How does a 3D printer work ?
For the past ten years, the 3D printer has been democratized and can be found in more and more homes. Previously reserved for an audience of passionate enthusiasts, it is now accessible to all. The recent drop in prices, initiated by a few Chinese brands, has allowed rapid democratization.
Why a 3D printer?
A 3D printer can be used in many domains, so I will talk here only about home printers.
The printer can be used for many things: printing spare parts, creating spare parts for makers, objects of daily life, toys, decorative objects, etc. The main interest is that the realization of parts has a low cost, to which is added a great satisfaction to have made the piece by yourself.
What does a 3D printer look like?
A 3D printer can take different forms, but for practical reasons I will limit myself to the cartesian printer. This for a simple reason: it is the ideal printer to start in 3D printing, because of its simple operation.
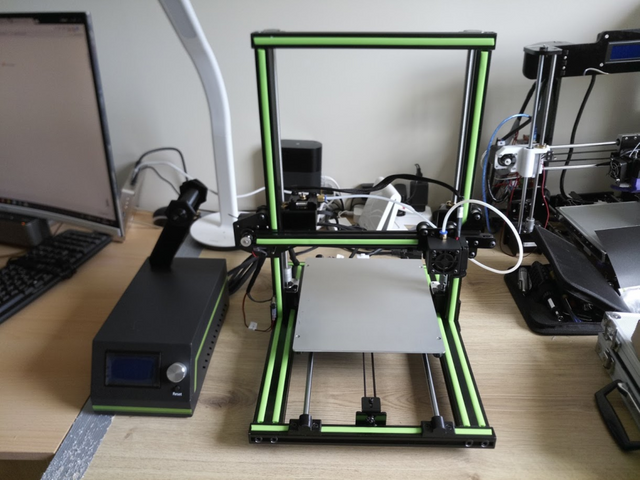
The cartesian printer works by moving a nozzle along the X, Y and Z axis. This nozzle delivers a thin filament of heated plastic that solidifies on cooling. By superimposing layers of plastic, the object is formed. Let's see how a cartesian printer is built.
The chassis
Most often plastic (acrylic) or metal (aluminum profile) made, it receives all the other elements. Looked from the side, it usually takes the form of a T upside down, the vertical part representing the Z axis (which will allow to superimpose the different layers of plastic).
The chassis must be as rigid as possible, in order to avoid as much printing defects as unwanted vibrations could generate: wavelets, zig-zag etc.
The bed
The bed is the flat part that will receive the printed model. It moves on the Y axis, so in the direction of the depth.
The main challenge for the bed is to keep the printed model stuck on it, so that its base does not come off during printing. This detachment, if it is partial, causes a deformation of the base called warping, but if the detachment is total, it is unfortunately an outright failure of printing, which can result in a large pile of entangled filament .
There are several ways to achieve this adhesion. The first is to use a heated bed, which will allow the material to retain some elasticity and avoid delamination. Unfortunately, most of the time, that's not enough. So we will use other stratagems, such as covering the tray with a painter's adhesive, or a glass plate on which we will spray hair spray or stick glue.
Carriage
The carriage moves on the X axis, from left to right, and embeds a centerpiece: the extruder. It receives the filament (most often 1.75mm in diameter) and heats it with a heating resistor at temperatures around 200 degrees centigrade. The fused plastic accumulates in the nozzle, and thanks to the pressure exerted upstream by the filament, driven by the extrusion motor, it is ejected through the orifice of the nozzle to a diameter of a few tenths of a millimeter. The most frequently encountered nozzle diameter is 0.4mm.
Depending on the type of material used, the plastic, just out of the nozzle, must immediately be cooled, in order to solidify without causing deformation. A fan (or two) attached to the cart, blows fresh air at the immediate exit of the nozzle.
Finally, the extrusion motor, which pushes the filament into the extruder is sometimes attached to the carriage. But more and more often, it remains fixed to the chassis, according to a mounting called Bowden, which lighten the carriage and avoids additional vibrations, which could cause printing defects.
