DIRO: Profiting through a Decentralized Platform that Secures your Contact Directories.
INTRODUCTION TO THE DIRO BLOCKCHAIN PLATFORM.
The lack of a genuine identity system that is universally recognized and accepted by counter parties across all industries is a major deficiency in today’s digital world.
This problem which has been part technical and part political arises because it is difficult to get all governments consumers and industries in all zones to accept a common verification and identification system which is credible.
Cyber security has never been of a much greater need as we introduce and make use of technologies such as IOT, AR/VR along with digital currencies which are in the process of popular adoption.
Fake identities are very much prevalent on social networks today because social networks are limited by the number of people or users who join and corporations who hold identity data are having different monetization goals. Furthermore, user passwords are fragile thereby making accounts very hackable because social networks need constant supply of updated information from users who freely volunteer data without real encryption guarantee or genuine verification.
The industry is looking for a solution.
The importance of providing legal identities to people all over the world can be over stated or emphasized that is why governments are now holding banks and businesses responsible for AML and KYC and a complete overhaul of data privacy is been witnessed across Europe and it is very possible that other continents and countries will follow suit.
UNDERSTANDING THE TECHNICAL CHALLENGES.
It is very hard to own an identity
Since the average person is not technologically savvy owning an identity without the knowledge of proper safety and recovery procedures the danger of permanent loss of control or hacking is very high and this challenge occurs because of the inability to:
• Associate public keys with identity
• Modify and control private profiles
• Recover and gain control of identity
• Collect third party claims and authorizations
• Select which attributes to share
It requires consensus to verify identity
On a general note there are 2 Major concerns of digital identities namely:
Synthetic identities; where a non-exiting person is digitally created
Identity theft; there is an imposter using the identity of some on else.
There must be consensus from the masses or organizations if these two are to be solved and it should be noted that biometrics will not solve any of these two problems contrary to popular view.
Centralized systems are unreliable and take a long time
Centralized systems are not trustworthy when it comes to global identity because it can be attacked from both within and without also, since identity systems control financial transactions on a global scale their centralization makes them more prone to cyber-attacks and hacking therefore systems with such significance should not be placed at such a risk.
Identities need to be validated and updated constantly
This is because confusion must be avoided and people need loose phones and ID’S expire and changes are constant in the lives of people.
Challenges of further decentralization of identities
- Managing and securing the keys
- Validating and authenticating the identity which includes:
• The public blockchain
• Private blockchain
• Transaction layer
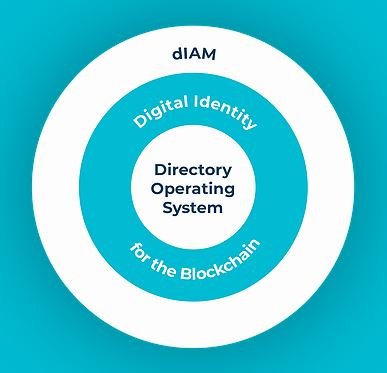
GLOBAL CONTACT DIRECTORIES
A multi-directory platform wherein users can tag their existing contacts on smartphones into one or more directories shared in closed user groups.
Aggregate unverified identity data (contacts)
The system allows every user to upload all their existing contacts to the platform as private directories.
This innovation of the discovery engine is a key enabler for the crowd-mining of these directories to become possible. Forming such universally complete connected and unconnected directories is unprecedented and has many use cases across domains.
Crowd-linked contact layers
This combine contacts contextually on different nodes to build profiles across directories. There is a linking algorithm which places priority to each piece of the information whilst privacy of the contact is respected. New concepts like Archive, discard & Hide are introduced at appropriate levels. This gives a hassle-free experience.
Building Identity Consensus through directories
To drive consensus across international borders, active MSDINs (mobile numbers) are the most authentic source of identification. For blockchain users to stake claim at any time, the digital identity will remain dormant, private and secure. Each user on an average is a member of about 9-10 connected directories. This consensus based identity is recorded on blockchain.
For smartphone users, directories enable an automatic social KYC which may be controlled or built.
Narrow-casting Engine
The profile cards contain custom combination of profile information. These cards are narrow-casted to each directory in two ways
• IN Patent No. PCT/IB2017/053622 2017
• IN Patent No. Universal Original Document Validation platform 2015
Directories can be connected (groups) and Unconnected (contact lists). In a connected directory, users can control complete information whereas in unconnected directory users can narrow cast their information to a list to supplement the contact information stored in their devices in a separate layer. Note that profile cards solve privacy concerns in
Crowdsourced Directories.
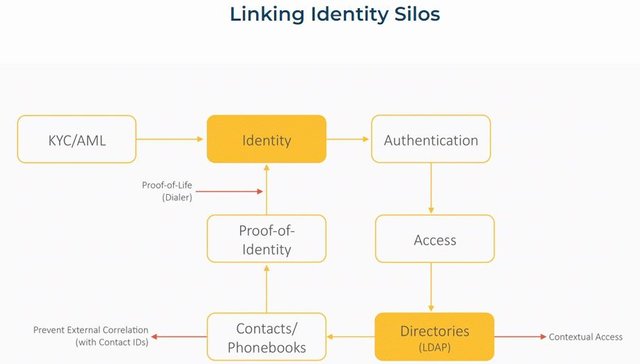
Using Distributed Database to Decentralize Contact Directories
It is pertinent to note that for decentralizing the directories, it’s best to use record-chaining to manage conflicts across devices while decentralizing the control.
