[Education in Uganda #2] Vocational Education
Hello STEEMIT. We previously introduced the current educational status in Uganda which holds a high education exclusion rate. Let’s take a look into the paths 98% of the children walk.
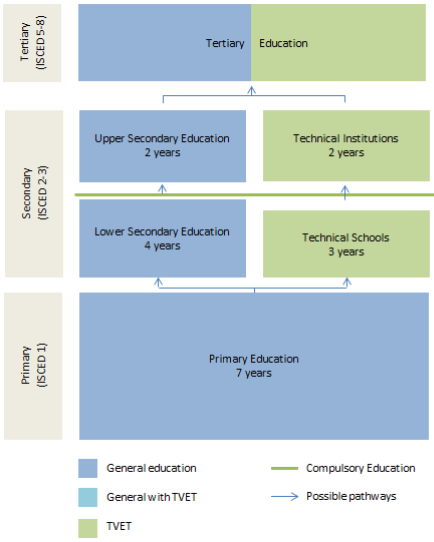
After 7 years of primary school, children have 3 main options.
- Proceed to secondary school for further studies.
- Opt for a 3 year craftsman training course in technical schools.
- Start working at industry, service, agriculture sectors.
Since we took a peek into the 1st option in our last post, we’ll discuss some more about the 2nd and 3rd option in our following posts.
Uganda’s vocational education system is better established than South Korea. Technical schools and vocational training centers offer a 3-year course of craftsman training which help to learn basic skills needed to work. The quality of training courses differ greatly, and informal sectors often lack resources and specific training. Ironically however, the informal sector accounts for approximately 60% of non-agricultural employment. The government of Uganda is constantly struggles to expand training in the informal sector by improving the effectiveness and building systematic approaches to informal sector training.
(Reference: https://unevoc.unesco.org/wtdb/worldtvetdatabase_uga_en.pdf)
After the 3 years’ course, the trainees can either enroll in an additional 2-year advanced course at a technical institute, or start working at industry, service, or agriculture sectors. Uganda’s organized vocational education system strives to come forth as a comprehensive system of skills development for employment.
Then what differences might there be for children who start working without skills training?
The story continues…
SNS
RUN USA Facebook
RUN Korea Facebook
RUN USA Instagram
RUN Korea Instagram