Understanding cryptocurrencies

When it comes to the future of money, there is a growing consensus that cryptocurrencies are set to play a major role. One cryptocurrency, in particular, has entered the public lexicon as the go-to digital asset: Bitcoin.
Understanding digital currency.
When the digital currency Bitcoin came to life in January 2009, it was noticed by almost no one apart from the handful of programmers who followed cryptography discussion groups. Its origins were shadowy: it had been conceived the previous year by a still-mysterious person or group known only by the alias Satoshi Nakamoto1. And its purpose seemed quixotic: Bitcoin was to be a 'cryptocurrency', in which strong encryption algorithms were exploited in a new way to secure transactions. Users' identities would be shielded by pseudonyms. Records would be completely decentralized. And no one would be in charge — not governments, not banks, not even Nakamoto. !
bitcoin-podcast.jpg
Essentially, cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin, Ethereum,Litecoin ooperate by creating a massive, open ledger that records every transaction that has ever occurred on the currency’s network. Individual users are given a “public key” (basically, a long stream of digits than can be represented as a QR code), which can be used to either send or receive funds for a small fee. Where things get really interesting, though, is that every single device that records a balance in a given digital currency -- whether Bitcoin, Ethereum.Litecoin or another alternative -- maintains a record of the full network’s transactions. So while traditional banks and services such as Paypal are vulnerable to system-wide outages stemming from major hacks, digital-currency markets can carry on as usual, thanks to their decentralized nature. Is digital currency safe? For the most part, cryptocurrencies’ infrastructure keeps them safe, as developers would need to get more than 51 percent of the network to agree to changes in the way that the currency operates. Even the fees generated by digital-currency transactions contribute minimally to fraud because the fees go to the data miners who push updates to the network successfully, not to owners or investors who could abuse the system for profit. That’s not to say that safety issues don’t exist. The Mt. Gox bankruptcy, for instance, demonstrates that services built of digital currencies can be as susceptible to hacking attacks as traditional banking institutions. PCWorld also acknowledges that digital currencies aren’t protected or insured by anybody, so if your computer (or your cryptocurrency wallet-hosting service, as in the case of InstaWallet) is hacked, these irreversible transactions could result in losses.
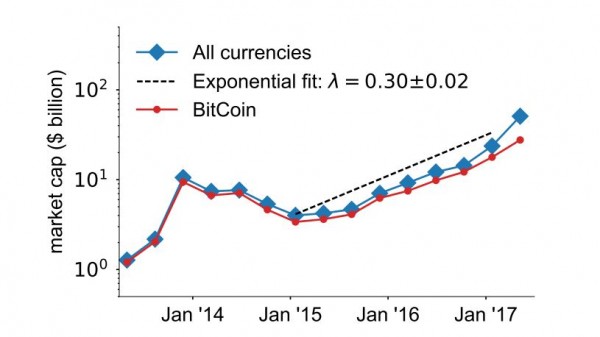
Yet the idea caught on. Today, there are some 14.6 million Bitcoin units in circulation. Called bitcoins with a lowercase 'b', they have a collective market value of around US$46.4 billion. Some of this growth is attributable to criminals taking advantage of the anonymity for drug trafficking and worse. But the system is also drawing interest from financial institutions such as JP Morgan Chase, which think it could streamline their internal payment processing and cut international transaction costs. It has inspired the creation of some 700 other cryptocurrencies. And on 15 September 2015, Bitcoin officially came of age in academia with the launch of Ledger, the first journal dedicated to cryptocurrency research.
What fascinates academics and entrepreneurs alike is the innovation at Bitcoin's core. Known as the block chain, it serves as the official online ledger of every Bitcoin transaction, dating back to the beginning. It is also the data structure that allows those records to be updated with minimal risk of hacking or tampering — even though the block chain is copied across the entire network of computers running Bitcoin software, and the owners of those computers do not necessarily know or trust one another.
Many people see this block-chain architecture as the template for a host of other applications, including self-enforcing contracts and secure systems for online voting and crowdfunding. This is the goal of Ethereum, a block-chain-based system launched in July by the non-profit Ethereum Foundation, based in Baar, Switzerland. And it is the research agenda of the Initiative for CryptoCurrencies and Contracts (IC3), an academic consortium also launched in July, and led by Cornell University in Ithaca, New York.
Nicolas Courtois, a cryptographer at University College London, says that the Bitcoin block chain could be “the most important invention of the twenty-first century” — if only Bitcoin were not constantly shooting itself in the foot.
Into the ether The block chain is a remarkably powerful idea that could be applied to much more than just transaction records, says Gavin Wood, co-founder of Ethereum and chief technology officer of its foundation. One use might be to develop computerized, self-enforcing contracts that make a payment automatically when a task is complete. Others might include voting systems, crowdfunding platforms, and even other cryptocurrencies. Wood says that Ethereum is best used in situations for which central control is a weakness — for example, when users do not necessarily trust one another. In 2014, to make it easier to develop such applications, Wood and fellow programmer Vitalik Buterin devised a way to combine the block chain with a programming language. Ethereum raised 30,000 bitcoins through crowdfunding to commercialize this system.To prevent the basic cryptography-related mistakes that have plagued Bitcoin, Ethereum has recruited academic experts to audit its protocol. Shi and Juels are looking for ways that Ethereum could be abused by criminals. “The technology itself is morally neutral, but we should figure out how to shape it so that it can support policies designed to limit the amount of harm it can do,” says Juels.
Congratulations @caliberisha! You have completed some achievement on Steemit and have been rewarded with new badge(s) :
Click on any badge to view your own Board of Honor on SteemitBoard.
For more information about SteemitBoard, click here
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOPCongratulations @caliberisha! You received a personal award!
You can view your badges on your Steem Board and compare to others on the Steem Ranking
Vote for @Steemitboard as a witness to get one more award and increased upvotes!