What You Need To Know About That Lump Behind Your Ear
It’s completely natural to get frightened by something abnormal going on with your body, such as a most evident lump right behind your ear. Along with making you worry about its overall unsightliness, it is also bound to make you frantically wonder as to what is causing it, and whether it can even be treated. And if the lump is accompanied by a feeling of pain or discomfort, it’s only going to make matters worse.
The good news is, there’s usually nothing to worry about. Nonetheless, you do need to be aware of a few things – like what’s causing those lumps to begin with, and what sort of a treatment you may have to seek.
Let’s start with what we really mean by a lump behind the ear.
What Is A Lump Behind The Ear?
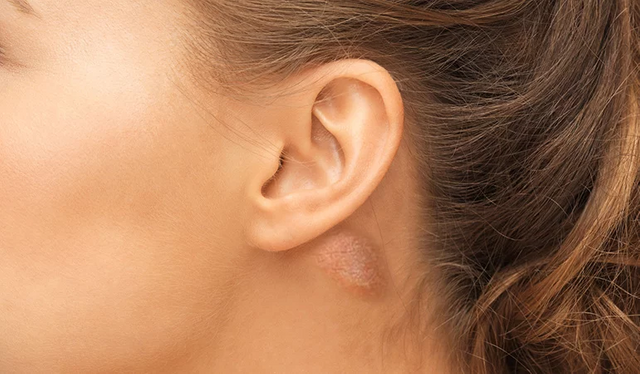
A lump behind the ear is usually referred to a localized area of swelling of certain glands called auricular lymph nodes. This can result in the formation of one or multiple lumps that can occur not just behind but on any part of your ear. These parts may include your earlobe or your ear canal. There are some other terms that are often used to describe a lump behind ear, such as a tumor, cyst, bump, and nodule.
Nature, appearance, and size: Lumps behind the ear have the tendency to swing both ways. They can either be completely painless or very painful, they can either be soft or firm to touch, and they may either be big or small in size.
Sometimes, these lumps may maintain the same size all throughout, while in some cases lumps can grow larger either very rapidly or very slowly. Luckily, lumps behind the ear rarely grow larger than the size of a pea.
Some people may also notice either a single lump or multiple lumps, growing in a cluster.
Lumps behind the ear are usually a common occurrence and as mentioned earlier, is usually not an indication of something serious.
A painless lump behind the ear can be associated with a variety of causes such as:
Sebaceous cysts: Noncancerous lumps that develop around oil-producing sebaceous glands.
Lipoma: A harmless, fatty lump that can develop between the layers of our skin and may grow larger in size eventually.
Benign tumors: Soft, painless, movable lumps that gradually develop from the salivary gland tissues to parts behind the ears. Although mostly harmless, one particular form called cholesteatoma can destroy the tissues around which may result in dizziness, drainage in the ear, and hearing loss.
Malignant cancer: Very similar to skin cancers, these (mostly) painless lumps develop behind the ears and may require medical attention if they grow larger in size.
Painful lumps, on the other hand, may be caused by:
Abscess: Warm, painful lumps that develop when tissue or cells become infected. Our bodies respond to the infection by sending white blood cells to the affected area. As a result, pus begins to develop in a lumpy form.
Dermatitis: A condition often caused by fatigue, stress, yeast infections, and neurological conditions, dermatitis leads to the buildup of waxy dead skin cells or dry skin. This may result in lumps behind the ear and is often accompanied by inflammation and redness.
Mastoiditis: A condition caused by an infection of the mastoid bone found behind the ear which can lead to swelling and the formation of lumps behind the ear. Some of the common symptoms associated with this condition are headaches, fevers, and hearing loss.
Swollen lymph nodes: The swelling of lymph nodes often associated with health issues like the common cold that can cause small tender, soft lumps behind the ears that are painful.
Acne: A condition that is caused by hormonal changes, stress, or high levels of staph infections on the surface of the skin, including behind the ears.
Otitis media: An official term for an ear infection, this can result in a swelling behind the ear to give you a lump.