RESEARCH REPORT ABOUT KYBER NETWORK
Author: Gamals Ahmed, CoinEx Business Ambassador

ABSTRACT
In this research report, we present a study on Kyber Network. Kyber Network is a decentralized, on-chain liquidity protocol designed to make trading tokens simple, efficient, robust and secure.
Kyber design allows any party to contribute to an aggregated pool of liquidity within each blockchain while providing a single endpoint for takers to execute trades using the best rates available. We envision a connected liquidity network that facilitates seamless, decentralized cross-chain token swaps across Kyber based networks on different chains.
Kyber is a fully on-chain liquidity protocol that enables decentralized exchange of cryptocurrencies in any application. Liquidity providers (Reserves) are integrated into one single endpoint for takers and users. When a user requests a trade, the protocol will scan the entire network to find the reserve with the best price and take liquidity from that particular reserve.
1.INTRODUCTION
DeFi applications all need access to good liquidity sources, which is a critical component to provide good services. Currently, decentralized liquidity is comprised of various sources including DEXes (Uniswap, OasisDEX, Bancor), decentralized funds and other financial apps. The more scattered the sources, the harder it becomes for anyone to either find the best rate for their trade or to even find enough liquidity for their need.
Kyber is a blockchain-based liquidity protocol that aggregates liquidity from a wide range of reserves, powering instant and secure token exchange in any decentralized application.
The protocol allows for a wide range of implementation possibilities for liquidity providers, allowing a wide range of entities to contribute liquidity, including end users, decentralized exchanges and other decentralized protocols. On the taker side, end users, cryptocurrency wallets, and smart contracts are able to perform instant and trustless token trades at the best rates available amongst the sources.
The Kyber Network is project based on the Ethereum protocol that seeks to completely decentralize the exchange of crypto currencies and make exchange trustless by keeping everything on the blockchain.
Through the Kyber Network, users should be able to instantly convert or exchange any crypto currency.
1.1 OVERVIEW ABOUT KYBER NETWORK PROTOCOL
The Kyber Network is a decentralized way to exchange ETH and different ERC20 tokens instantly — no waiting and no registration needed.
Using this protocol, developers can build innovative payment flows and applications, including instant token swap services, ERC20 payments, and financial DApps — helping to build a world where any token is usable anywhere.
Kyber’s fully on-chain design allows for full transparency and verifiability in the matching engine, as well as seamless composability with DApps, not all of which are possible with off-chain or hybrid approaches. The integration of a large variety of liquidity providers also makes Kyber uniquely capable of supporting sophisticated schemes and catering to the needs of DeFi DApps and financial institutions. Hence, many developers leverage Kyber’s liquidity pool to build innovative financial applications, and not surprisingly, Kyber is the most used DeFi protocol in the world.
The Kyber Network is quite an established project that is trying to change the way we think of decentralised crypto currency exchange.
The Kyber Network has seen very rapid development. After being announced in May 2017 the testnet for the Kyber Network went live in August 2017. An ICO followed in September 2017, with the company raising 200,000 ETH valued at $60 million in just one day.
The live main net was released in February 2018 to whitelisted participants, and on March 19, 2018, the Kyber Network opened the main net as a public beta. Since then the network has seen increasing growth, with network volumes growing more than 500% in the first half of 2019.
Although there was a modest decrease in August 2019 that can be attributed to the price of ETH dropping by 50%, impacting the overall total volumes being traded and processed globally.
They are developing a decentralised exchange protocol that will allow developers to build payment flows and financial apps. This is indeed quite a competitive market as a number of other such protocols have been launched.
In Brief
- Kyber Network is a tool that allows anyone to swap tokens instantly without having to use exchanges.
- It allows vendors to accept different types of cryptocurrency while still being paid in their preferred crypto of choice.
- It’s built primarily for Ethereum, but any smart-contract based blockchain can incorporate it.
At its core, Kyber is a decentralized way to exchange ETH and different ERC20 tokens instantly–no waiting and no registration needed. To do this Kyber uses a diverse set of liquidity pools, or pools of different crypto assets called “reserves” that any project can tap into or integrate with.
A typical use case would be if a vendor allowed customers to pay in whatever currency they wish, but receive the payment in their preferred token. Another example would be for Dapp users. At present, if you are not a token holder of a certain Dapp you can’t use it. With Kyber, you could use your existing tokens, instantly swap them for the Dapp specific token and away you go.
All this swapping happens directly on the Ethereum blockchain, meaning every transaction is completely transparent.
