Culture of Russia
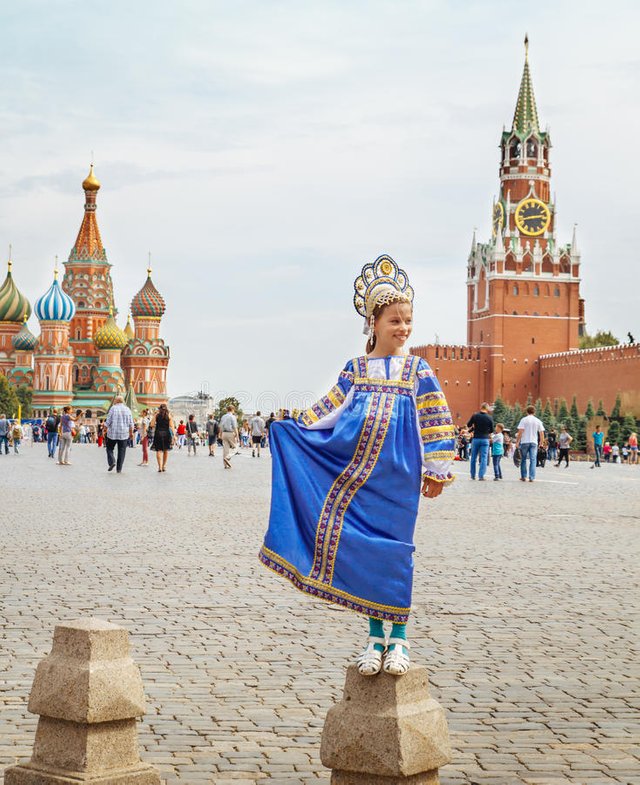

Russia, officially known as the Russian Federation, is a state in northern Eurasia, with a republican rule with a semi-presidential system of 83 federal entities.
Capital: Moscow
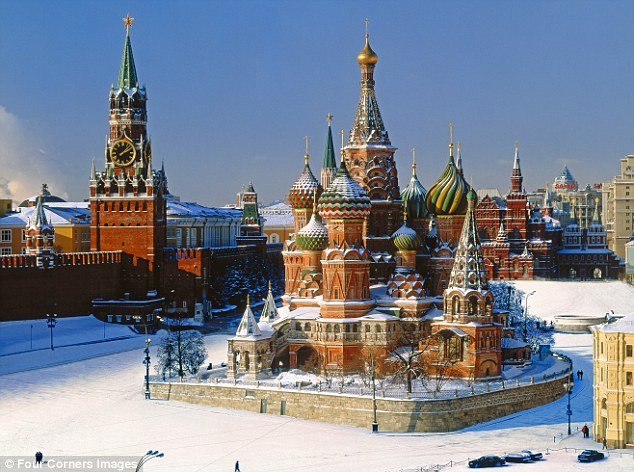

Area: 17, 100, 000 km²
Currency: Russian ruble
Continent: Europe, Asia
The government is a semi-presidential federal republic

history

Russia's unique location and its expansion in Asia and Europe had an impact on its history and the formation of its destiny. It was neither a purely Eastern nor a purely Western state, raising questions among its intellectuals about the role of their country and its contributions to the history and development of the world.
In 1917, the revolutionaries isolated the Tsarist government and changed the name of Russia to the Socialist Federal Republic of USSR, which in 1922 formed with three other republics a new state known as the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics known as the Soviet Union until 1991, when it collapsed into independent republics , Later met in a loose federation called the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS).
Important dates for Russia
Ninth century Eastern Slavs established the state of Kiev.
1237-1240 The Mongols took over Russia.
1318 AD The Mongols named Prince Yuri, the governor of Moscow, the chief Russian princes.
1480 CE Ivan III defeated the Mongols and liberated Russia from their grip.
1547 CE Ivan IV became the first Czar of Russia.
1604-1613 Russia was torn apart by civil wars, foreign invasion, and political turmoil during the period of unrest.
In 1613, Mikhail Romanov became the Czar of Russia and the founder of the Romanov Dynasty, which remained in power until 1917.
1703 AD Peter I laid the foundation of the city of St. Petersburg and began to build a capital there.
1812 Napoleon conquered Russia, but was forced to retreat.
1861 CE Alexander the Second freed the peasants.
1905 Japan defeated Russia in the Russo-Japanese War. The revolution in Russia forced Tsar Nicholas II to establish a parliament.