Steppers
The steppers are essential also on a 3D printer, and they must be of a formidable precision. We use most often:
- an stepper for the extruder
- a stepper for the X axis
- a stepper for the Y axis
- one to two steppers for the Z axis.
- The X-axis motor is located on the trolley arm, and moves the trolley through a pulley and a belt. The same system is used for the Y axis, whose stepper is under the bed.
The motors of the Z axis are located at the bottom of the gantry, on both sides of the bed. They are coupled to worm gear, which will act as a gearbox to achieve maximum accuracy and the lowest possible vertical displacement.
Power supply
The power supply must be powerful enough, because it must provide energy to heat the bed (between 50 and 110 degrees) and the extruder (between 180 and 220 degrees). The wiring must be as neat as possible to avoid any risk of fire. Of course, it must be cooled to avoid any risk of overheating.
The motherboard
The motherboard is reminiscent of Arduino microcontrollers or Raspberry Pi microcomputers. It sends the necessary information to each element to which it is connected: nozzle and bed heating, motor displacement, extrusion, fans.
The software
In order to print a model correctly, it is out of the question to send it to the printer as it is. Admittedly, it could print on the fly a model in STL format, but it would then ignore many parameters. This is where the slicer comes in.
The slicer
This software makes it possible to convert a 3D model into a language understandable by the printer, consisting of a simple sequence of actions to be performed.
The slicer allows you to set some parameters, which will affect the print quality:
- print speed
- layer height
- bed temperature
- hotend temperature
- material flow
- many other parameters such as shell thickness, fill rate, shrinkage and many other settings that will also affect the final quality of the printed model.
The settings made, the GCODE language will be generated and sent to the printer via USB, USB key or memory card. A few hours later, hopefully, your model will be finished.
The material
Of course, the best printer in the world will not go far without supply. We will need here plastic filament to melt. It can be composed in several ways, but the most common are ABS and PLA. They are usually found in rolls of 1kg, which represents about 400m of material and a few tens of models to print.
These two materials are distinguished by their composition, oil-based for ABS and plant for PLA, but also by their temperature of use, higher for ABS than for PLA. And if the PLA is less subject to printing defects, including warping, it is more difficult to give it a perfectly smooth surface condition than for ABS. Each material will have its pros and cons.
Conclusion
The printer is only the first brick. To succeed a beautiful impression is a real pleasure, so much the parameters to be mastered are numerous. And once the right settings found, the only limit is the imagination!
Resources
Downloadable templates: https://thingiverse.com
All about Reprap printers: https://reprap.org/wiki/RepRap
Photo credits
All photos are personal.
Posted from my blog with SteemPress : http://techno-bidouille.fr/how-does-a-3d-printer-work
Congratulations! Your post has been selected as a daily Steemit truffle! It is listed on rank 17 of all contributions awarded today. You can find the TOP DAILY TRUFFLE PICKS HERE.
I upvoted your contribution because to my mind your post is at least 7 SBD worth and should receive 119 votes. It's now up to the lovely Steemit community to make this come true.
I am
TrufflePig, an Artificial Intelligence Bot that helps minnows and content curators using Machine Learning. If you are curious how I select content, you can find an explanation here!Have a nice day and sincerely yours,
TrufflePigHello! I liked your post because it was really original and written by someone who is actually using this device. Join us on Discord, steemSTEM channel, and see what you could potentially do... There are also several mentors that will help you.
Thanks a lot !
This post has been voted on by the steemstem curation team and voting trail.
There is more to SteemSTEM than just writing posts, check here for some more tips on being a community member. You can also join our discord here to get to know the rest of the community!
Hi @sebbbl!
Your post was upvoted by utopian.io in cooperation with steemstem - supporting knowledge, innovation and technological advancement on the Steem Blockchain.
Contribute to Open Source with utopian.io
Learn how to contribute on our website and join the new open source economy.
Want to chat? Join the Utopian Community on Discord https://discord.gg/h52nFrV