1.1.1 WHY BUILD THE KYBER NETWORK?
While crypto currencies were built to be decentralized, many of the exchanges for trading crypto currencies have become centralized affairs. This has led to security vulnerabilities, with many exchanges becoming the victims of hacking and theft.
It has also led to increased fees and costs, and the centralized exchanges often come with slow transfer times as well. In some cases, wallets have been locked and users are unable to withdraw their coins.
Decentralized exchanges have popped up recently to address the flaws in the centralized exchanges, but they have their own flaws, most notably a lack of liquidity, and often times high costs to modify trades in their on-chain order books.

Some of the Integrations with Kyber Protocol
The Kyber Network was formed to provide users with a decentralized exchange that keeps everything right on the blockchain, and uses a reserve system rather than an order book to provide high liquidity at all times. This will allow for the exchange and transfer of any cryptocurrency, even cross exchanges, and costs will be kept at a minimum as well.
The Kyber Network has three guiding design philosophies since the start:
- To be most useful the network needs to be platform-agnostic, which allows any protocol or application the ability to take advantage of the liquidity provided by the Kyber Network without any impact on innovation.
- The network was designed to make real-world commerce and decentralized financial products not only possible but also feasible. It does this by allowing for instant token exchange across a wide range of tokens, and without any settlement risk.
- The Kyber Network was created with ease of integration as a priority, which is why everything runs fully on-chain and fully transparent. Kyber is not only developer-friendly, but is also compatible with a wide variety of systems.
1.1.2 WHO INVENTED KYBER?
Kyber’s founders are Loi Luu, Victor Tran, Yaron Velner — CEO, CTO, and advisor to the Kyber Network.
1.1.3 WHAT DISTINGUISHES KYBER?
Kyber’s mission has always been to integrate with other protocols so they’ve focused on being developer-friendly by providing architecture to allow anyone to incorporate the technology onto any smart-contract powered blockchain. As a result, a variety of different dapps, vendors, and wallets use Kyber’s infrastructure including Set Protocol, bZx, InstaDApp, and Coinbase wallet.
Besides, dapps, vendors, and wallets, Kyber also integrates with other exchanges such as Uniswap — sharing liquidity pools between the two protocols.
A typical use case would be if a vendor allowed customers to pay in whatever currency they wish, but receive the payment in their preferred token. Another example would be for Dapp users. At present, if you are not a token holder of a certain Dapp you can’t use it. With Kyber, you could use your existing tokens, instantly swap them for the Dapp specific token and away you go.
Limit orders on Kyber allow users to set a specific price in which they would like to exchange a token instead of accepting whatever price currently exists at the time of trading. However, unlike with other exchanges, users never lose custody of their crypto assets during limit orders on Kyber.
The Kyber protocol works by using pools of crypto funds called “reserves”, which currently support over 70 different ERC20 tokens. Reserves are essentially smart contracts with a pool of funds. Different parties with different prices and levels of funding control all reserves. Instead of using order books to match buyers and sellers to return the best price, the Kyber protocol looks at all the reserves and returns the best price among the different reserves. Reserves make money on the “spread” or differences between the buying and selling prices.
The Kyber wants any token holder to easily convert one token to another with a minimum of fuss.
1.2 KYBER PROTOCOL
The protocol smart contracts offer a single interface for the best available token exchange rates to be taken from an aggregated liquidity pool across diverse sources.
● Aggregated liquidity pool. The protocol aggregates various liquidity sources into one liquidity pool, making it easy for takers to find the best rates offered with one function call.
● Diverse sources of liquidity. The protocol allows different types of liquidity sources to be plugged into. Liquidity providers may employ different strategies and different implementations to contribute liquidity to the protocol.
● Permissionless. The protocol is designed to be permissionless where any developer can set up various types of reserves, and any end user can contribute liquidity. Implementations need to take into consideration various security vectors, such as reserve spamming, but can be mitigated through a staking mechanism. We can expect implementations to be permissioned initially until the maintainers are confident about these considerations.
The core feature that the Kyber protocol facilitates is the token swap between taker and liquidity sources. The protocol aims to provide the following properties for token trades:
● Instant Settlement. Takers do not have to wait for their orders to be fulfilled, since trade matching and settlement occurs in a single blockchain transaction. This enables trades to be part of a series of actions happening in a single smart contract function.
● Atomicity. When takers make a trade request, their trade either gets fully executed, or is reverted. This “all or nothing” aspect means that takers are not exposed to the risk of partial trade execution.
● Public rate verification. Anyone can verify the rates that are being offered by reserves and have their trades instantly settled just by querying from the smart contracts.
