MEET "IAGON" - OPEN SOURCED CLOUD COMPUTING AND STORAGE SERVICES PLATFORM
What is IAGON?
IAGON is a stage for bridling the capacity limits and handling intensity of different keen gadgets over a decentralized Blockchain/Tangle network. IAGON uses and empowers putting away huge information, documents and archives, and also smaller sizes of records, and completes complex computational procedures, for example, those required for man-made brainpower and machine learning activities. IAGON works a completely secure and scrambled stage that coordinates block chain/tangle, cryptographic and Artificial Intelligence (AI) advancements in an easy to understand way.

Under IAGON's stage you can envision an existence where anybody can benefit by joining a monstrous preparing lattice. IAGON will give a completely robotized stage to doing the capacity and preparing undertakings of clients based on unutilized capacity and handling limits that are contributed by the "diggers". The excavators will have the capacity to change over the tokens back to fiat cash, to aggregate them or to pay for comparative administrations that they require with the tokens. For every exchange, IAGON will charge 10% commission and whatever is left of the tokens will be exchanged to the excavator. This decentralized cloud stage will work two lattices, i.e. a capacity matrix and a preparing framework. The two lattices work on a Blockchain stage fueled by Machine Learning capacities to upgrade the portion of errands and records to mine workers.
IAGON, oversees corporate and individual uses; Allowing a money related practicality of the task is incredible conditions. Advancing the upsides of sharing assignments and this is the embodiment of arranged PCs, mitigating chip away at the subject of innovation and everything that this prompts their advance, and making frameworks must have the capacity to work with the minimum human control conceivable.
Introducing IAGON VIDEO:
How IAGON will change the cloud computing business:
As we all know that Cloud is transforming the world in one way or another. The market size of cloud services is expanding; similarly, the demand for sophisticated storage capacities and computational processing capabilities is also rising. Right now, this market is captured by four prominent players—Google Cloud, AWS, IBM, and Microsoft. These cloud service providers use centralized storage and processing facilities, and that’s how they will become less trusted. These service providers successfully eliminate any competition because they have a huge client base. They manage to attract more clients just because they’ve substantially invested in data centers, storage facilities, and servers.
.jpg)
With IAGON, the emergence of two tech trends—AI and big data—the storage and processing demands will rise to a whole new level. This rise may not be efficiently managed by big players because they rely on centralized resources. That’s exactly where a need will be born to revolutionize web services and cloud markets—a revolution that’ll be built on a completely decentralized grid of processing power and storage outlets.
How businesses benefits from IAGON:
IAGON’s major aim is to revolutionize the cloud and web services market by offering a decentralized grid of storage and processing. By joining the unused storage capacity in servers and personal computers and their processing power, we can create a super-computer and super data center that can compete with any of the current cloud computing moguls.

We aim at providing companies and individuals storage and processing services at a fraction of the market prices and at a better security level by connecting data centers, business computers and personal users and utilizing their free storage capacities and their CPU and GPU processors during idle times. Doing so, IAGON overcomes the entry barriers imposed by the high level of investments required to compete in this market. Our token-based economy is based on computer, server and data center owners who join the storage and processing power grids. In return for sharing the capabilities of their machine, they will be granted IAGON tokens that can be traded back to fiat money.
How will IAGON impact on AI and Big-data industry:
The idea that’s driving IAGON is quite revolutionary because it’s putting AI at the heart of blockchain. The platform will join up all the unused storage capacity and processing power of personal computers and servers. In this way, the ecosystem will create one big supercomputer and a huge data center. With a super-powerful data center and hi-speed computer, the platform is actually well-equipped to compete with every single market mogul out there.
addition, this crypto project wants to tackle the rising issues of cybersecurity by reducing the number of hacks that target every other Big Data–empowered database. As large companies’ databases are getting hacked, the need for a cloud that can safely store data is growing every day. (This growth accelerated even faster when the news of the latest US elections being potentially hacked by Russians came out.)

IAGON’s answer to this is the native Secure Lake. This is a form of cloud that’s based on blockchain. Now, this cloud is so special because it has become unbreakable due to foolproof encryption. The encryption works extremely well for file slicing and even storing anonymous, small strongly encrypted slices. As a result of this high-level encryption, the protection of data files is complete. As the blockchain relies on high-end integration, it even protects databases of a range of sizes.
MARKET OUTLOOKOFCLOUDSTORAGESERVICES:
Cloud data storage is based on the delivery of fles from local computers and servers into the remote
servers and storage facilities that are obscure to the user, but can be accessed and managed at any time.
Thereby, the reliability of cloud storage services and the privacy of users (i.e. protecting the fles from being
accessed by any party other than their owner) are paramount to subscribing to and implementing any cloud
services.
