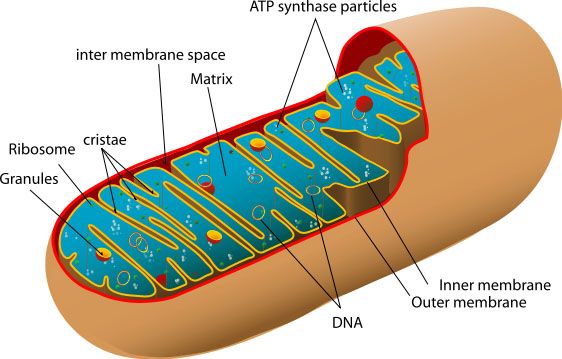
3.Mitochondria:
membrane-bound organelle found in the cytoplasm of almost all eukaryotic cells (cells with clearly defined nuclei), the primary function of which is to generate large quantities of energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondria are typically round to oval in shape and range in size from 0.5 to 10 μm.
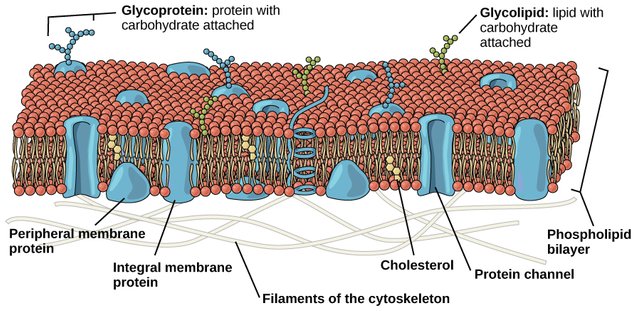
5.The plasma membrane
Like bacteria and archaea, eukaryotic cells have a plasma membrane, a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins that separates the internal contents of the cell from its surrounding environment. The plasma membrane controls the passage of organic molecules, ions, water, and oxygen into and out of the cell.
6.Rough ER is named for its rough appearance, which is due to the ribosomes attached to its outer (cytoplasmic) surface. Rough ER lies immediately adjacent to the cell nucleus, and its membrane is continuous with the outer membrane of the nuclear envelope. The ribosomes on rough ER specialize in the synthesis of proteins.
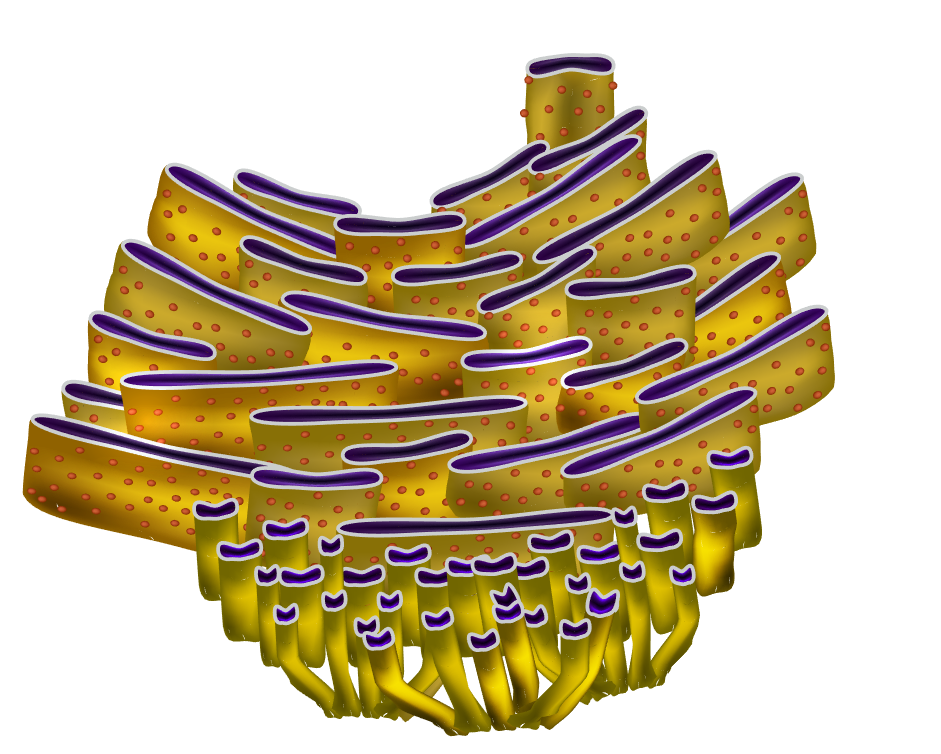
6.Golgi Apparatus:
The Golgi apparatus, or Golgi complex, functions as a factory in which proteins received from the ER are further processed and sorted for transport to their eventual destinations: lysosomes, the plasma membrane, or secretion. In addition, as noted earlier, glycolipids and sphingomyelin are synthesized within the Golgi.
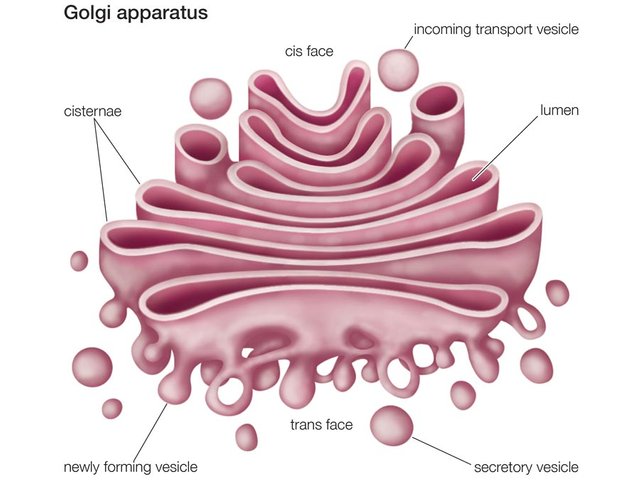
source:https://www.khanacademy.org/science/biology/structure-of-a-cell/introduction-to-cells/v/cell-theory




nice post doctor steemit thanks for sharing nice information about cell body and the work of it i love your job my friend love this post please try make the post about the prokaryotic cell and bactrial cell thanks for your support
yes sure i will try make it man you have huge information about the medical health
upvote me ,up vote me , pls iam new and i need power
what cell exactly plant or animal
(animal)
thanks for the comment my friend
Great post!
This post has received a -16.67 % downvote from @meanpeoplesuck thanks to: @blacklist-a.