Introduction to Basic Electronic Components #1: Come Learn How to Build Basic Electronic Devices
Good morning steemit.
I want to introduce my new series of posts titled "Introduction to Basic Electronic Components".
In this series I will try to introduce in each post different electronic components and try as much as possible to break it down, explain how it functions in an electronic circuit, possible connections and more. I will use diagrams as often as possible, to illustrate the information I am trying to present.
If at any point in time, you have any questions or you disagree with my point of view, feel free to drop a comment and I will try to clarify myself in the replies or in subsequent posts.
Through out this series I will be taking a new approach with my content. Well before now, I usually used my steemit blog as a dumping ground.
What do I mean?
I mean I would go through the internet, learn about one or two topics, create a post about it and then dump the knowledge for my audience to consume hoping for some upvotes
This time around, as I have learnt from users who are doing well on the steemit platform, I will try to engage as much as possible with my audience through my post to make it more fun and easier to consume.
It's my utmost desire that at the end of this series, anyone who has followed from the very first post to the last post would be able to design, interpret and implement simple electronic circuits using standard electronic components.
What are we waiting for, let's begin with the basics
What is Electric Voltage
Simply put, electric voltage also known as electric potential difference or electric pressure is defined as the difference in potential between two terminals. It is that driving force that brings about the flow of current.
A good example of voltage or electric potential is a tank placed at a height above the ground which supplies water to a tap somewhere close to the ground

The higher the water tank above the ground the faster the flow of water. Similarly, the higher the potential difference the more current will flow.
Electric Voltage is measured in Volts and its symbol is V. For example 30V would mean 30 Volts.
What is Electric Current
Electric current is the rate of flow of electric charge with time. These charges are supplied by electrons within a wire. Electric current is measured in Ampers and its symbol is A.
Electric current just as water flowing from a tank to a tap, results from the potential difference between two terminals.
What is Resistance
Resistance is the opposition to the flow of current through a circuit. Resistance is that force of opposition offered by an electronic device. Resistance is measured in ohms and its symbol is given as.... Am finding it difficult to type its symbol, any suggestions?
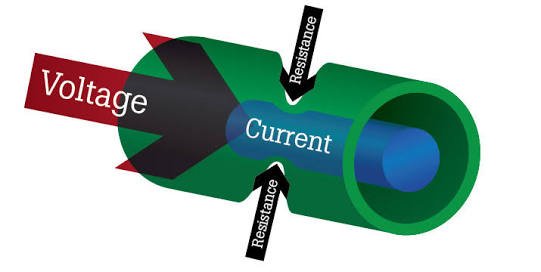
As we will get to see in subsequent posts, virtually all basic electronic components tend to offer some form of opposition to current flow.
Power/ Voltage Sources
Basically, there are two sources of electricity - Alternating Current (AC) source and Direct Current (DC) source
An AC source supplies AC current. A typical example of an AC source is our generators. The direction of flow of alternating current through a circuit changes in direction with time, that is, forward and backward direction. For example somebody moving 3 steps forward and 3 steps backward is engaged in an alternating motion. Graphically, an AC current would look like a sine wave as shown below
A DC source supplies, well, DC current. Direct current flows in one direction. A typical example of a DC source is the battery. DC current does not change unlike the AC current, and graphically would look like a straight line as shown below
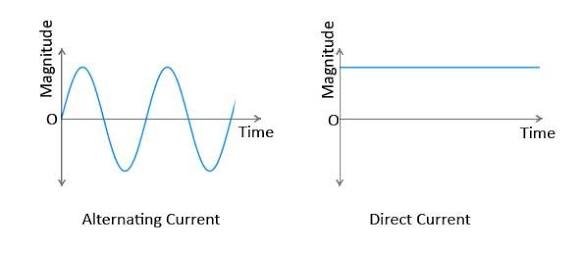
Basic electronic components are powered by DC sources and not AC sources. This is because alternating current changes in direction and would damage most of our electronic components if they are powered by an AC source.
Battery
As discussed above, a battery is a DC source. Batteries are measured by their Voltage and Current ratings. The voltage rating tells us the potential difference the battery can offer or the maximum driving force offered by the battery. While the current rating tells us the maximum current the battery will supply to a circuit.
Battery Configurations
Batteries can be connected in either series or parallel.
Series Connection
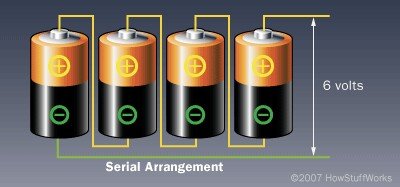
When we connect batteries in series as shown in the figure above the same amount of Current will flow through the circuit but the potential difference across the circuit will be increased.Parallel Connection

When batteries are connected in parallel as shown in the figure above, the potential difference across the circuit will be the same but the current flowing through the circuit would be increased.
Well, this is it for now. This was just an introduction and I hope you enjoyed it. More posts to come, meaning more electronic components to explore. Don't miss out in this adventure into the basic electronic world.
Reference:
- Mostly my work and some citing from Wikipedia
Image Credit:
- Image 1, 2 from pixabay
- Image 3, 4, 5 from instructables
- Image 4 from electrical community blog

@originalworks
The @OriginalWorks bot has determined this post by @kenadis to be original material and upvoted(1.5%) it!
To call @OriginalWorks, simply reply to any post with @originalworks or !originalworks in your message!