ORAL HEALTH AND HYGIENE
ORAL HEALTH AND HYGIENE
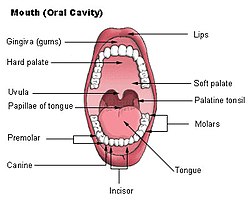
Oral health
is multifaceted and includes the ability to speak, smile, smell, taste, touch, chew, swallow, and convey a range of emotions through facial expressions with confidence and without pain, discomfort, and disease of the craniofacial complex.Oral health is essential to general health and quality of life. It is a state of being free from mouth and facial pain, oral and throat cancer, oral infection and sores, periodontal (gum) disease, tooth decay, tooth loss, and other diseases and disorders that limit an individual’s capacity in biting, chewing, smiling, speaking, and psychosocial wellbeing. Risk factors for oral diseases include unhealthy diet, tobacco use, harmful alcohol use, and poor oral hygiene.
Anything oral involves and basically is referring to the teeth, tongue and tonsil.
THE TEETH
The teeth are the hardest substances in the human body. Besides being essential for chewing, the teeth play an important role in speech.
There are 4 different types of teeth and each serve different functions:
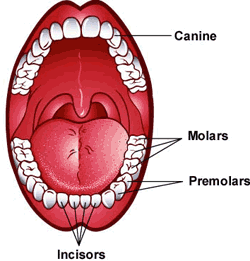
- The incisors (8 in total) are the teeth at the very front of your mouth. They are the sharpest and help to cut up your food.
- The canines (4 in total) are the pointed teeth either side of your incisors. They help to hold and tear the food.
- The pre-molars (8 in total) are behind your canine teeth. They have a flat chewing surface because they help to crush your food.
- The molars (8 in total) are the very back teeth. They are big ‘double' teeth and are also flat. They help to chew and grind your food into small pieces ready to swallow.
...Wisdom teeth or third molars (4 in total) which erupt at around age 16 to 21.
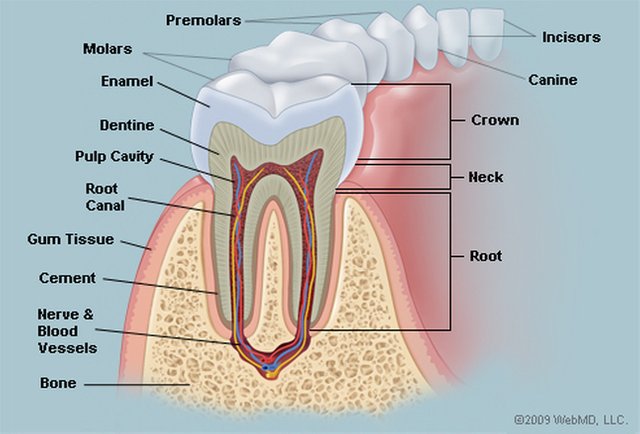
Parts of the teeth include:
• Enamel: The hardest, white outer part of the tooth. Enamel is mostly made of calcium phosphate, a rock-hard mineral.
• Dentin: A layer underlying the enamel. It is a hard tissue that contains microscopic tubes. When the enamel is damaged, heat or cold can enter the tooth through these paths and cause sensitivity or pain.
• Pulp: The softer, living inner structure of teeth. Blood vessels and nerves run through the pulp of the teeth.
• Cementum: A layer of connective tissue that binds the roots of the teeth firmly to the gums and jawbone.
• Periodontal ligament: Tissue that helps hold the teeth tightly against the jaw.
Teeth Conditions:
Cavities (caries): Bacteria evade removal by brushing and saliva and damage the enamel and deeper structures of teeth. Most cavities occur on molars and premolars.
Tooth decay: A general name for disease of the teeth, including cavities.
Periodontitis: Inflammation of the deeper structures of the teeth (periodontal ligament, jawbone, and cementum). Poor oral hygiene is usually to blame.
Gingivitis: Inflammation of the surface portion of the gums, around and between the crowns of the teeth. Plaque and tartar buildup can lead to gingivitis.
Plaque: A sticky, colorless film made of bacteria and the substances they secrete. Plaque develops quickly on teeth after eating sugary food, but can be easily brushed off.
Tartar: If plaque is not removed, it mixes with minerals to become tartar, a harder substance. Tartar requires professional cleaning for removal.
Overbite: The upper teeth protrude significantly over the lower teeth.
