BEAM: The Future of Blockchain Privacy
"Scalable Confidential Cryptocurrency"

Introduction
Since the launch of Bitcoin in 2009, cryptocurrencies have been constantly evolving and new applications are being developed every day. Exciting projects often arise with the promise of improving service delivery, speed and efficient distribution of resources using blockchain technology. These projects are primarily aimed at business solutions and applications in all fields of human knowledge from medicine to the automotive industry. Current trends suggest a massive transition from centralized systems to decentralized solutions with cryptocurrency technology.
However, the basic need of people is to store their money and conduct transactions safely without relying on a centralized authority, so we can ensure that the main use of Blockchain is to ensure the safe and private storage of finances, without being victims of hackers. But, does the Blockchain really provide a private method for storing funds?
The Bitcoin Blockchain, as in most cryptocurrencies since then, represents the balance of a user through a series of transactions, and these transactions go back to the beginning of a chain of blocks. The nodes and miners of Bitcoin have the main function of proving the validity of each transaction, this is to ensure that no central entity can enter the system. Before a transaction is approved, all parties involved must reach a consensus, that is, reach an agreement, and this consensus is achieved without trusting one another. The operation of the Bitcoin Blockchain is enviable in all modes, except in the term of privacy.
Privacy is the biggest problem with cryptocurrencies. The Blockchain technology is a public database of all transactions made by its users. Anyone can have access to these blocks of financial records. It is an open book where you can trace the identity of the party making the transaction or the parties and the commercial volume. Virtually nothing and nobody is anonymous in the chain of blocks, so there is no privacy.

Source

What is Beam?
"Beam is a truly anonymous store-of-value coin". It is a decentralized platform oriented to maintain the anonymity of the user, improving scalability by omitting intermediate transactions that do not have a direct effect on the result. This also reduces the bulky size of Blockchain transactions, making them more portable. Beam achieves speed, scalability and privacy by using an improved version of the Mimblewimble protocol, which ensures that the entire Blockchain can grow to accommodate the massive adoption of cryptocurrencies. Beam has all the enviable operation of Bitcoin, however, privacy is completely guaranteed.
Mimblewimble is a new protocol developed and published in August 2016 by an anonymous author. This protocol provides an intelligent way to achieve a truly private and confidential Blockchain. It is named after the tongue-tying spell from Harry Potter, and is based on two concepts, viz-a-viz, confidential transactions and transaction cut. These concepts were originally proposed by Greg Maxwell.
Confidential transactions: these are implemented through the cryptographic commitment scheme. This scheme has two fundamental characteristics, which are hidden and binding. To understand these characteristics, we will use an example case: a man gives a gift to his beloved wife for her wedding anniversary. When the desired date arrives, he gives the key to open the box where the gift is, to show that his commitment to her is valid (binding), while the wife does not know that it contains the box until she opens it and can see its interior (hidden).
Transaction cut: a chain of blocks consists of different blocks, and in turn each block consists of a series of transactions, each transaction has its own respective inputs and outputs. Therefore, a block can be considered a large transaction that can be "cut". This means, the unification of all intermediate outputs that exist in a block. When this principle is applied to the entire chain of blocks, that is, unifying all the unified outputs of each respective block, a system is obtained that only needs the current state of the transactions instead of the entire transaction history from its origin.
"With this system, unspent transactions outputs (a transaction received by a user which has persisted in the blockchain) can be proved to belong to the receiving user via the value of the message and the value of the blinding factor. After creating the transaction, only the commitment is recorded on the blockchain; not the addresses of the users or the amounts exchanged."