1914-1917 Russia fought both Germany and the Empire of Austria and Hungary in the First World War.
In 1917, a revolution overthrew Nicholas II in March and the Bolsheviks seized power. They were later known as the Communists, in November 1917. He became a f. a. Lenin is prime minister. Russia withdrew from the First World War.
1918-1920 The Communists defeated their opponents after a civil war.
1922 founded the Soviet Union.
1991 Communist rule ended, the republic declared its independence, and the Soviet Union dissolved on 25 December.
1993 President Boris Yeltsin dissolved parliament after he objected to Yeltsin's reformist policies.
Ancient history of Russia
In the period leading up to 1200 BC, the people of the Semites were inhabited by the Balkans in the northern Black Sea, the region of southern Ukraine now. In about 700 BC they were defeated by the Sethites, groups of Iranian origin living in Central Asia. The Sithion remained in control of the region until about 200 BC. On that date they were defeated by the Sarmatians, another Iranian group. Both the Scythians and the Saracists lived with the Greek colonies that were spread on the northern Black Sea coast in close contact, until the Roman conquest ended. These groups have taken many Greek and Roman ways of life through commerce, mating and other connections. In the year 200 AD, the Goths of the Goths invaded the West and took over the territory. They ruled the country until 370 AD when they were attacked by the Hun and defeated. Hun was an Asian militant group. This group then collapsed after the death of its king Attila al-Huni in 453 AD. It was followed by the Hunan tribe, known as the Avars, which ruled the region in the mid-6th century. The Khazars, an Asian group that took control of southern Volga and the northern Caucasus in the mid-7th century, became Jews and established prosperous trade with other groups.
The oldest history of books about Russia in the ninth century AD is the first history written in Kiev around the year 1111 AD. According to this novel, some Slavic groups differed and fought in the city of Novgorod. They asked one of the Viking tribes to rule them and spread security in their country. These Viking were called the Russian Farangis.
Historians who believe in the truth of the early history believe that the Russians took their name from this group. According to the initial date, the group of Farang families led by Rurik arrived in 862 and settled in Novgorod, and that area became known as the land of the Russians
A map of approximate European cultures in Russia in the reach of the Varangians
State of Kiev Rus
Main article: Ross of Kiev
In the 11th century
The preliminary history book states that Oleg Varnegi took over Kiev in 882 and became governor there. In the tenth century AD, the other emirates inhabited by the Rus-Kiev recognized the important Kiev role. Kiev is located on the main trade route between the Baltic Sea, the Black Sea and the Byzantine Empire. At the same time, Kiev was defending Kiev's Rus against invading tribes from the east and south. The prince of Kiev was known as the Great Prince and had a higher status than that of other Kievan princes.
In 988 AD, Prince Vladimir I adopted Christianity. The Eastern Slavs at that time worshiped natural forces. But Vladimir made Christianity the official religion of the state, and then embraced many of the people of his Christian state. Vladimir later became a saint of the Russian Orthodox Church.
National Government
http://slideplayer.com/slide/9108855/27/images/6/Russia:+Political+Institutions+(continued).jpg
In 1992, Russia was governed by a transitional government headed by Boris Yeltsin, who was elected president of the Russian Federation in 1991 after the collapse of the Soviet Union. But the political situation remained unstable to oppose a number of former Soviet leaders and members of the Communist Party in the Russian parliament, to the economic changes put forward by Yeltsin, and called for the formation of the government. This opposition led to a bloody confrontation between Yeltsin and his opponents in October 1993, which culminated in the storming of the White House by force of arms and the capture of opponents and their imprisonment.
In December, he voted on the constitution, which gave broad powers to the Russian president, and elections were held in which nationalists and communists won many seats.
The Russian president is the highest executive authority in the country. He is the head of state and chief of staff. The Russian people elect the President for a four-year term. The President, with the approval of the State Duma, appoints the Prime Minister, who presides over the Council of Ministers, and he and his ministers are in charge of the Government.
The Russian Parliament is called the Federal Assembly and consists of two chambers: the State Duma, 450 members, and the Federation Council with 178 members. The Duma proposes bills and is approved by the Federation Council and the President before they become effective laws. The Duma may override the Federation Council and deposit the bills directly with the President. The Federation Council approves government appointments and approves some of the president's decisions, such as the declaration of martial law and the use of armed forces outside Russia. The people elect the members of the State Duma for a term of four years. Members of the Federation Council are employees of local governments. Members of the Council of the Union are either provincial governors or heads of legislative bodies of the Territories and are elected ex officio rather than by election.
The People's Assembly has the highest legislative authority in Russia, with more than 1,000 preachers
Local Government
Russia consists of 49 administrative districts (Ablast), six large, low-population districts, and 30 other predominantly ethnic (national) provinces. But the future of these units is ambiguous, because their people demand greater powers to manage their affairs. Some have called for complete independence and the right to self-determination, such as the Chechen Republic. These divisions are divided into smaller centers and run local affairs councils in urban and rural areas.
In 1991, the People's Assembly gave President Yeltsin wide powers to stabilize the political situation, isolating many local officials and appointing new members to implement his new reforms.
Politics

The Communist Party remained the only party in the Soviet Union until March 1990, when Article 6 of the Constitution, which gave power to the Communist Party, was abolished. The movement began reforming and ensured Yeltsin's success in the June 1991 elections. With the collapse of the Soviet Union, the movement was divided. 13 separate parties were formed in the last elections: the Russian Option Party, the Movement for Democratic Change, the Peasant Party, the Communist Party of the Russian Federation, the Liberal Democratic Party, the Bloc of Unity and Understanding and the Bloc of Gregory Yavlinsky. In the mid-1990s, these parties split into three large groups: Yeltsin's nationalist, leftist, and centrist parties, closer to Yeltsin, then Yeltsin's supporters and finally independent coalitions. In the 1995 elections, the Communist Party of the Russian Federation won most of the seats in the Duma. In 1996, Russia won the second presidential election, in which Yeltsin won his second term until his resignation on December 31, 1999. Every 18-year-old Russian citizen has the right to vote in the elections.
Elimination

The former Soviet government had a political political system known as the KGB and had the right to intervene in the legal system, resulting in numerous violations of human rights. . The 1993 Constitution protects the civil rights of all Russian citizens. The President shall nominate the Attorney-General and be approved by the Council of the Union.
The Constitutional Court, the country's highest court established in 1992, is examining the legality of Russian laws. In 1993, President Yeltsin suspended the work of the Constitutional Court. Local courts are called people's courts.
Armed forces
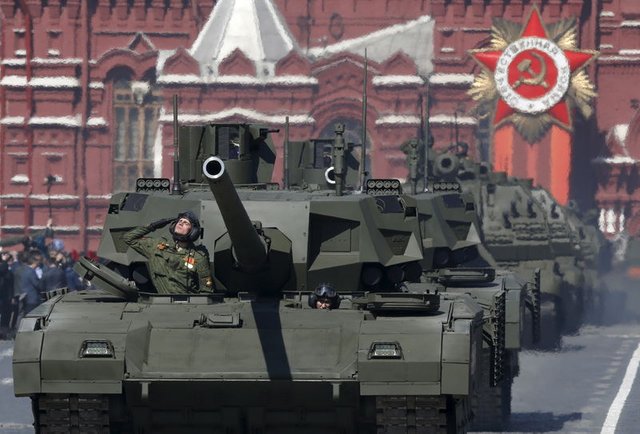

The former Soviet Union had the largest army of more than 4 million soldiers in all sectors of the military. After the collapse of the Soviet Union, the army leadership became the Commonwealth of Independent States, and several republics, including Russia, expressed their desire to form their own army. In 1992, Russia began to form an army to absorb former Soviet forces. Russia and three other nuclear-armed republics - Belarus, Ukraine and Kazakhstan - have agreed to destroy or return nuclear weapons to Russia in seven years. Russia and the United States of America signed a treaty to limit the spread of nuclear weapons, but Ukraine's failure to move in this direction led to new talks that finally agreed. As for the naval fleet, there was a dispute between Russia and Ukraine on the ownership of the Black Sea Fleet. After strenuous negotiations, it was agreed to divide the fleet between the two countries.
Administrative Divisions
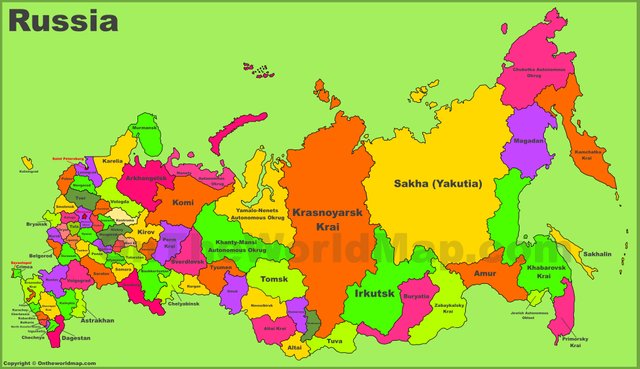
The Russian Federation consists of 89 federal entities:
2 Most of the republics have autonomy in their internal affairs. Each republic often represents one or more ethnic groups.
49 Opelst (counties)
6 Kray (counties)
10 Okrug (Autonomous Region)
2 Federal Cities
Federal Regions and Economic Zones
Recently, 7 large federal regions (4 in Europe and 3 in Asia) have been declared as the top administrative class above the 89 entities under the national level.
Economy
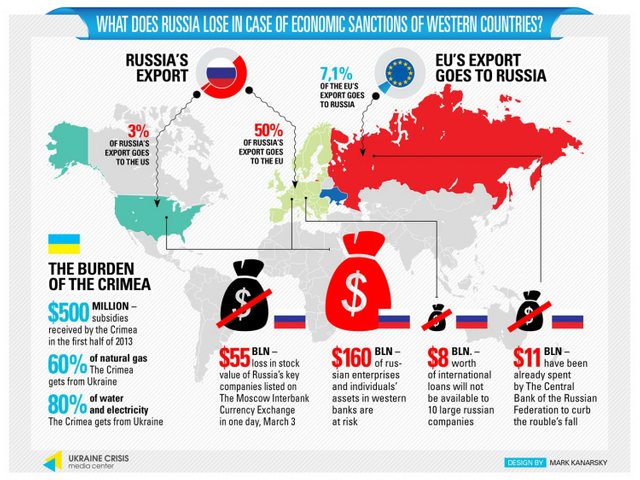
It was the agencies of the central government under the Soviet regime that planned everything about the country's economy. The government owned and controlled all factories and farms, and private businesses were forbidden. At the hands of the Soviet government, Russia was transformed from an agricultural state into an industrial giant. Heavy industries such as chemicals, construction, machinery and steel have developed rapidly. Government ministries provide the necessary raw materials and equipment for industries and farms, determine production quotas, determine the quality of the products and those who sell the products. The result of this rigorous central planning has been that industrial development has seen tremendous progress and made significant gains. But this centralized control with the industry's progress has suppressed new ideas, affecting product quality.
Russia has inherited the Soviet industry with its success and problems. Currently, the Russian government is turning factories and government farms into private property. Small businesses and joint ventures with foreigners have begun to emerge. The country has gone to Western countries and Japan to help modernize and rebuild the industrial sector.
The economic situation in the country worsened after the collapse of the Soviet Union, and the stability of its economy was shaken. To reduce inflation and attract foreign investment, the government has turned its ruble currency into a currency that facilitates the exchange of foreign currency in the world's financial markets and the establishment of a modern banking system. With the abolition of government subsidies on several commodities in 1992, consumer prices rose, and the situation of many families whose incomes remained at their previous level worsened. Despite the chaos that hit the Russian economy at the beginning of the 1990s and the decline in industrial production, Russia has skilled workers and abundant natural resources, helping it to rebound under the new economic order. Since the end of the socialist regime, Russia has experienced a period of transition from the central economy to the market economy, although the state has remained in control of some basic sectors (transport and energy). There have been extensive reforms in the areas of price liberalization, privatization and agrarian reform.
Russia has significant mineral and energy resources that have only been partially exploited. The export of oil, natural gas and minerals is a major source of hard currency.
Russian industry covers many types of products: iron, metals, agricultural machinery, weapons, precision machinery and textiles. In order for Russian industry to remain competitive with foreign industries, it has to be restructured - agriculture (cereals, potatoes ...), livestock breeding, fishing, and forestry (the most important sectors of the Russian economy) - tourism is a significant sector in terms of its financial revenues.
Natural Resources
Russia is one of the world's richest countries in terms of its natural resources. It has the world's largest reserve of forests with large energy resources, vast agricultural land, large mineral deposits, enormous hydropower potential, and many species of flora and fauna.
Industry is an important economic activity in Russia. There are many steel mills and their products in the Ural Mountains.
Industry
Heavy industries are among the most developed industrial sectors in Russia. Heavy equipment factories are concentrated in Moscow, St. Petersburg, along the Volga River and in the Urals, producing heavy machinery and electrical equipment. Chemical industry, chemical fertilizers, mineral fertilizers, petrochemicals and industrial resins are among the most important products of the chemical industry.
The Moscow region is one of the most important industrial centers of the state. Its products include: chemicals, electrical equipment, electronics, cars, foodstuffs, steel and textiles. The factories of St. Petersburg are concentrated in the manufacture of ships and industrial equipment, while in the Ural Mountains, metal industries and machinery. Most of the refineries are in the Volga and Urals. New industries are being built in Siberia to exploit the country's vast hydropower potential. The paper industry is found along the Volga River, while light industries, such as textiles, are concentrated around Moscow.
Collective or collective farms are state owned and partly managed by farmers. The picture shows potatoes harvested at one of these farms.
The level of industrial and agricultural development and progress is low, due to the interest of the former Soviet policy in the heavy metal industries and the war and neglect of the manufacturing and food industries. Because they followed the principle of self-sufficiency, they did not open up economically to the world markets and remained far from the scientific and economic developments and did not open the way to the entry and employment of foreign capital, all these factors cast a very negative impact on the development and industrial and agricultural production, The situation was exacerbated by the unchecked transition from the Communist regime to the quasi-capitalist economic and social system.
Population
Russia has a population of about 146,120,000. The country's population is irregular, most of them living in the western part of the country, while the population in the remote and rugged eastern regions is low.
Four-fifths of the population is concentrated in the European part of Russia and southern Urals, so the density here is high (100200n / km 2), in important industrial areas. In the rural areas, the density is 50-100. In the Asian part, the density is low because the forests and the polar regions cover three quarters of the land. Here, the density does not exceed one person per km2, but it rises to 1025 in the warmer mountain and in the mountains. About 9 n / km 2.
Until the beginning of the 1990s, population growth was normal. The annual birth rate was higher than the mortality rate. The birth rate in this period was 20% and the mortality rate was 10%. Therefore, the annual population growth rate was 10%.
In the last decade of the last century, the mortality rate was significantly higher, with 14.9% of births and 9.6% of deaths. It should be noted that this decline includes Russians in particular, while the birth rate of other races, especially the Islamic higher than the mortality rate is estimated at 10% 12.
The population of Russia was 137 million in 1979 and reached 148 million in 2000, an increase of 11 million in 21 years, an average of half a million a year.
Unemployment was very low in the Communist era, not more than 10%, while today it is not less than 30%, as a result of the negative economic and social changes experienced by Russia recently, which explains the increasing migration of rural people to major cities and industrial in search of a living, The percentage of urban residents has increased from 65% previously to 70% currently at the present time, the highest ratio in the capital and the administrative capitals as in Moscow, Petersburg, Rostov, Nadano and Kazan.
The number of cities is estimated at 1015, many of which are more than one million, while the number of small cities and towns is 2077. The most important cities are Moscow (10 million), Petersburg (6 million) and Gorki (2.5 million).
demographics
About 83% of Russia's people are of Russian descent. This race belongs to the Slavic peoples and lives in Russia more than 100 nationalities, the most important: groups of Tatars, Ukrainians, Bashkiris, Russians, white, Moldovans and Chechens. Most live in autonomous regions, and there are small groups in Siberia such as the Iskimo. After a period of persecution of minority cultures, the present Government granted special privileges to the Russians in order to meet the growing desire for independence of some races.
The ancestors
Russian ethnic origins descend from the Slavic race, which lived in Eastern Europe several thousand years ago. Slavic migrations were divided into three groups: the Eastern Slavs, the Western Slavs and the Southern Slavs. The Russians return their origins to the Eastern Slav state, the Kievans, who emerged in the ninth century.
Rus-Kiev suffered frequently and frequently from the invasions of the Asian tribes including the Bisnik, the Polovets and the Mongols. The repeated Mongol invasion forced some people to migrate to safer and more secure places, and those forested places were close to Moscow's present location. Moscow became an important Russian state in the fourteenth century AD. This region has been in the heart of Russia ever since. There were groups of different races had settled in Russia especially since the sixteenth century, when he began great expansion and colonialism.