● Ease of integration. Trustless and atomic token trades can be directly and easily integrated into other smart contracts, thereby enabling multiple trades to be performed in a smart contract function.
How each actor works is specified in Section Network Actors.
- Takers refer to anyone who can directly call the smart contract functions to trade tokens, such as end-users, DApps, and wallets.
- Reserves refer to anyone who wishes to provide liquidity. They have to implement the smart contract functions defined in the reserve interface in order to be registered and have their token pairs listed.
- Registered reserves refer to those that will be cycled through for matching taker requests.
- Maintainers refer to anyone who has permission to access the functions for the adding/removing of reserves and token pairs, such as a DAO or the team behind the protocol implementation.
- In all, they comprise of the network, which refers to all the actors involved in any given implementation of the protocol.
The protocol implementation needs to have the following:
- Functions for takers to check rates and execute the trades
- Functions for the maintainers to register/remove reserves and token pairs
- Reserve interface that defines the functions reserves needs to implement
1.3 KYBER CORE SMART CONTRACTS
Kyber Core smart contracts is an implementation of the protocol that has major protocol functions to allow actors to join and interact with the network.
For example, the Kyber Core smart contracts provide functions for the listing and delisting of reserves and trading pairs by having clear interfaces for the reserves to comply to be able to register to the network and adding support for new trading pairs. In addition, the Kyber Core smart contracts also provide a function for takers to query the best rate among all the registered reserves, and perform the trades with the corresponding rate and reserve.
A trading pair consists of a quote token and any other token that the reserve wishes to support. The quote token is the token that is either traded from or to for all trades. For example, the Ethereum implementation of the Kyber protocol uses Ether as the quote token.
In order to search for the best rate, all reserves supporting the requested token pair will be iterated through. Hence, the Kyber Core smart contracts need to have this search algorithm implemented.
The key functions implemented in the Kyber Core Smart Contracts are listed in Figure 2 below. We will visit and explain the implementation details and security considerations of each function in the Specification Section.
1.4 HOW KYBER’S ON-CHAIN PROTOCOL WORKS?
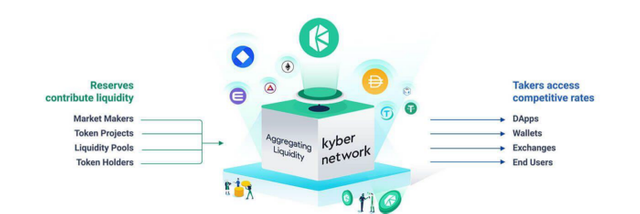
Kyber is the liquidity infrastructure for decentralized finance. Kyber aggregates liquidity from diverse sources into a pool, which provides the best rates for takers such as DApps, Wallets, DEXs, and End users.
1.4.1 PROVIDING LIQUIDITY AS A RESERVE
Anyone can operate a Kyber Reserve to market make for profit and make their tokens available for DApps in the ecosystem. Through an open reserve architecture, individuals, token teams and professional market makers can contribute token assets to Kyber’s liquidity pool and earn from the spread in every trade. These tokens become available at the best rates across DApps that tap into the network, making them instantly more liquid and useful.
MAIN RESERVE TYPES
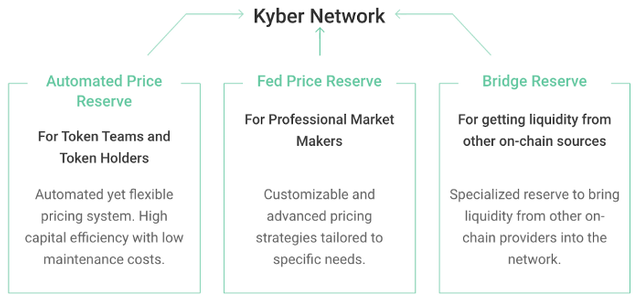
Kyber currently has over 45 reserves in its network providing liquidity. There are 3 main types of reserves that allow different liquidity contribution options to suit the unique needs of different providers.
- Automated Price Reserves (APR) — Allows token teams and users with large token holdings to have an automated yet customized pricing system with low maintenance costs. Synthetix and Melon are examples of teams that run APRs.
- Fed Price Reserves (FPR) — Operated by professional market makers that require custom and advanced pricing strategies tailored to their specific needs. Kyber alongside reserves such as OneBit, runs FPRs.
- Bridge Reserves (BR) — These are specialized reserves meant to bring liquidity from other on-chain liquidity providers like Uniswap, Oasis, DutchX, and Bancor into the network.