How Beam works?
A typical transaction in Beam that involves a user A and a user B is done in this way:
Each user creates their wallets: these wallets represent new nodes connected to the system and signed by the participants using the Schnorr protocol.
Initiate a transaction: when a user A sends a transaction to a user B, a transaction block is created and executed using the Pedersen Commitments. The transaction block contains rates and the difference between the blindness factors of the parties that carry out the transaction. To ensure that the transaction is a positive value, a range test is included, the system contains a way to verify the transaction values in a confidential manner to prevent the user from creating transactions with a negative value.
Verification of transaction: to validate a new transaction that is the current state, the header of the previous block is stored. This header contains the validity test of the most recent transaction and proof of work to correctly indicate the correct header string.
Mining: once the validation is successful, the transaction is scheduled for mining. Each mined transaction is validated again by the node and distributed to the system.
Mined transactions transferred to the receiver: after validation by the node, the block extends the entire chain of blocks and creates the current state to which a new transaction will be linked once connected to the node.
The entire process is illustrated in the graphic below:
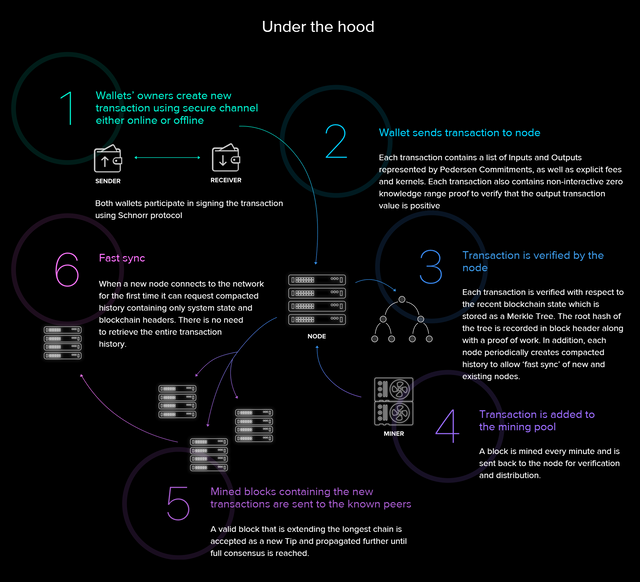
Source

Beam Use-Case
Ernesto is a successful investor and philanthropist. He grew up among orphanages and foster homes until he was old enough to go to college to study finance.
As a consequence of his accident childhood and youth, Ernesto has been anonymous benefactor for some years of a children's hospital, however, he lives constantly with the fear that his identity may come to light, losing his anonymity, in addition to the amounts of your contributions.
One day, his secretary suggested using Beam, which would allow him to continue with his charitable works without his address and identity being known, because confidentiality is a value much appreciated in his charitable works.

Advantages
- User in Control (Anonymity)
- High End Performance and Scalability at an Enviable Level
- Sustainability
- Usability
- Compatibility
- True Privacy
- Versatility

The Leadership Team

Source

The Engineering Team
Source

Advisors

Source

Finally, I want to share with all this introductory video about Beam:
Source
For more Information & Resources:
- Beam Website
- Beam Position Paper
- Mimblewimble Paper
- Beam YouTube
- Beam Telegram
- Beam Facebook
- Beam Twitter
This is an entry for the OriginalWorks Sponsored Writing Contest: Beam, you can participate by clicking here: CONTEST RULES Thanks so much to @originalworks for this Contest.
Twitter Bonus Click

This post has been submitted for the @OriginalWorks Sponsored Writing Contest!
You can also follow @contestbot to be notified of future contests!
@manuelgil64 upvoted this post via @poetsunit
Poetsunited - DISCORD - @poetsunited - witness upvote)
Congratulations! This post has been upvoted from the communal account, @minnowsupport, by manuelgil64 from the Minnow Support Project. It's a witness project run by aggroed, ausbitbank, teamsteem, someguy123, neoxian, followbtcnews, and netuoso. The goal is to help Steemit grow by supporting Minnows. Please find us at the Peace, Abundance, and Liberty Network (PALnet) Discord Channel. It's a completely public and open space to all members of the Steemit community who voluntarily choose to be there.
If you would like to delegate to the Minnow Support Project you can do so by clicking on the following links: 50SP, 100SP, 250SP, 500SP, 1000SP, 5000SP.
Be sure to leave at least 50SP undelegated on your account.
Great entry, good luck in the Contest!
Thanks @imagen!
Excelente amigo. Tienes mi apoyo.
Gracias por tu apoyo. Saludos @jonelescalona.