The language of russia

Russian is the official language of the state and has three main regional dialects: Northern dialect, Southern dialect, and middle dialect. Little differences are hindered by understanding. Russian is written in Cyrillic. Minorities speak their own languages and speak Russian in a second language.
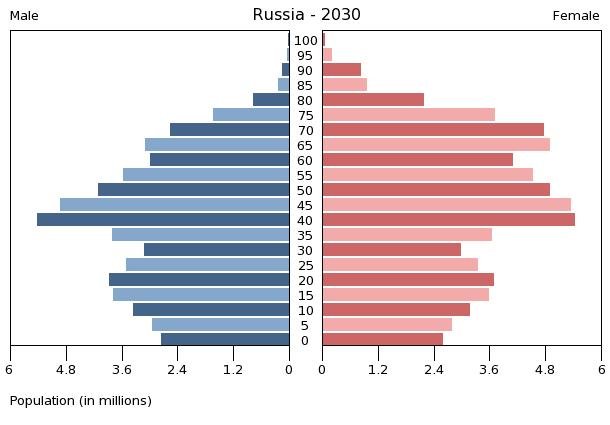
Demographic growth curve in Prussia
The Russian Federation has been the victim of a demographic disaster caused by the civil war and the two world wars in which Russia has suffered the most casualties. The pyramid of the Russian population is known to be small in the age group ranging from 0-15 years, due to several factors, including abstinence from childbearing and late marriage age, as well as a high rate of infantile and infant mortality.
The proportion of active population aged between 20-55 is weak.
Education