The market of cloud storage services is composed by a large number of companies that operate and offer
data storage programs, from small data centers who cater to the needs of individuals and SMEs to large
storage facilities of companies (such as Amazon, Google and Microsoft), aiming at managing their own
gigantic volumes of data, but also offered to external customers. However, since the frst days of cloud
storage services and until recently concerns over the protection of data, the reliability of centralized data
centers, the liability of cloud storage companies in cases of lost or incorrectly stored fles and the privacy of
users are often expressed by experts (see for example Hu et al., 2010; Dai et al., 2017).
Faults associated with technical performance of the cloud emerge from its servers, from retrieval systems
(Content Distribution Networks, or CDNs) and from clients. Some are faults are defned as crash faults while
others are performance-degrading faults. Crash faults are the most common category, categorized by
service “blackouts”, whereas services that are temporarily disabled or exhibit lower degrees of performance
are performance-degrading faults. For example, an incident in which fle that were uploaded to the cloud
are not accessible due to writing errors to a folder is a crash fault, while CPU leaks that cause lower performance
of a server (and therefore slower retrieval of a fle) are performance-degrading faults (Wang, 2017).
When data and fles are managed through a centralized data centers (or through a series of them), a wide
scale fault, and in particular a crash fault that terminates the access of users to their stored fles, can cause
the termination of operations of companies, organizations and individuals as long as the outage persists.
For example, AWS’ recent outage in March 2017 continued for several hours, causing damages that are estimated
by more than 300 million USD (Sverdlik, 2017).

IAGON’S AI-BASEDCOMPUTATIONALPROCESSES:
Just like a human brain, AI and machine learning algorithms require inputs of data to deduce an inference.
Data mining is the computing process of discovering patterns in large data sets and helps reduce large sets
of data structures to allow machine learning algorithms to make decisions and inferences. Consequently, as
organizations and companies accumulate large datasets as a part of their day-to-day operations virtually on
every aspect of their performance , suppliers and clients , they seek new ways to apply AI and machine
learning methods to derive new managerial insights from the data on a continuous basis.
Nonetheless , AI and machine learning tools for analyzing vast amounts of data require large volumes of
computational power that organizations often lack, hence requiring them to subscribe to a commercial cloud
service and uploading their sensitive data fles into another company ’s servers . Due to the confdential
nature of data and its commercial value , many companies avoid doing so, hence not beneftting from the
potential value of analyzing their databases with advanced AI methods.
The Blockchain technology provides a unique and fully secure solution towards processing, storing and
distributing data and maintaining their consistency and integrity that can be used for use cases like
decentralized processing . The Blockchain is simply blocks of data hashed together and chained
using previous hashes and its current block to maintain consistency across the chain (Viayan , 2017 ).
Blockchains use the SHA 256 algorithm to create a hash. The unique nature of the hash makes its
resource intensive to crack as the SHA 256 hash can only be broken today through brute force with
computational power that is not avail- able yet in the commercial hardware market (Viayan, 2017).
Distributed data mining of large datasets was introduced by the SETI Institute through its BOINC program
(Estrada et al., 2009). The introduction of ‘Bitcoin’ and the proof of work mechanism allowed a framework
for providing incentives to data miners for work and energy to accomplish a large series of computations
expanded to process data over a decentralized network (Nakamoto, 2008).
There are many projects ongoing in terms of providing secure storage over a decentralized network.
A decentralized storage network is defned as a cloud platform where nodes either store a part of the data or fle
or the entire chain of data in a blockchain. Some of the more well-known names in this space are FileCoin,
IPFS, SiaCoin, Storj, NextCloud, and NEM’s Miin project (see e.g. Protocol Labs, 2017). Reliability and privacy
on a decentralized network can be a major issue. Most decentralized networks are not equipped to recover
lost data in the event the hosting node experiences hardware crashes or nodes with malicious intent confgure
fles in order to hack the fle recipient (a common problem that plagues torrent).
IAGON was built not only to serve the decentralized network but also work with current data storage facilities
like SQL and NoSQL databases . The approach taken with IAGON is unique to the point that IAGON
utilizes is machine learning algorithm to distribute load across a decentralized network for processing and
then encrypts/decrypts data which fows through its system.
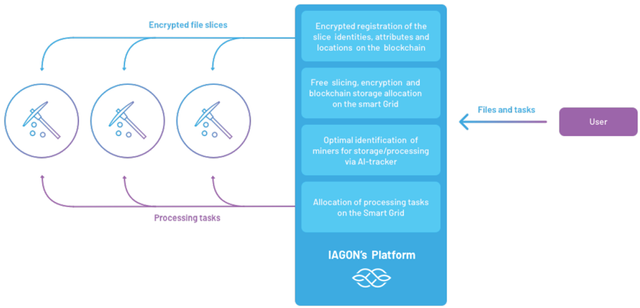
There are many use cases that IAGON can serve. IAGON can provide secure storage over centralized, clustered
or decentralized networks, distribute data processing load across its network of data miners for data
analytics, provide a secure solution for creating smart contracts over the Blockchain, or serve to identify
honest and attacking nodes within a system.
8IAGON’S MULTIPLEBLOCKCHAINS
How does IAGON work?
