[Eng] What is Blockchain by Shai Rubin, CTO of Citi Innovation Lab from YouTube
This is the script of the video that well describes Blockchain very simply. Please read and let me know any misconcepts I've understood and delivered wrong. Hopefully everyone can get a little more knowledge of Blockchain technology.
What is Blockchain by Shai Rubin, CTO of Citi Innovation Lab
( )
)
So, the first thing that we need to understand two basic terms.
Bitcoin and Blockchain.
Bitcoin is the digital coin. It's money which is digital. We're not going to talk about Bitcoin this time, we're going to talk bout Blockchain. Blockchain is technology that enables moving digital coins or assets from one individual to another individual. It's very important to understand that Bitcoin is not Blockchain. It is important to understand in our common language because I heard some complaints people are saying 'oh we cannot talk about Bitcoin'. Maybe because it has bad reputation, but about Blockchain, we should and can talk.

Okay, so after we understood basic terms of Bitcoin and Blockchain, it's time to go into problems that Blockchain attempts to solve. The problem is Money Transfer. I'm going to explain it conceptually, only to focus on concept, I'm not going into its implementation how it is done in practice. The important thing is to keep in mind its concept only.
If a person A wants to move or transfer money to person B, let's say from Israel to Japan. It's typically done using a Third Trusted Party. (person A: Israel, person B: Japan) This typically takes about 3 days or more but it takes some time. What blockchain is attempting to solve is
- to transfer money with 3rd trusted party
- to do it faster (immediately)
- cheaper fee.
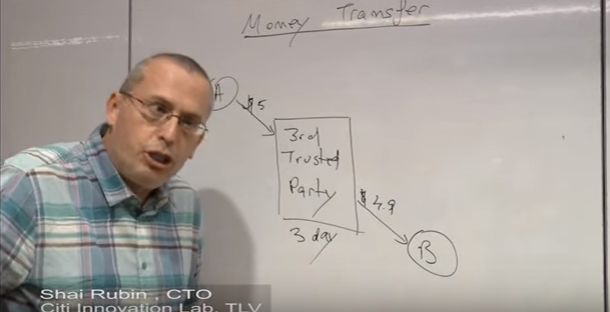
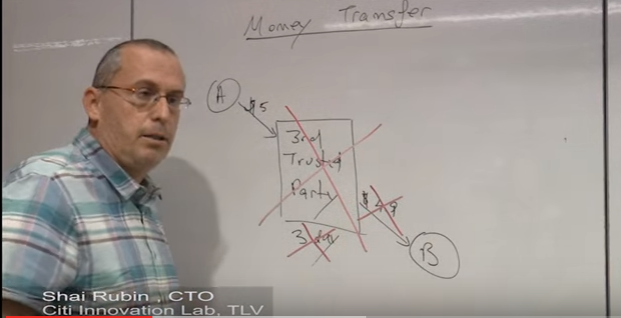
Let's dive into how blockchain addresses money transfer problem- The first principle is the concept of Open Ledger.
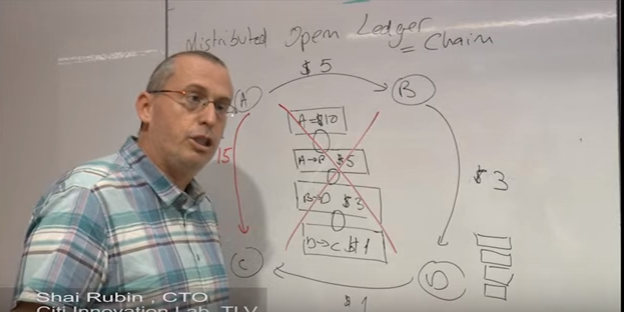
Let's say we have the network of 4 people who want to move money from one another. Let's assume at the moment of inception of this network, A has $10, and A wants to move $5 to B. What is going to happen is we're going to add this transaction (A→B $5) and we're going to link it to existing transaction. Then, let's assume that B wants to move D $3, so we want to link another transaction. (B→D $3). Same process happens. (D→C $1)
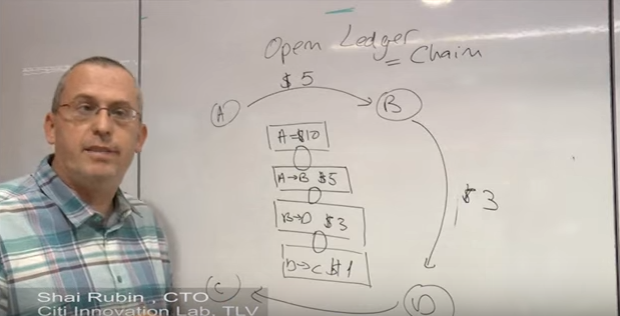
This is the concept of Open Ledger. It is essentially the chain of transaction, this is one of the reasons that this is called BlockChain. This is the chain of transaction that is open and public to everyone. What is gives us is that
- Everyone that own network can see how much money each one has in its pocket
- Everyone can decide whether the transaction is valid or not
For example, if A wants to move C $15, everyone immediately sees this is not a valid transaction because at the start we stand A only had $10. And this transaction will not be added to Open Ledger, and be a part of Chain.
Moving on to the second principle: Distributed Ledger.
Blockchain is going to trying to centralize the ledger and distribute nodes. For example, D can have a copy of ledger and can hold it in his nodes. A can do the same. Now what we got is ledger is distributed and eventually we don't need centralized place that holds ledger.
We achieve the goal getting rid of centralized trusted party. But we created a new problem already. Now when various copies of ledger are in the network, we have to make sure that they synchronize. All the participants in the network sees the same copy of ledger. This moves to the third principle.
The third principle - The concept of Synchronization and Miners
We're understood already that the ledger is open and public, distributed across various nodes. And now what we need to understand is how in this kind of distributed ledger knows and synchronize the ledger.
Let's say B wants to move C $5, What B is going to do is publish intended transaction through network. Everyone in the network will immediately see this transaction. This is the un-validated transaction, it is not getting yet into the ledger. In order to get into the ledger, we need to understand the concept of miners.

Miners own special nodes which can hold ledger. In this case, let's say A and D are miners. Miners are going to compete among themselves who will be the first to take this transaction (un-validated one) and be able to validate and put it into its ledger. The first miner who do that will and shall get reward - this time Bitcoin. Let's try to understand what it is to win the competition. A miner has to do 2 things.
- to validate new transaction - it is easy, ledger is open
- to find a special key that will enable this miner to take previous transaction locks in new transaction - in order to this, a miner needs to invest computation power and time to search for the key.
D was able to solve the puzzle, be able to take this transaction and add to its own ledger. What D is going to do now is publish the solution to the entire network. Miner A will immediately take this transaction and add to its own ledger and look for another transaction to work on and hopefully to get the reward next time.
Summary
Blockchain is based on basic principles of the fact that the ledger is open, public, and distributed.
Miners are who own special nodes in its network whose role is to validate transaction and add them to ledger. The economic incentive of miners essentially ensures what is official ledger that should be used.
incase people want to see the video.
thank you, i didn't know how to upload the video. Thank you :)
Hello. I mention your article on my blog :)
https://golos.io/swinca/@czaiqueenbee/svinka-preimushestvo