1.5 KYBER NETWORK ROLES
There Kyber Network functions through coordination between several different roles and functions as explained below:
- Users — This entity uses the Kyber Network to send and receive tokens. A user can be an individual, a merchant, and even a smart contract account.
- Reserve Entities — This role is used to add liquidity to the platform through the dynamic reserve pool. Some reserve entities are internal to the Kyber Network, but others may be registered third parties. Reserve entities may be public if the public contributes to the reserves they hold, otherwise they are considered private. By allowing third parties as reserve entities the network adds diversity, which prevents monopolization and keeps exchange rates competitive. Allowing third party reserve entities also allows for the listing of less popular coins with lower volumes.
- Reserve Contributors — Where reserve entities are classified as public, the reserve contributor is the entity providing reserve funds. Their incentive for doing so is a profit share from the reserve.
- The Reserve Manager — Maintains the reserve, calculates exchange rates and enters them into the network. The reserve manager profits from exchange spreads set by them on their reserves. They can also benefit from increasing volume by accessing the entire Kyber Network.
- The Kyber Network Operator — Currently the Kyber Network team is filling the role of the network operator, which has a function to adds/remove Reserve Entities as well as controlling the listing of tokens. Eventually, this role will revert to a proper decentralized governance.
1.6 BASIC TOKEN TRADE
A basic token trade is one that has the quote token as either the source or destination token of the trade request. The execution flow of a basic token trade is depicted in the diagram below, where a taker would like to exchange BAT tokens for ETH as an example. The trade happens in a single blockchain transaction.
- Taker sends 1 ETH to the protocol contract, and would like to receive BAT in return.
- Protocol contract queries the first reserve for its ETH to BAT exchange rate.
- Reserve 1 offers an exchange rate of 1 ETH for 800 BAT.
- Protocol contract queries the second reserve for its ETH to BAT exchange rate.
- Reserve 2 offers an exchange rate of 1 ETH for 820 BAT.
- This process goes on for the other reserves. After the iteration, reserve 2 is discovered to have offered the best ETH to BAT exchange rate.
- Protocol contract sends 1 ETH to reserve 2.
- The reserve sends 820 BAT to the taker.
1.7 TOKEN-TO-TOKEN TRADE
A token-to-token trade is one where the quote token is neither the source nor the destination token of the trade request. The exchange flow of a token to token trade is depicted in the diagram below, where a taker would like to exchange BAT tokens for DAI as an example. The trade happens in a single blockchain transaction.
- Taker sends 50 BAT to the protocol contract, and would like to receive DAI in return.
- Protocol contract sends 50 BAT to the reserve offering the best BAT to ETH rate.
- Protocol contract receives 1 ETH in return.
- Protocol contract sends 1 ETH to the reserve offering the best ETH to DAI rate.
- Protocol contract receives 30 DAI in return.
- Protocol contract sends 30 DAI to the user.
2.KYBER NETWORK CRYSTAL (KNC) TOKEN
Kyber Network Crystal (KNC) is an ERC-20 utility token and an integral part of Kyber Network.
KNC is the first deflationary staking token where staking rewards and token burns are generated from actual network usage and growth in DeFi.
The Kyber Network Crystal (KNC) is the backbone of the Kyber Network. It works to connect liquidity providers and those who need liquidity and serves three distinct purposes. The first of these is to collect transaction fees, and a portion of every fee collected is burned, which keeps KNC deflationary.
Kyber Network Crystals (KNC), are named after the crystals in Star Wars used to power light sabers.
The KNC also ensures the smooth operation of the reserve system in the Kyber liquidity since entities must use third-party tokens to buy the KNC that pays for their operations in the network.
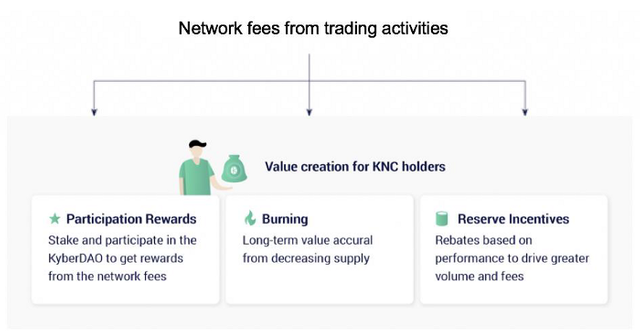
KNC allows token holders to play a critical role in determining the incentive system, building a wide base of stakeholders, and facilitating economic flow in the network. A small fee is charged each time a token exchange happens on the network, and KNC holders get to vote on this fee model and distribution, as well as other important decisions. Over time, as more trades are executed, additional fees will be generated for staking rewards and reserve rebates, while more KNC will be burned.