• Directory Ledger- contains changes to member’s role, permissions for block distribution with other identities.
• Contact Ledger- contains changes to identity related attribute, certificates, claims, authorizations, change log etc.
• Identity Ledger- contains log of MSISDN, devices, keys, claims, certificates, invalid claims, privacy stings, profile etc.
Consensus Protocol
On the basis of applicability and efficacy, a consensus protocol has three key properties:
- Safety
- Liveness
- Fault Tolerance
Other properties include:
-Blockchain type
-Transaction finality
-Transaction rate
-Cost of participation
-Scalability of peer network
-Trust model
-Orphaned blocks
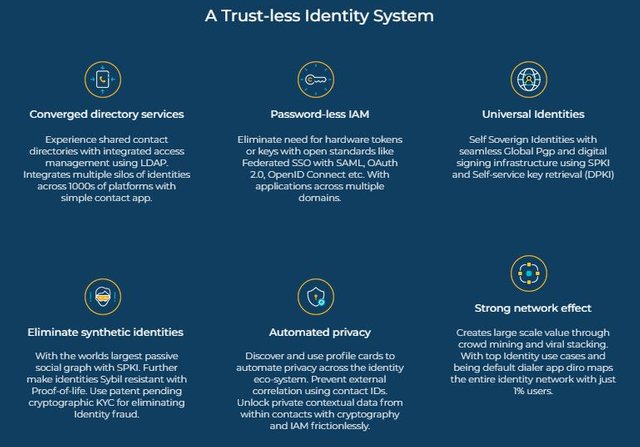
Using mobiles for password less MFA experience
Since based on research 95% of cyber-attacks make use of stolen passwords, the LDAP system will help in authentication to father enquire about signing in.
Using cryptography and blockchain to decentralize Identity
We are getting to a point in the evolution of technology where the real world and the virtual world are being merged together to create better UX based on augmented reality.
Since trustless identities are needed for this to occur, by having accountability across the ecosystem through reliable identities, Diro solves multiple issues like theft, corruption, tax evasion or fraud.
A digital identity is:
• Globally unique
• Non-synthetic
• Singularly representing a living person
• Having irrevocable ownership
• Control over identifier
The three aspects of a digital identity include:
- Proof of global unique identity
- Proof of aliveness
- Fault of tolerance
Using Smart Contracts to manage the Public Key
A method of decentralizing the Maintainance of public keys has been suggested by uport which involves the use of Bloch chain and smart contracts by the identity owner.
dPKI for recovering private keys
Decentralized identity data needs secure cloud storage that can be recovered in case of data loss. The security and usability problems of DNS and PKIX can be addressed through the use of decentralized key-value data stores, such as block chains, to create a specification for a Decentralized Public Key Infrastructure (dPKI).
SPKI to sign identity data to validate identity
Digital identities need to be certified by other agencies or social consensus to become more reliable.
Directories can be domain verified using email verification or better still signed using a domain validated certificate.
Cryptographic KYC
Since a digital identity may be validated by a browser and therefore ownership can be proved with cryptographic validation through SSL certificate which has been captured, allowing such remote KYCs once and adding it as a verified claim could make the whole KYC process frictionless.
Validating authentic digital identity owner with proof-of-life
Identity trust cores can be built for privilege access using live human voice and video interactions from smartphones which are more secure than any biometric systems.
Authentication levels
- User identified with one-time password
- User authenticated with social fingerprint using directories
- User previously confirmed by having live conversations
- User transaction confirmed by subsequent live conversations
The user, on sign up, may select a list of individuals to validate his/her own identity based on interactions. The trusted members would then digitally sign the device as authentic for a short period. The user may then declare authorization level before signing transactions based on collected signatures and share with trusted devices. In case of incorrect declaration, the trusted devices could revoke the signing key of the user.
Scaling trust with block chain
Identity and security for establishing trust are critical building blocks on blockchain. Contact directories or social graphs are a central component in decentralizing the identity and access management. Without using social confirmation building a reliable decentralized identity and security architecture is not possible.
Conclusion
Contact directories offer a rapid method to validate digital identities using SPKI to do social KYC.A decentralized identity platform requires a safe public & private key management and recovery process to make owning identities possible, therefore, social KYC is a critical factor for authentication across different aspects of creating a decentralized identity structure.
Contact directories based on MSDINs open up a new realm of decentralized identity and access management infrastructure across multiple domains like web, apps, blockchain, AR/VR & all other industries as user directories for context and security (LDAP).
Sources
Website: https://www.diro.io
Whitepaper: https://docs.wixstatic.com/ugd/fae167_26798553a540495d9c8189932e9c088f.pdf
Facebook: https://web.facebook.com/DiroBlockchain
Reddit: https://www.reddit.com/r/DiroLabs/
Twitter: https://twitter.com/DiroLabs
Telegram: https://t.me/DiroToken
AUTHORED BY: cliffdex
AUTHOR’S BITCOINTALK URL: https://bitcointalk.org/index.php?action=profile;u=1781660
ETHEREUM WALLET ADDRESS: 0x29d1Fff9f61dcB1508454BfF52eAeA0881D81e43