Underbite: The lower teeth protrude significantly past the upper teeth.
Teeth grinding (bruxism): Stress, anxiety, or sleep disorders can cause teeth grinding, usually during sleep. A dull headache or sore jaw can be symptoms.
Tooth sensitivity: When one or more teeth become sensitive to hot or cold, it may mean the dentin is exposed.
THE TONGUE
The tongue is a muscular organ in the mouth of most vertebrates that manipulates food for mastication, and is used in the act of swallowing. The tongue is covered with moist, pink tissue called mucosa. Tiny bumps called papillae give the tongue its rough texture. Thousands of taste buds cover the surfaces of the papillae.
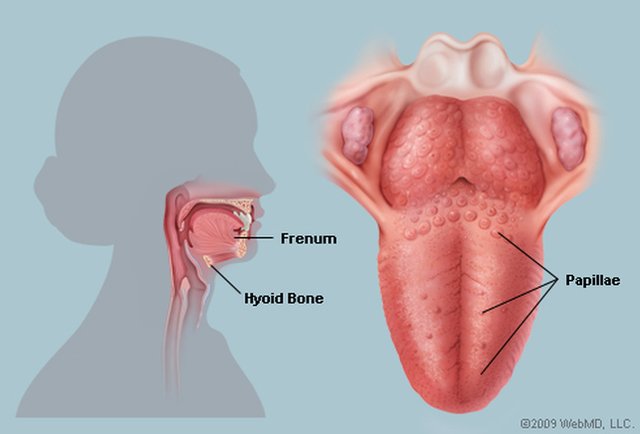
It is sensitive and kept moist by saliva, and is richly supplied with nerves and blood vessels. The tongue also serves as a natural means of cleaning the teeth. A major function of the tongue is the enabling of speech in humans and vocalization in other animals.
The four common tastes are sweet, sour, bitter, and salty. A fifth taste, called umami, results from tasting glutamate (present in MSG). The tongue has many nerves that help detect and transmit taste signals to the brain. Because of this, all parts of the tongue can detect these four common tastes; the commonly described “taste map” of the tongue doesn’t really exist.
Tongue Conditions:
Thrush (candidiasis): Candida albicans (a yeast) grows over the surface of the mouth and tongue. Thrush can occur in almost anyone, but it occurs more often in people taking steroids or with suppressed immune systems, the very young, and the elderly.
Oral cancer: A growth or ulcer appears on the tongue and grows steadily. Oral cancer is more common in people who smoke and/or drink alcohol heavily.
Macroglossia (big tongue): This can be broken down into various categories based on the cause. These include congenital, inflammatory, traumatic, cancerous, and metabolic causes. Thyroid disease, lymphangiomas, and congenital abnormalities are among some of the causes of an enlarged tongue.
Geographic tongue: Ridges and colored spots migrate over the surface of the tongue, periodically changing its appearance. Geographic tongue is a harmless condition.
Burning mouth/burning tongue syndrome: a relatively common problem. The tongue feels burned or scalded, or strange tastes or sensations develop. Apparently harmless, burning mouth syndrome may be caused by a mild nerve problem.
Atrophic glossitis (bald tongue): The tongue loses its bumpy texture, becoming smooth. Sometimes this is due to anemia or a B vitamin deficiency.
Canker sores (aphthous ulcers): Small, painful ulcers appear periodically on the tongue or mouth. A relatively common condition, the cause of canker sores is unknown; they are unrelated to the cold sores caused by herpes viruses. Canker sores are not contagious.
Oral leukoplakia: White patches appear on the tongue that can’t be scraped off. Leukoplakia may be benign, or it can progress to oral cancer.
Hairy tongue: Papillae can overgrow the surface of the tongue, giving it a white or black appearance. Scraping off the papillae corrects this harmless condition.
Herpes stomatitis: The herpes virus can uncommonly cause cold sores on the tongue. Herpes virus cold sores are usually on the lip.
Lichen planus: A harmless condition that can affect the skin or the mouth. The cause is unknown; however, it is believed to be caused by the immune system attacking the skin and lining of the mouth.
