9 billion light years away, this is the furthest star we’ve ever seen
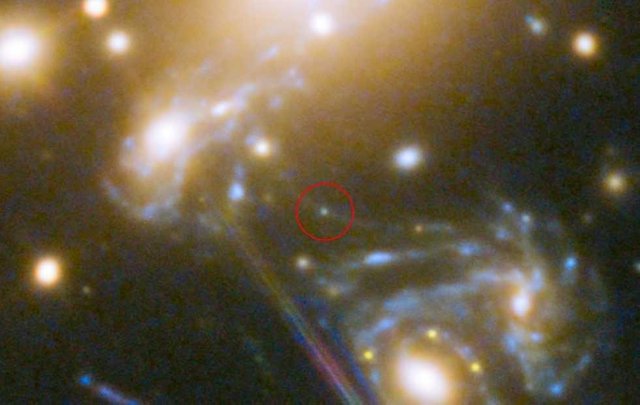

We’re used to telescopes bringing us a glimpse of distant galaxies, but just how far away can we actually see through the universe? According to NASA, the answer is “more than halfway across”: the American space agency has released a new photo from the Hubble Space Telescope, and it’s mind-blowing in more ways than one.
The image shows a blue star that has been nicknamed Icarus, and it’s the farthest individual star that we’ve ever seen. Officially known as MACS J1149+2223 Lensed Star 1, it’s approximately 9 billion light years away from Earth. Light from the star began emitting 4.4 billion years after the Big Bang that created the universe, scientists believe.
At that distance, by every single one rights, we in truth shouldn’t be competent to make out Icarus. However, a pattern of unexpected factors – as well as the universe interim as an improvised particularly solid of lenses – hold certain us a a long way extra isolated sneak a quick look across the cheerful existence than we could’ve achieved with Hubble alone.
It’s called gravitational lensing, and it’s promising for the reason that there’s essentially any more galaxy cluster in-between us and Icarus. Called MACS J1149+2223, it’s approximately 5 billion radiance being from Earth. for the reason that of its vast size, its gravity acts as a inherent lens in space, NASA says, bending and amplifying the noiseless from Icarus behind it.
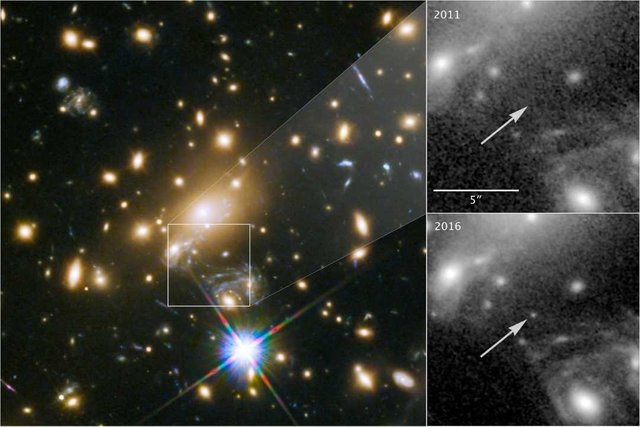
Combined with Hubble’s own optical excellence, the gravitational amplification of the light put out by the star allowed it to be studied for the first time. The first evidence came back in 2016, when a point of light was caught near a supernova in the galaxy cluster that the Hubble team was monitoring. However, unlike a supernova, the newly-spotted star wasn’t getting hotter or exploding.
Upon analysis, it was confirmed to be a blue supergiant star. Even though that could make it hundreds of thousands of times brighter than our own Sun, not to mention much larger and hotter, it still should be too dim, on its own luminance alone, to be visible with Hubble. That led the scientists to realize that it was being amplified by gravitational .
It’s not presently a neat observation, either. The astronomers may well exhaust the discovery of Icarus, and its amplification, to experiment the characteristics of depressing matter. That’s the still-mysterious notes that, although invisible, makes up the bulk of the universe’s mass.
“By interested what’s hanging around in the fore cluster, scientists were adept to trial one concept that sad material force be prepared up habitually of a enormous digit of primal black holes created in the birth of the universe with ample tens of epoch better than the Sun,” NASA explains. “The fallout of this exceptional investigation ill-treatment that hypothesis, as pastel fluctuations from the surroundings star, monitored with Hubble for 13 years, would produce looked poles apart if near were a crowd of intervening black holes.”
For the moment, Icarus is in a course group of its own. However, the James Webb legroom Telescope may perhaps admirably exchange the complete that. It will be greatly additional susceptible than Hubble, and is estimated to unlock equal larger point on hazy stars, as well as whether they are rotating and more.
People who liked this post also liked:
Active shooter reported at YouTube HQ by @hamida93687
Mother birds and their babies by @khanjhan
Feeding African Catfish - Big Big Size Catfish Reaction While Throwing Food To Them. by @sadbin
We recommended this post here, here, here and here.
Hello! I find your post valuable for the art community! Thanks for the great post! ARTzone is now following you! ALWAYs follow @artzone and the artzone tag, and support our artists!
Hello! I find your post valuable for the wafrica community! Thanks for the great post! @wafrica is now following you! ALWAYs follow @wafrica and use the wafrica tag!