Electronic digital signature: Simply and visually
Electronic digital signature (EDS) of the document is an analog of the usual signature, but its possibilities are much wider.
How does the EDS work? How to send a certified and signed electronic document via communication channels (for example, by e-mail)? Let's try to figure it out ...
With regular, paper mail, there are no problems - sign the document; Assure it from a notary; Send by registered mail. All! Your address, having received such a letter, is sure that the document was signed by you personally.
With e-mail (e-mail) this will not work. Of course, you can scan a document certified by a notary and send it as a file attached to an e-mail. But, printing this file will not be legitimate.
How to be? Cryptography comes to the rescue!
Earlier in the article "Public Key Encryption: A Visual Illustration" I talked about asymmetric encryption when the sender encrypts the message with an open (public) key, and the recipient decrypts it with the corresponding open private key.
The sender and the recipient have completely different keys, but they are algorithmically linked - by an open (public) key one can only encrypt (lock) the message, and private (private) - only decrypt (unlock).
How it works with the example of a padlocks with two keyholes and two different keys, I clearly showed in the above article.
And now imagine the opposite situation: the sender encrypts his message with his private key, and recipients can decrypt this message with the corresponding public (public) key that they received earlier from the sender. Of course, these keys (private sender and public recipient) are algorithmically related pair - you can decrypt the message only with a public key that corresponds to the private key of the sender.
The problem is solved! The recipient of the public key knows that the letter was sent by a specific sender who has the corresponding private key.
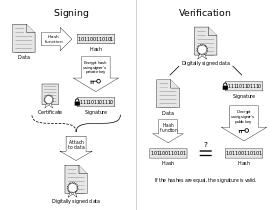
But, in reality, there is no need to encrypt the message itself. It is enough to calculate its hash code (see the article "Hashing: Simply and visually"), then encrypt this hash with a private key and attach it to the message text. This encrypted hash is the digital signature - the electronic digital signature of the message.
The recipient of the message also extracts the hash code of the message and compares it with the decrypted public key of the EDS. If they coincide, then all Ok - the letter is sent by the person who has the corresponding private key.
But that is not all! The use of message hashing also makes it possible to control its integrity - were not unauthorized changes made to the letter along the way to the addressee?
Indeed, if the decoded EDS does not coincide with the hash of the message text, then two things may follow from this:
The letter was signed by another person (the public key does not correspond to the private one).
The text of the message was changed after it was sent.
In any case, the recipient can not consider the received message to be reliable - it is forged!
The question remains: How does the recipient of the message know which public key to decrypt the EDS? After all, for each private key there is a unique public key.
To do this, there are so-called. Store of certificates EDS. Each sender of a signed EDS document must receive a special electronic certificate in the relevant authority together with a private key, which he will encrypt the hashes of his messages. This certificate is essentially an electronic document containing a public key and information about the owner of the key.
The body that issued the certificate is a trust organization that confirms that the relevant EDS certificate has been issued to a specific designated person.
The certificate together with the EDS is attached to the sent message and the recipient on the certificate identifies the identity of the sender and receives a public key corresponding to the private key of the sender.
Electronic digital signature (EDS) is used not only for sending correspondence. With the help of EDS documents (for example, contracts) are certified, banking transactions and much more.
EDS technology is also used in cryptocurrency.