A must read for Business people : Economics Concept
Economics: Its Nature and Concept
Learning Objectives
After reading this post, you will be able to:
- know and understand the nature of Economics and its relations to other social sciences
- define Economics and its division
- identify the basic economic problems of society, the economic resources and its importance to the economy.
- discuss scarcity through the production possibility frontier (PPF).
Ours is a busy world. People are ever on the move. Countless factories in the world work over hum to turnout goods. Farmers plow fields to satisfy basic foods, shelter, and clothing requirements. Business and industry, commerce and trade go on incessantly. We are all producers of some category; we are clients. We conceive plans to make living more pleasant and abundant. Work we must constantly we crave for goods and services to satisfy our wants. Somehow, goods and services fall short of satisfying our needs and desires. We sentient in a world of economics. Many individuals have no pure understanding of economics. And nevertheless it is an essential part of our lives. Almost always, if not all, human activities involve economics. We cannot separate ourselves from economics as our physical existence relies on it. We cannot live without production and consumption, which are the major activities of economics. Clearly, a good knowledge of economics offers many favorable possibilities. With the use of appropriate economic decision and implementation, life for everybody is mot likely better.

Economics, a social science concerned with the production, distribution, exchange, and consumption of goods and services. Economists emphasis on the way in which individuals, groups, business enterprises, and governments look for to achieve proficiently any economic objective they picked. Other fields of study also subsidize to this knowledge: psychology and ethics try to explain how objectives are formed; history chronicles changes in human purposes; sociology construes human behavior in social situations.
Division of Economics

Standard economics can be divided into two major fields. The first, price theory or MICROECONOMICS, explains how the interplay of supply and demand in competitive markets creates a multitude of individual prices, wage, rates, profit margins, and rental changes. Microeconomics assumes that people behave rationally. Consumers try to spend their income in ways that give them as much pleasure as possible. As economists say, they maximize utility. For their part, entrepreneurs seek as much profit as they can extract their operations.
The second field, MACROECONOMICS, deals with modern explanations of national income and employment. Macroeconomics dates from the book, The General Theory of Employment, Interest, and Money (1935), by the British economist John Maynard Keynes. His explanation of prosperity and depressions centers on the total or aggregate demand for goods and services by consumers, business investors, and governments. Because, according to Keynes, inadequate aggregate demand increases unemployment, the indicated cure is either more investment by businesses or more spending by government, and consequently larger budget deficits.
MICROECONOMICS analyzes the details of economy. Typically, it deals with the study of the economic behavior of individual units, such as consumer, firms and entrepreneurs which constitute a very small segment of the whole economy.
MACROECONOMICS deals with the economic behavior of the whole economy or its aggregates. An aggregate is composed of individual units. Both of them are equally important. One cannot study the while without studying the parts; neither can break down aggregate into components without knowing what components made up the aggregates.
These meanings were according to the site Cosmeo
The Basic Economic Problems
All countries have economic problems, including the riches countries. However, the poorest countries have the biggest and longest economic problems. Thee are no possibilities of erasing completely economic problems from the face of the earth. Productive resource are scarce and maldistributed while the needs of the people are increasing due to population explosion. Moreover, human wants unlimited. That is why even the rich countries have economic problems.
Scarcity of Resources
Is a problem that always confronts the production of wealth, goods and services. But while the availability of resources is limited, the human wants are insatiable. Economics comes in to harmonize human wants.
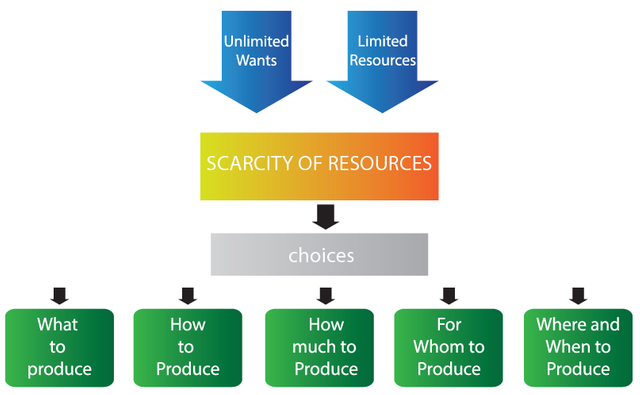
The basic economic problem may be derived from the above-cited definitions and discussions. Since the available resources are not enough and sufficient to satisfy the unlimited wants of the people, decisions must be made with the said constraints in mind. Thus, the following questions must be considered:
1. What Goods and Services to Produce
- It is not really possible to produce all the goods and services that people want their satisfaction. To remedy such problem, a system of priorities has to be established. Clearly, basic needs of the people are given top priority. Conducting a feasibility study to determine the goods and services that people need can solve this problem. However, in the case of the poor countries, there is no need to conduct a survey to determine the real needs of the people. This is only necessary to determine the quantity of goods to be produced.
2. How to Produce the Goods and Services
- The ideal situation is to produce the goods with the most efficient method. This involves machines, technology, management and skills. As a universal rule, goods and services must be produced in the most efficient manner. This means maximum output with the minimum input without sacrificing quality. The rich countries use advanced technology while the poor use low technology in their production of goods and services.
3. How much to Produce
- The cost of production would depend on the quantity of goods and services that people need.
4. For Whom are the Goods and Services
- This is a problem of the distribution of goods and services. The distribution of goods and services are determined by the economic system.
5. Where and When to Produce
- The accessibility to transportation, communication, market and to the sources of raw materials are the bases for the entrepreneur to choose the best location of the business. However, the policy of the government must also the considered.
Economic Resources
These are things needed to carry on the production of goods and services. They are also called as factors of production.
a. Land
- refers to all natural resources, which are given by and found in nature, and are therefore, not man-made. It is one of the factors of production which include land used for agricultural or industrial purposes as well as natural resources taken from above or below the soil. Rent is the payment for the use of lands.
b. Human Capital/Labor
- any form of human efforts exerted in the production of goods and services. Labor covers to that basic factor of production which are productive services embodied in human physical effort, skills, intellectual powers, and others. It consists of human time spent in production like driving buses or jeepneys, feeding cattle, pigs, chicken or horses, singing in night clubs, acting in movies and theaters or repairing household appliances. Wagers are the payment for human efforts exerted.
c. Real Capital
- man-made goods used in the production of goods and services. This third basic factor of production simply pertains to durable goods produced in order to produce other goods. It consists of buildings, plant and machineries, roads and bridges, computers, ships and airplanes, keyboards, etc. Savings refer to the part of a person's income which is not spent on consumption.
d. Entrepreneurial Ability
- person who combines the other resources used in the production of goods and services. Actual production needs the ability of an entrepreneur to decide on and implement the right combination of the first three factors of production. Profit is the amount that is left behind after all allocations to the other economic resources.
The Production Possibility Frontier (PFF)
In the filed of macroeconomics, the production possibility frontier represents the point at which a country's economy is most efficiently producing its goods and services and, therefore, allocating its resources in the best way possible. There are just enough apple orchards producing apples, just enough car factories making cars, and just enough accountants offering tax services. If the economy is not producing quantities indicated by the PFF, resources are being managed inefficiently and he stability of the economy will dwindle. The production possibility frontiers shows us that there are limits to production, so an economy, to achieve efficiency, must decide what combination of goods and services can and should be produced.
Can you explain the concept of the limit of production ? I believe the concept is difficult to describe as it is influenced by some factors unspecified.