Main article: Education in Russia
Moscow State University
the health
Religions
Main article: Religion in Russia
The Cathedral of Christ the Savior (Moscow) was removed during the Soviet era and rebuilt in 1990-2000
The official religion of Russia is Orthodox Christianity and Islam comes second. In addition to Buddhism and Judaism, the state regards them as a "historical heritage" of the state under a law passed in 1997.
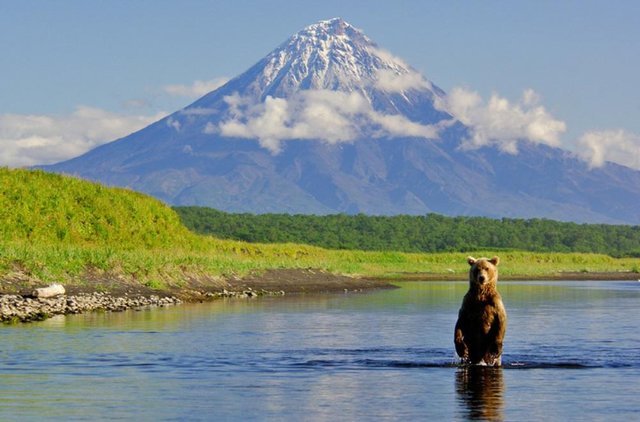
nature



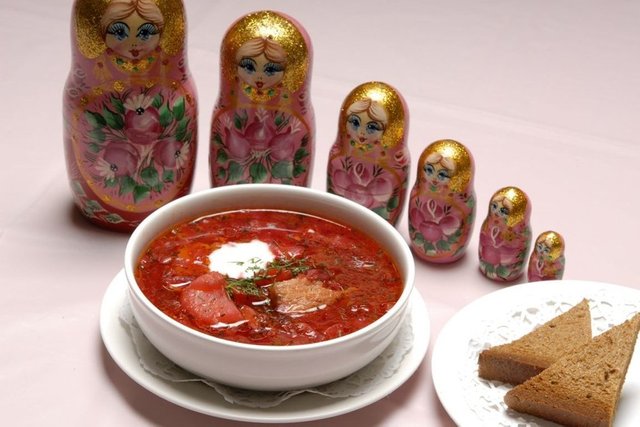
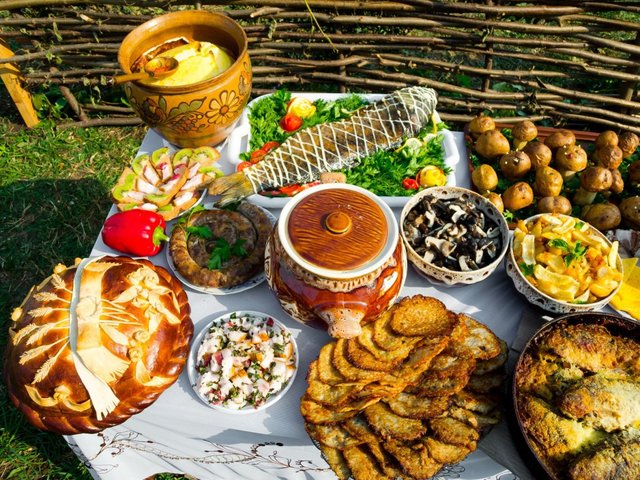
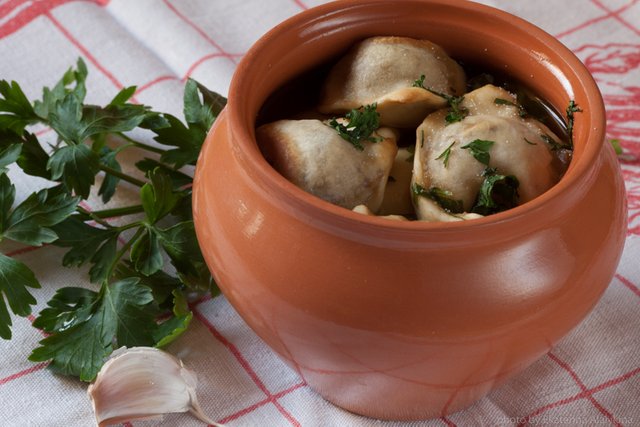
food



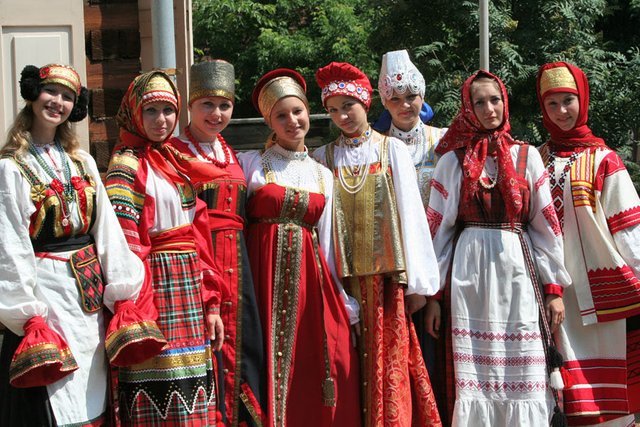
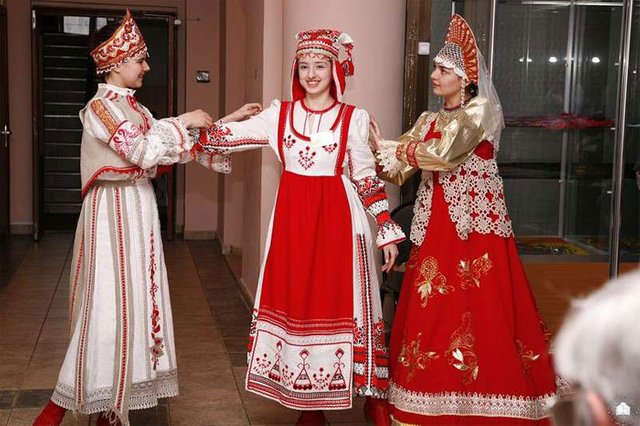
clouthes



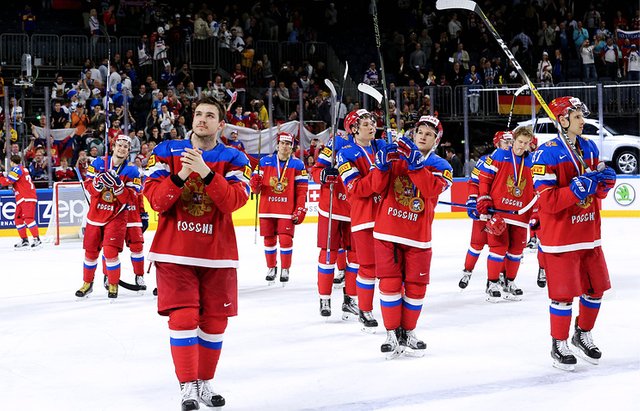
sport



really like the work you put in! great information, i traveled for four years and post about, went to Russia aswell.
nice
that is so amazing!