Internet of Things and Blockchain
In the connected world we live in today, we surround ourselves with IoT (Internet of Things) technologies. IoT are hardware and mechanical devices that have unique identifiers and the ability to transfer data without requiring human-to-computer or human-to-human interaction. IoT is expected to reach $267 billion by 2020 according to the Boston Consulting Group and projected to grow 7.3 CAGR (compound annual growth rate). A classic example of an IoT device is the Amazon Echo, the table-top device that is powered by AI and voice-activated skills.

Another common device is the Nest, a thermostat that programs itself according to the schedule and environment set which also has algorithms to help conserve energy and reduce bills overall. As society adopts more IoT devices, blockchain has the unique position to order this phenomenon we live in today. We will take a look at two IoT blockchain projects that often get misinterpreted, Waltonchain and Vechain.

Waltonchain ($WTC)

The Korean-based team is founded by Xu Fangcheng (Director of Septwolves Group) and Do Sanghyuk (VC of China-Korea Culture Exchange Development). Waltonchain is utilizing RFID technologies to alleviate counterfeiting and helps track products. RFID tags are flexible in that it can be active, passive, or semi-passive. An example of RFID would be tagging of clothing at retail stores. If a RFID tagged item is shoplifted and goes through a security gate, an alarm will go off. This is done via a certain signal each unpurchased RFID tagged item sends out.
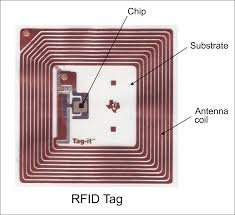
Backed by several patents, Waltonchain is first implemented in Nan King City’s furniture industry, China’s central furniture depot. Waltonchain aims to then act as a cheap source of tagging for luxury brands, cargo deployment, and electronics. RFID is a standard that was first created in the 1940s and gained adoption by the 1980s. It is by no mean a hot commodity, but it is a technology that is consistent. RFID can activate without contact like barcodes or QR codes with read times of a few milliseconds. Waltonchain aims to utilize RFID and provide the ability to create transactions right on top of the blockchain. The main pro that Waltonchain has is that the RFID chips designed will not require an intermediary application layer. This means that Waltonchain applications do not require interfacing a software API. If a chip was to go bad or even hacked, it does not disrupt the entire application of that product. Waltonchain is a proof-of-stake-and-trust system, which means that your contributions utilizing the RFID chips is vetted a certain score. The project is partnered with the China Mobile IoT Alliance, Alibaba Cloud, Mobius, NIDs Sensors, and numerous other RFID/sensor factories.

Vechain ($VEN)

The Singapore-based team is founded by the founder of QTUM, Sunny Lu. Vechain approaches the IoT market by using NFC and utilizing the blockchain on each. NFC is passive in nature as they rely on radio-frequencies and do not require active circuitry. An example of NFC is the chip on your smartphone that allows proximity mobile payments. The Apple Airdrop feature is a derivative of NFC data transfer.

Vechain doesn’t use an API and instead uses a “consensus mechanism.” This means that for RFID tags deployed by Vechain to actuate, each transaction has to be verified on the blockchain. Vechain utilizes an innovative “proof-of-authority” system where nodes are validated with a trust score based on previous transactions and financial stake in the network. This accruing asset is issued as Thor (THOR) where users can stake them to contribute to the PoA calculations. Although this sounds like the PoS system of Waltonchain, THOR acts as a secondary form of tokenization and can be utilized to run applications (dApps) and power smart contracts. Vechain has acquired partnerships with PwC, Kuehne & Nagel, and China Unicom. Vechain allows suppliers to utilize a range of existing standards instead of strictly being limited to RFID. This allows QR, NFC, hybrid-RFID, and barcode technology to utilize Vechain.
Final Thoughts
IoT and blockchain is a perfect match as the scope for market disruption with the benefit of blockchain technology can have wide market adoption. IoT technologies that use RFID or NFC tagging is expected to compound in annual growth. Big technology companies are pouring vast engineering resources to create the next IoT device for market adoption, such as the recent Google Home and Apple HomePod launch. The tradeoffs between RFID and NFC slated earlier will always have use-cases in the IoT market, but are also able to co-exist. It will be exciting for what these projects will become and how IoT devices overall will be able to adopt blockchain technology.

Cheers,
The Blockchain Musketeers
Follow Us!
Facebook
Instagram
Twitter
Youtube
Discord
Disclaimer: The information provided by the Blockchain Musketeers is our own opinions and should not be taken as investment advice, financial advice, or any other sort of advice. Nor should this information be used to determine if you should buy, sell, or hold a cryptocurrency. Please conduct your own due diligence and consult your financial advisory before making any investment decisions. Only invest money which you are willing to lose, as cryptocurrencies is not suitable for all users.
Coins mentioned in post: