How stuff works: Structures
Everywhere we go, we see them all around us. Buildings, bridges and even mountains and trees.
A structure is something that is built, made or put together in a particular way. It must be rigid, stable and strong, and it must be able to support a load. There are two broad categories of structures: natural and manufactured structures.
Manufactured structures also include packaging that is made to contain manufactured objects. All manufactured structures are based on the principles found in natural structures.
The functions and purposes of structures are:
- To protect things
- To support things
- To enclose a space
- To span or reach across a distance.
For example, the functions of a house are to protect the people inside it, support the roof, enclose a space and contain property.
Types of structures
Frame structures
Frame structures are made up of different parts. These parts are joined together to make a frame, and they create a framework that supports something. For example, a skeleton is the framework that supports the body.
Image source
A frame structure is made up of parts that are joined together. Sometimes this framework is hidden, as it protects something from within.
Shell structures
A shell structure is not made up of different parts. Rather, it is one whole piece. It does not have a frame as a support, but a shell on the outside, so the strength comes from the shell itself. For example, the body of a car is a shell structure. Many structures are combinations of shell and frame structures. All structures can support a load, which could be an object, a person or a force. The structure must be able to support both itself and the load.
Image source
Cool drink cans and egg boxes are also examples of shell structures.
Extension:
Forces
There are five main forces that act on structures.
Image source
1)Compression
This force pushes the members (parts) of a structure together or towards each other. Struts usually use compression to keep a structure in position.
2)Tension
Tension forces try to pull members apart. For example, when someone jumps on a trampoline, the material stretches and pulls on the springs. Ties are usually in tension and give support by pulling away from the structure.
Ties around the tent are in tension
3)Bending
A bending force causes a structure to bend. A beam is the part of a structure that resists bending.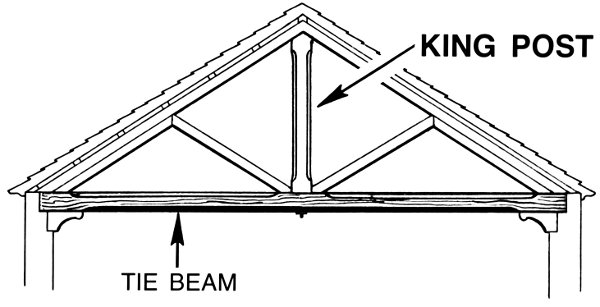
Bending forces
4)Torsion
Torsion is a force that causes twisting and can make members of a structure spin or distort. You use torsional force to close a tap. When this happens, we say the structure is in torque.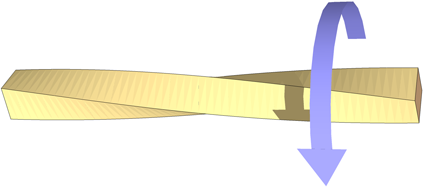
Torsion forces
5)Shearing (or tearing)
A shearing force pushes at right angles to the structure and causes it to break or split.
A crack or tear is an example of a shearing force.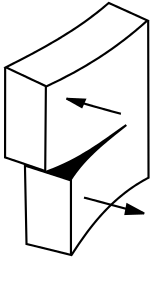
Shearing force
Experiment with resisting forces
You will need:
- A pile of books or support blocks
- A strip of cardboard
- A few weights
- Place the strip of cardboard on the support blocks or pile of books. Now gradually load the center of the strip with more and more weights.
- What happens to the strip of cardboard?
- What can you say about the stiffness of the cardboard?
- Now replace the strip of cardboard with a piece of wood and repeat the experiment. What do you notice?
- Turn the strip of wood or cardboard on its side and repeat the experiment. What do you notice?
This experiment shows you that beams are not always able to resist equal amounts of forces from various directions. The shape that is best suited to resisting forces from all angles is the cylinder. You will see examples of cylinders all around you, such as stems, bicycle frames, tree trunks. If you look closely at the inside of a bone, you will see that the thickest part is in the middle as this is where the bone is at its weakest when both joints are under pressure. Tubes that are thicker in the middle are stronger.
Bibliography & Extra reading:
- Structures for kids
- Structures and forces
- Wikibooks
- Man-made and natural structures
- PDF structures
- Struts and frame structures
- Skeleton structure
- Forces & Structures
- Shell structures PDF
- Structures - technology
- Grade 8 structures
- Forces on structures
- Forces types
- Tension & compression
- Bending Beam structure
- Torsion Flashcards
- Shear force