THE TONSILS
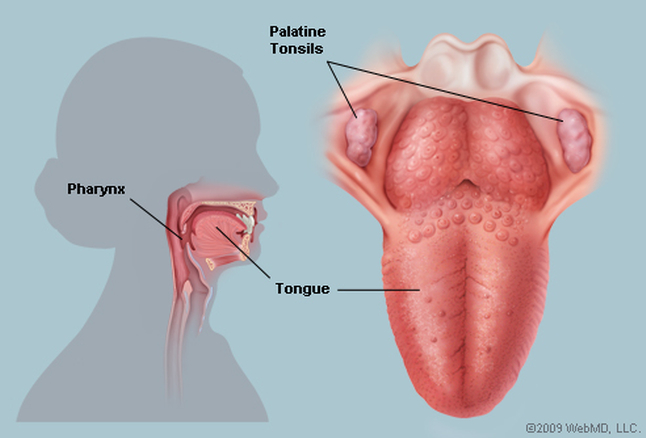
Palatine tonsils, commonly called the tonsils and occasionally called the faucial tonsils, are tonsils located on the left and right sides at the back of the throat, which can often be seen as flesh-colored, pinkish lumps.
Tonsil Conditions:
Acute tonsillitis: A bacteria or virus infects the tonsils, causing swelling and a sore throat. The tonsil may develop a gray or white coating (exudate).
Chronic tonsillitis: Persistent infection of the tonsils, sometimes as a result of repeated episodes of acute tonsillitis.
Peritonsillar abscess: An infection creates a pocket of pus next to the tonsil, pushing it toward the opposite side. Peritonsillar abscesses must be drained urgently.
Acute mononucleosis: Usually caused by the Epstein-Barr virus, “mono” causes severe swelling in the tonsils, fever, sore throat, rash, and fatigue.
Strep throat: Streptococcus, a bacterium, infects the tonsils and throat. Fever and neck pain often accompany the sore throat.
Enlarged (hypertrophic) tonsils: Large tonsils reduce the size of the airway, making snoring or sleep apnea more likely.
Tonsilloliths (tonsil stones): Tonsil stones, or tonsilloliths, are formed when trapped debris hardens, or calcifies.
ORAL HYGIENE
Oral hygiene is the practice of keeping one's mouth clean and free of disease and other problems.
Tips for having a good oral hygiene:
- Proper brushing
.jpeg)
Also, don't forget to also scrub the tongue gently.
- Flossing
.jpeg)
Flossing can help you remove food particles and other detrimental substances that brushing regularly cannot. Flossing allows you to reach deep between your teeth where the toothbrush bristles cannot reach or even mouthwash cannot wash away.
Avoid Tobacco
Limit Sodas, Coffee and Alcohol
Although these beverages contain a high level of phosphorous, which is a necessary mineral for a healthy mouth, too much phosphorous can deplete the body’s level of calcium. This causes dental hygiene problems such as tooth decay and gum disease. Beverages containing additives such as corn syrup and food dye can make pearly white teeth appear dull and discolored. Therefore, it is best to choose beverages like milk, which helps strengthen teeth and build stronger enamel, giving you a healthy, beautiful smile and water which hydrates your body longer than sugary drinks.
Consume Calcium and other Vitamins that are good for the body.
Visiting the Dentist at least once a year for check ups and proper oral hygiene.
Use Mouthwash along side brushing and flossing.
Mouthwash is not particularly necessary and not all mouthwashes are useful. Mouthwashes containing Listerine or chlorine dioxide are very helpful because they help to kill and maintain the bacteria in your mouth. It can help maintain good breath as well as help maintain strong teeth.
REFERENCES:
https://www.webmd.com/oral-health/picture-of-the-tonsils
https://www.google.com.ng/amp/s/m.wikihow.com/Clean-Your-Throat%3famp=1
https://www.arrowsmiledental.com/blog/10-great-dental-hygiene-tips/
https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Palatine_tonsil
https://en.m.wikipedia.
/wiki/Human_tooth
https://www.webmd.com/oral-health/picture-of-the-teeth
https://www.webmd.com/oral-health/picture-of-the-tongue
https://kidshealth.org/en/kids/teeth.html!
Congratulations @a-condor! You have completed some achievement on Steemit and have been rewarded with new badge(s) :
Click on any badge to view your own Board of Honor on SteemitBoard.
To support your work, I also upvoted your post!
For more information about SteemitBoard, click here
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOPFree Auto Upvotes! Plus you get 0.1 STEEM Free just to signup! http://j.gs/Anmi
WARNING WARNING -->> phishing alert !!!
The comment above from @simi420 contains a new phishing URL address, where you can lose your passwords. Avoid this by all means .
WARNING WARNING !!!