- Participation rewards — KNC holders can stake KNC in the KyberDAO and vote on key parameters. Voters will earn staking rewards (in ETH)
- Burning — Some of the network fees will be burned to reduce KNC supply permanently, providing long-term value accrual from decreasing supply.
- Reserve incentives — KNC holders determine the portion of network fees that are used as rebates for selected liquidity providers (reserves) based on their volume performance.
Finally, the KNC token is the connection between the Kyber Network and the exchanges, wallets, and dApps that leverage the liquidity network. This is a virtuous system since entities are rewarded with referral fees for directing more users to the Kyber Network, which helps increase adoption for Kyber and for the entities using the Network.
And of course there will soon be a fourth and fifth uses for the KNC, which will be as a staking token used to generate passive income, as well as a governance token used to vote on key parameters of the network.
The Kyber Network Crystal (KNC) was released in a September 2017 ICO at a price around $1. There were 226,000,000 KNC minted for the ICO, with 61% sold to the public. The remaining 39% are controlled 50/50 by the company and the founders/advisors, with a 1 year lockup period and 2 year vesting period.
Currently, just over 180 million coins are in circulation, and the total supply has been reduced to 210.94 million after the company burned 1 millionth KNC token in May 2019 and then its second millionth KNC token just three months later.
That means that while it took 15 months to burn the first million KNC, it took just 10 weeks to burn the second million KNC. That shows how rapidly adoption has been growing recently for Kyber, with July 2019 USD trading volumes on the Kyber Network nearly reaching $60 million. This volume has continued growing, and on march 13, 2020 the network experienced its highest daily trading activity of $33.7 million in a 24-hour period.
Currently KNC is required by Reserve Managers to operate on the network, which ensures a minimum amount of demand for the token. Combined with future plans for burning coins, price is expected to maintain an upward bias, although it has suffered along with the broader market in 2018 and more recently during the summer of 2019.
It was unfortunate in 2020 that a beginning rally was cut short by the coronavirus pandemic, although the token has stabilized as of April 2020, and there are hopes the rally could resume in the summer of 2020.
2.1 HOW ARE KNC TOKENS PRODUCED?
The native token of Kyber is called Kyber Network Crystals (KNC). All reserves are required to pay fees in KNC for the right to manage reserves. The KNC collected as fees are either burned and taken out of the total supply or awarded to integrated dapps as an incentive to help them grow.
2.2 HOW DO YOU GET HOLD OF KNC TOKENS?
Kyber Swap can be used to buy ETH directly using a credit card, which can then be used to swap for KNC. Besides Kyber itself, exchanges such as Binance, Huobi, and OKex trade KNC.
2.3 WHAT CAN YOU DO WITH KYBER?
The most direct and basic function of Kyber is for instantly swapping tokens without registering an account, which anyone can do using an Etheruem wallet such as MetaMask. Users can also create their own reserves and contribute funds to a reserve, but that process is still fairly technical one–something Kyber is working on making easier for users in the future.
2.4 THE GOAL OF KYBER THE FUTURE
The goal of Kyber in the coming years is to solidify its position as a one-stop solution for powering liquidity and token swapping on Ethereum. Kyber plans on a major protocol upgrade called Katalyst, which will create new incentives and growth opportunities for all stakeholders in their ecosystem, especially KNC holders. The upgrade will mean more use cases for KNC including to use KNC to vote on governance decisions through a decentralized organization (DAO) called the KyberDAO.
With our upcoming Katalyst protocol upgrade and new KNC model, Kyber will provide even more benefits for stakeholders. For instance, reserves will no longer need to hold a KNC balance for fees, removing a major friction point, and there will be rebates for top performing reserves. KNC holders can also stake their KNC to participate in governance and receive rewards.
2.5 BUYING & STORING KNC
Those interested in buying KNC tokens can do so at a number of exchanges. Perhaps your best bet between the complete list is the likes of Coinbase Pro and Binance. The former is based in the USA whereas the latter is an offshore exchange.
The trading volume is well spread out at these exchanges, which means that the liquidity is not concentrated and dependent on any one exchange. You also have decent liquidity on each of the exchange books. For example, the Binance BTC / KNC books are wide and there is decent turnover. This means easier order execution.
KNC is an ERC20 token and can be stored in any wallet with ERC20 support, such as MyEtherWallet or MetaMask. One interesting alternative is the KyberSwap Android mobile app that was released in August 2019.
It allows for instant swapping of tokens and has support for over 70 different altcoins. It also allows users to set price alerts and limit orders and works as a full-featured Ethereum wallet.