The Introduction to EOS
EOS is a blockchain-based multi-functional platform that can be used for transactions and creating of decentralized applications. It was created in 2017 by the company block.one governed by Steemit and Bitshares co-finder Dan Larimer. The EOS functionality reminds of the Ethereum blockchain, but we all remember of serious flaws of Ethereum. The EOS developers didn't miss an opportunity to create an Ethereum-like project avoiding all the troubles such as scalability issues from the very beginning on the project-architecture level. The EOS network supports smart contracts, it is safe as the Bitcoin network, and at the same time, it has much bigger speed processing thousands of transactions per second (the developers promise to increase this speed to hundreds of thousands of transactions per second). More than that, DApps developers wanting to create their DApps on EOS won't have to know Solidity. EOS is much more accessible. The Sia-like decentralized data storage is also a part of the EOS ecosystem.

EOS Accounts
Users create EOS accounts. These accounts are universal for the projects built on top of the EOS blockchain. So the only account opens the gates to the plethora of opportunities and provides you with decentralized solutions for all possible needs. For security measures EOS supports numerous ways of authentication to prevent the stealing of the accounts (you can imagine how important it is to keep your account safe). If the account gets stolen there are ways to bring it back.
Data Storage & Bandwidth Service
One of the integral parts of the EOS ecosystem is the ability to host or rent some hard drive space. DApp developers can utilize this feature not to worry about the storage maintenance and bandwidth hassle (it's fair to say that the developers have a lot of other problems). EOS provides developers with bandwidth- and storage-related analytics directly. This EOS feature creates a very welcoming environment for people working on their projects. What EOS takes in return? The platform requires staking the EOS tokens.
Scaling
Bitcoin, Ethereum, and some other notable blockchains use the consensus algorithms that help to prevent fraud and validate transactions via verifying the state of the entire blockchain by all the actors of the network. Each node re-validates the entire blockchain with each new transaction. Is it a good algorithm in terms of scaling? No, it's a terrible way of validation of the blockchain.
What is the solution provided by EOS? The EOS blockchain is concentrated on the transactions, not on the entire state of the blockchain. Practically it means that the nodes are verifying the series of the events that took place, so the network state gets verified as a result. It increases the potential capacity of the network to a million of the transactions per second.
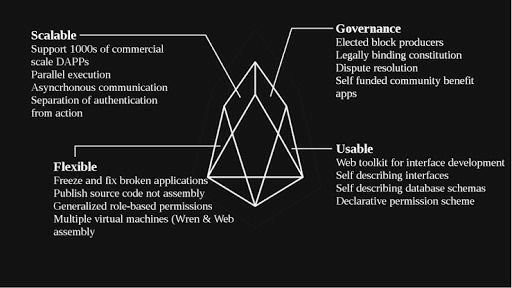
Other Features
One of the most notable features of EOS is that all the DApps are free (they require no micropayments) although transaction fees are possible.
The decisions are made by 21 block producers. All the block producers candidates are standing in line and get votes from the community members, so the list is refreshing every 10 minutes. It stimulates block producers to serve the community well.
The blocks on EOS get produced each 0.5 seconds thanks to sequential cycles method.
Conclusion
Currently, EOS tokens market cap ranks 4th. The team of developers has managed to raise a fabulous sum of money (around $4 billion) that will be allegedly used for the further development of the ecosystem. The project is about 1,5 years young, and there are all reasons to be optimistic about the future of this platform. Let's see what happens next.