The role of the polis in Archaic and Classical-era Greece
Geographically Greece is mountainous so lands are isolated by rugged mountains as a result city-states were separated by major barriers thus city-states were developed separately. So Archaic and Classical-era Greece was not a unified nation which was consisted of several hundred of small city-states. Each city-state is called polis which was introduced in Archaic period By around 800 BCE.
Most Archaic Greece poli consists of an acropolis, which is a hilltop where temples and a government building were built and outside of Acropolis there was agora (market Place) where people met and discussed. It is called urban area which was normally surrounded by a defensive wall. Greece polie also have a countryside located outside the urban area with small settlements that was used for farming.
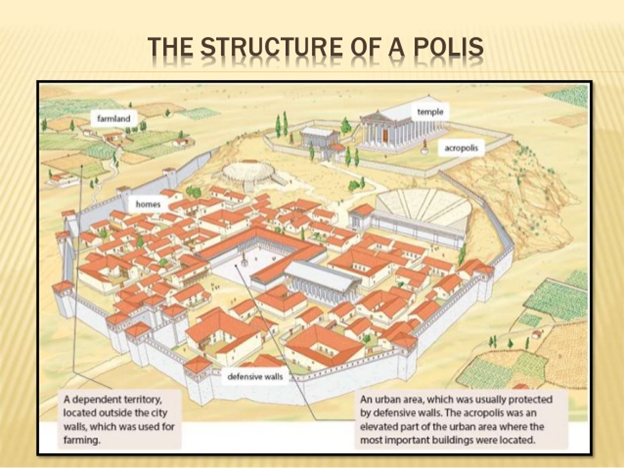
The polis developed indecently of one other and each polis has its own dialect, Culture, identity, and worshipped many of the same gods. They have independent government and rebellious to other polis. Like-minded poleis often made alliances for mutual protection. People loved their polies and were willing to die for own polis. Athens, Sparta, Corinth, Thebes, and Delphi are some most important polis in Archaic and Classical-era Greece.
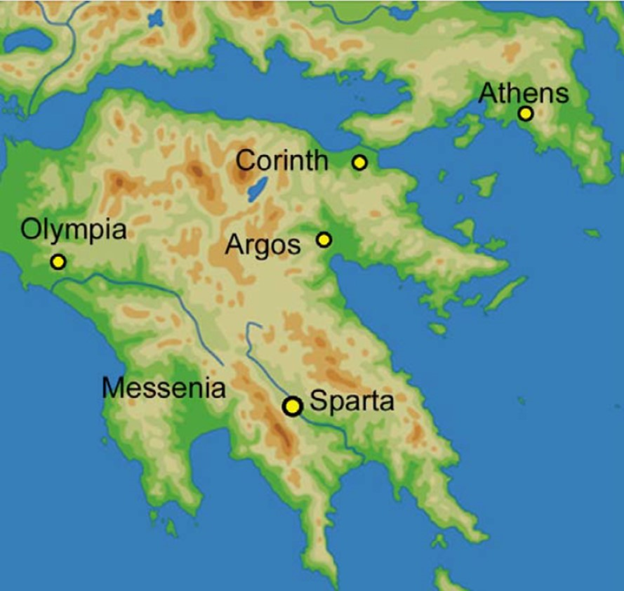
Different Greece polis have different government system for example Macedonia had monarch that was ruled by tyrant. Sparta had Oligarchies was ruled by small groups of influential individuals who ran polis government. Athens was the birthplace of democracy were governments that allowed citizens to vote on and join in making polis decisions. Main role of polis and its government to give protection of its own citizen from other polis attack and non- Greek attack.
Todays Greece
