How Does Cryptocurrency Work?
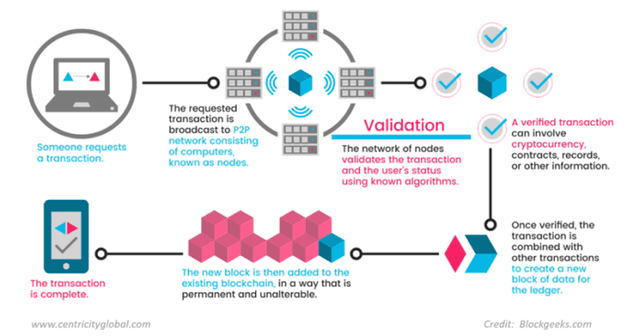
Cryptocurrency is an encrypted and decentralized digital currency that is transferred between friends and is confirmed in a public ledgers through a process known as mining. Below is a simple explanation of how cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin work. The explanation starts from the basics of cryptocurrency to a more in-depth look at other properties that have made cryptocurrency the way it is today.
Cryptocurrency Basics
To understand how cryptocurrency works, you need to learn some basic concepts:
¤ Public Ledgers: All transactions that are authenticated from the beginning of cryptocurrency creation are stored in the general ledger. Identity of the coin owner is encrypted and the system uses other cryptographic techniques to ensure the validity of the records. The ledger ensures that the corresponding wallet (wallet) can calculate the balance that can be spent accurately. Also, new transactions can be checked to ensure that each transaction only uses the coins currently owned by the user. Bitcoin calls this general ledger a "transaction block chain".
¤ Transactions: Transfers between two digital purses are called transactions. The transaction is submitted to the general ledger and awaiting confirmation. The wallet uses an encrypted electronic signature when a transaction is made. Signatures are pieces of encrypted data called cryptographic signatures and provide mathematical proof that transactions originate from the owner of the wallet. The confirmation process takes a little time (ten minutes for Bitcoin). Mining affirms the transaction and adds it to the general ledger.
¤ Mining (Mining): Mining is the process of confirming the transaction and adding it to the general ledger. To add transactions to the ledger, "miners" must solve more complicated computational problems (such as mathematical puzzles). Mining is an open source so anyone can confirm the transaction. The first "miner" in solving the puzzle can add "blocks" of transactions to the ledger. The way in which common blockchain transactions, blocks, and general ledger work together ensures that no one can easily add or alter blocks at will. After the blocks are added to the ledger, all related transactions are permanent, and they add a small transaction fee to the miner's wallet (along with the newly created coins). The mining process is about everything that gives value to coins and is known as a proof-of-work system.
Anatomy of Cryptocurrency
Although there are exceptions to the rule, there are several factors (beyond the basics above) that make cryptocurrency very different from the financial system of the past, namely:
¤ Adaptive Scaling: The adaptive scale means that cryptocurrency is built with measurements to ensure that cryptocurrencies are well constructed on a large and small scale. Example of adaptive scale: Bitcoin is programmed to allow a block of transactions to be mined approximately every ten minutes. The algorithm is adjusted after every block of 2016 (theoretically, it's every two weeks) to be easier or more difficult based on how long it will take for the 2016 blocks to be mined. So if it takes only 13 days for the network to mine the 2016 block, it would be too easy to mine, so the level of difficulty increases. However, if it takes 15 days for the network to mine the 2016 block, it indicates that it is too difficult to be mined, so the difficulty decreases. Other measurements are included in digital coins to enable adaptive scales including restricting supply over time (to create scarcity) and reduce rewards for mining as more coins are mined.
¤ Cryptographic: Cryptocurrency uses cryptographic systems (encryption) to control the making of coins and to verify transactions.
¤ Decentralized: Most of the circulating currency is controlled by a centralized government so that they are governed by a third party. Creation and transactions of cryptocurrencies are open source, controlled by code, and depend on "peer-to-peer" networks. No single entity can affect the currency.
¤ Digital: The traditional currency form is determined by physical objects (US $ exists as paper money and in the early years supported by gold, for example), but all digital cryptocurrency. Digital coins are stored in digital wallets and transferred digitally to someone else's digital wallet. No physical objects.
¤ Open Source: Cryptocurrency is open source. That means that developers can create APIs without paying a fee and anyone can use or join the network.
¤ Proof-of-work: Most cryptocurrencies use a proof-of-work system. The proof-of-work scheme uses computational puzzles that are hard to quantify, but are easily verified to limit the exploitation of cryptocurrency mining. Basically, this scheme is similar to the difficulty in solving "captcha" which requires a lot of computing power
¤ Pseudonymity: The cryptocurrency owner stores their digital coins in an encrypted digital wallet. The identity of the coin holders is stored in the encrypted address they control - not attached to a person's identity. The relationship between you and your coin is pseudonym, that is anonymous as a public ledger (and thus a ledger can be used to gather information about groups of individuals in a network).
¤ Value: In order for something to be an effective currency, it must have value. The US dollar is used to represent true gold. Gold is rare and requires work to mine and refine, so scarcity and value work, in turn, gives the value of the US dollar.
Cryptocurrency works on values. In cryptocurrency, "coins" (which are no more than publicly-approved records of ownership) are produced or produced by "miners" (miners). These miners are the ones who run programs on specially crafted hardware to solve the proof-of-work puzzles. The work behind mining coins gives them value, while the scarcity of coins and their demand causes their value to fluctuate. The work idea that values the currency is called the "proof-of-work" system. Another method of validating coins is called proof-of-stake. Values are also generated when transactions are added to the general ledger because making a verified "transaction block" requires work as well. Further, the value comes from several factors such as utility as well as supply and demand.
Learn More about How Cryptocurrency Works
If at this point you still feel a little confused, do not worry! This is because understanding the concepts of cryptocurrency is indeed a challenge. Tricks around cryptocurrency will not matter if you do not understand it at first, because every new video, explanation, or article you learn will make your understanding of cryptocurrency clearer and until you really get it. For that, for you who want to get more news cryptocurrency and blockchain, you can access it through CoinDaily news portal in coindaily.co.id.
By.@karimuddinn