Setup Docker CE on Ubuntu Linux 16.04 LTS
Setup Docker CE on Ubuntu Linux 16.04 LTS
Setup Docker on Ubuntu Linux 16.04 LTS is different compared to installing it on Mac OSX / Windows machines. We don’t have a dedicated installer for the Ubuntu Linux version. However, it’s still doable through following the steps suggested in the documentation. In this article, I will show you, how to do it through following these steps.
Prerequisite
Ensure that we are using machine which runs Ubuntu Linux version 16.04 LTS at least with an Internet connection. As for the mahcine, it could be your Desktop PC, Laptop or AWS EC2 Cloud Server.
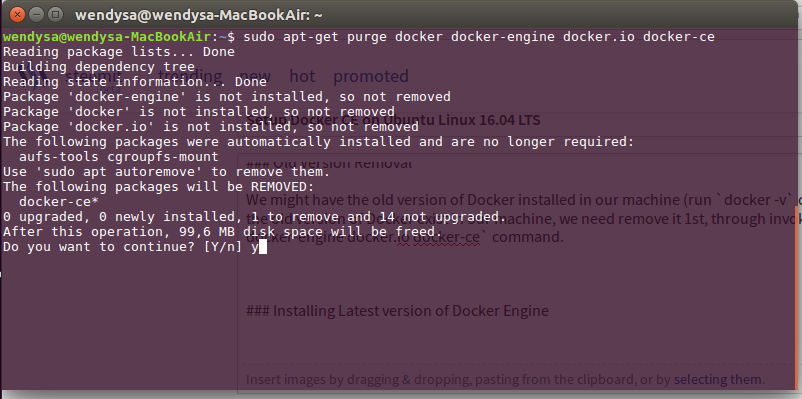
Old Version Removal
We might have the old version of Docker installed in our machine (run docker -v command to validate this ). In case the old version of Docker exist in our machine, we need remove it 1st, through invoking sudo apt-get purge docker docker-engine docker.io docker-ce command.
Installing Latest version of Docker Engine
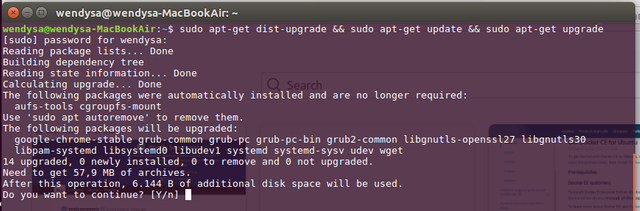
Before moving to the 1st step of Docker's installation, run this command to ensure the Ubuntu Linux's repositories are updated to the latest version:
sudo apt-get dist-upgrade && sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get upgrade
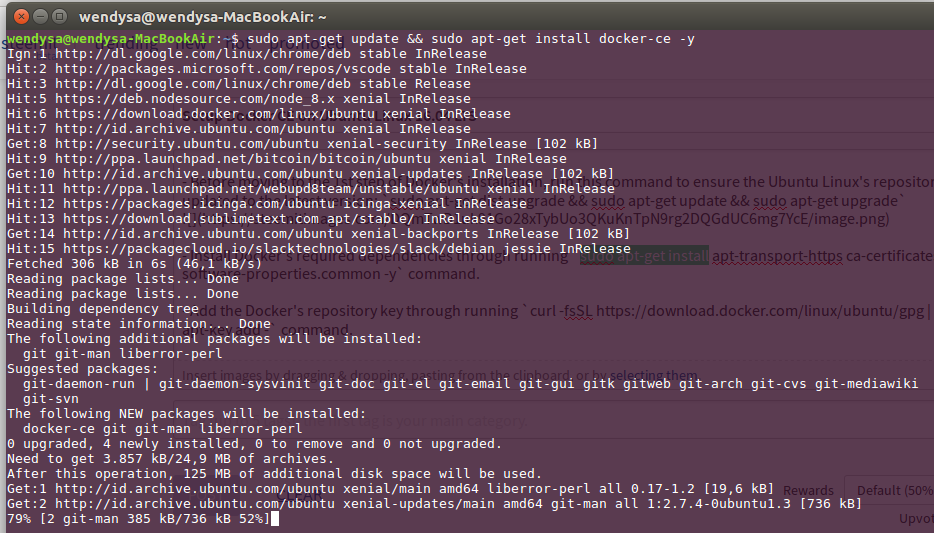
Install Docker's required dependencies through running
sudo apt-get install apt-transport-https ca-certificates curl software-properties.common -ycommand.Add the Docker's repository key through running
curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo apt-key add -command.Add the Docker's repository through running
sudo add-apt-repository "deb [arch=amd64] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu $(lsb_release -cs) stable"command.
If your machine is an ARM based Single Board Computer such as Raspberry Pi, Banana Pi, Odroid, etc, run this command:sudo add-apt-repository "deb [arch=armhf] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu $(lsb_release -cs) stable"Run this command to begin the Docker installation:
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install docker-ce -y
Post installation
At this point, we should have Docker installed in our machine. However, when we tried to invoke docker commands such as docker pull, docker start, docker run, the prompt kept asking us to invoke these commands using sudo prefix. This happens because our login is not member of docker group. Let us follow these step to resolve this annoyance:
Create a new group where the name is
docker, through invokingsudo groupadd dockercommand.Add your current login name into
dockergroup, through invokingsudo usermod -aG docker $USERcommand.Reboot your machine / do re-login, so that the prior changes take effect.
Testing Docker installation
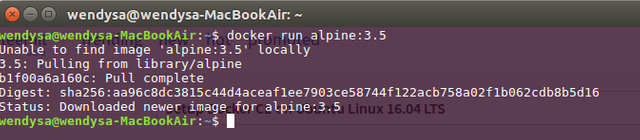
Finally, we can test our installation through running docker run command. In this case, we'll try to run a docker container of alpine linux's Docker image, through invoking docker run alpine:3.5 command.
Confirm that there is no sudo is required response error, and the command is processing. It may take sometime to finish the process, depending to your internet's connection speed.
Run docker images command to see if alpine:3.5 image has been downloaded into our machine.

Run docker ps -a command to verify if our container which was created from alpine:3.5, was running before. We notice the status of the container is Exited. This is because we have not changed the image to run any applications yet. Therefore, the container went exit immediately after docker run command was completed.

In case you find this article useful, please upvote this article. You could also follow my account here if you wish to see my future articles similar and or related to this one. Thank you.