causes of epiglottitis
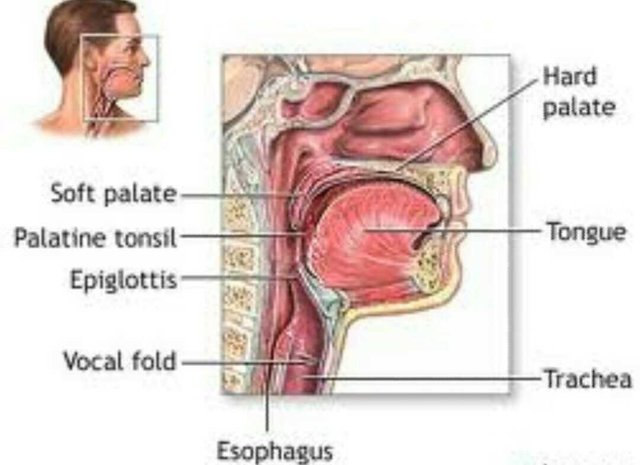
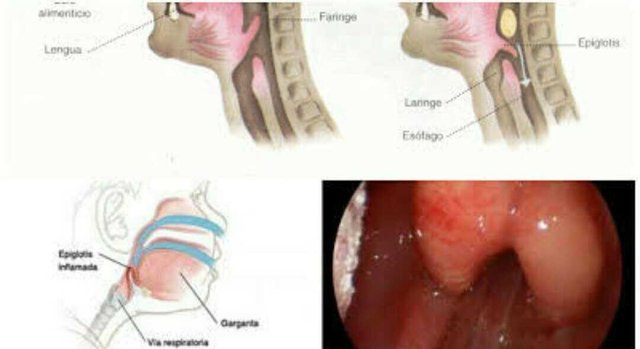
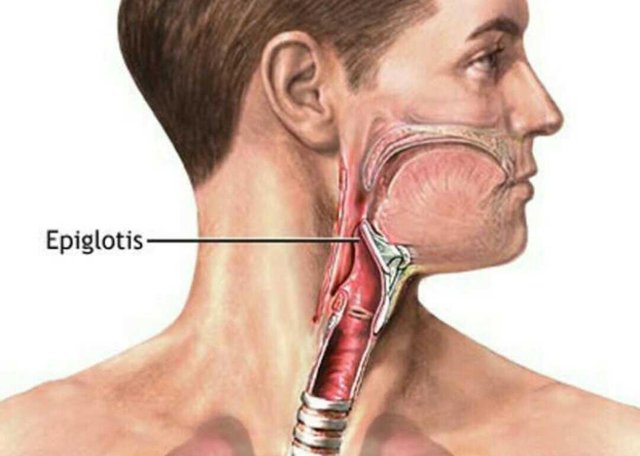
Epiglottitis is the medical term for inflammation of the epiglottis. Epiglottis is part of the throat, resembling a leaf-shaped valve that serves to close the airway so as not to enter the food / drink while swallowing.

Epiglottitis is most commonly experienced by children aged 2-5 years. Even so, even adults can experience this disease, especially if the immune system is weak, such as diabetes patients, tuberculosis, HIV, or chemotherapy patients.
The most common causes of epiglottitis are bacterial and viral infections, as well as from a collision or a foreign object in the throat.
Symptoms of epiglottitis in children tend to deteriorate rapidly. In contrast, adults gradually deteriorate. The following symptoms of epiglotitis:
fever
sore throat
pain and difficulty swallowing
shortness or difficulty breathing
breath sounds loud (stridor)
drool (common in children)
hoarseness
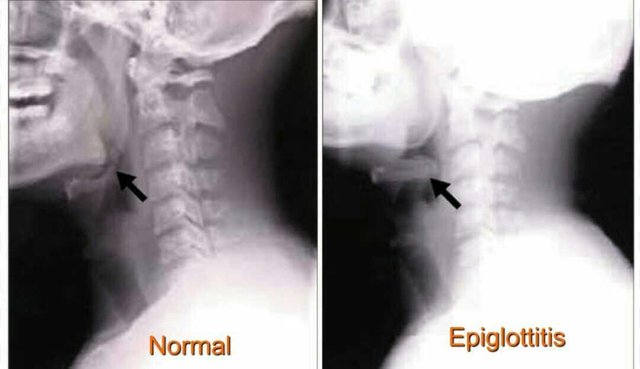
The diagnosis of epiglottitis is established through direct examination of special tests, such as laryngoscopy, nasopharyngoscopy, blood tests, chest x-ray and neck, to CT-scan or MRI. Epiglottitis should not be considered trivial because of the potential to threaten the airway.
Therefore, it is advisable to consult the patient as soon as possible to the hospital to get appropriate treatment according to the underlying cause.
May be useful