The platform is fueled by AI. In actual fact, it is connecting services and users through one big, robust, decentralized app or DApp. This app is well programmed and is quite easy to use across every available smart device. The platform is so intuitive that it won’t matter if the user is a simple person or a corporate organization.
1 – The core developers working on this platform have engineered it to be quite a secure cloud ecosystem.
2 – Through its highly innovative framework, IAGON is creating a one-stop platform for delivering decentralized cloud-based solutions.
3 – By using high-end machine algorithms and neural networks with AI, this blockchain-based network will definitely rewrite the future of the cloud.
4 – In addition, the ecosystem will allow the integration of DApps to expand its functionalities.
5 – The best part is that since it’ll be based on blockchain, this platform will be 100% trustworthy when accessed by any smart device.
6 – The team has definitely managed the issue of accessibility quite well. Being the system’s foundation, mining is one of the most crucial ways to create revenue with IAGON.
7 – By providing the network with their idle storage capabilities and processing power of their systems or servers, the users will generate revenue for themselves.
8 – The system leverages smart contracts that’ll allow anyone to build their personal form that’s simple to use.
9 – The best part is that the creation of such a form won’t ever require any understanding of programming.
10 – The decentralized network underlying the system is completely proprietary, secure, and unique.
11 – With the help of its blockchain, the network will deliver encrypted distributed storage services that use advanced sharding protocols.
12 – The blockchain powering this ecosystem is hybrid and uses Tangle technology.
13 – As a result, this ecosystem will definitely transform the way data is stored and how processing is done in the future.
This platform will offer secure storage over any clustered, centralized network. Plus, since the ecosystem will have its own network of data miners, data processing will be quick and well-distributed.
IAGON’S SECURE LAKE TECHNOLOGY:
Hacking a Data Lake of any organization exposes it to unlimited number of security, privacy and fnancial
risks, from online publication of private information of clients, through use and sale of suppliers and
commercially sensitive data to trading trade secrets, internal correspondence and digital goods (such as source
code and designs of new products).
The vulnerabilities as well as the hacking possibilities of databases of Big Data and Data Lake infrastructure
are publicly posted online, mainly warning organizations against security breaches that may rise due to use
of these platforms.
Few examples from the recent years illustrate the broad scope of threats and risks to organizations (as well
as to their customers and suppliers) that result from hacking their IT systems and databases:
.jpg)
• In January 2017, Camarda (2017) reported that "Hadoop attacks followed ongoing attacks
on MongoDB, ElasticSearch, and Apache CouchDB. In some cases, criminals have been know to
clone and wipe databases, claiming to hold the originals for ransom. In other attacks, they have
simply deleted databases without demanding payment".
• At the same period, Constantin (2017 ) reported that “It was only a matter of time until ransomware
groups that wiped data from thousands of MongoDB databases and Elasticsearch clusters start ed
targeting other data storage technologies ... 126 Hadoop instances have been wiped so far. The
number of victims is likely to increase because there are thousands of Hadoop deployments accessible
from the internet although it’s hard to say how many are vulnerable. The attacks against
MongoDB and Elasticsearch followed a similar pattern . The number of MongoDB victims jumped
from hundreds to thousands in a matter of hours and to tens of thousands within a week. The latest
count puts the number of wiped MongoDB databases at more than 34 ,000 and that of deleted
Elasticsearch clusters at more than 4,600.”
• Claburn (2017) indicates that the actions of the attackers on Hadoop based systems “may include
destroying data nodes, data volumes, or snapshots with terabytes of data in seconds”.
• Earlier reports explain how to hack into Hadoop systems and to exploit their vulnerabilities to
destroy of copy large volumes of data (see for example Gothard , 2015). Given the nature of the
vulnerabilities exposed , and those that have not yet been exploited by attackers, but may exist
in the systems , as well as the lack of policies of ongoing cyber security auditing in many
organizations , databases at large are exposed to other parties , should they decide to apply
these intrusion techniques . The results for any organization can be catastrophic and have a
large magnitude of impact on its operations. To illustrate, the Equifax hack, reported in
September 2017, exposed the personal data of 143 million customers, causing a daily fall of 19%
in Equifax’s market value.
IAGON’s Secure Lake is based on the Blockchain unbreakable encryption technology, on fle slicing and storage
of small, anonymous and strongly encrypted slices of the original fles ensures the complete protection of
data fles, other types of fles (such as scans , photos and videos ) and databases of any size and ensures the
rapid retrieval and update of any stored fle. Except from the user who securely uploads a fle and has the
password (key) to retrieve and encrypt it, no one can read the contents of the small fle slices, encrypt, delete,
change , retrieve them, identify their source or even associate them with other fle slices that are generated
from the original , uploaded fle . IAGON ’s technology ensures that even when information systems are
breached in any way, the data and fles that they use cannot be accessed, deleted or modifed in any way.
CASE STUDY:
IAGON intends to bring decentralization into mainstream businesses and consumer markets. In order to
achieve this, IAGON was designed and built to integrate seamlessly into existing IT infrastructure without
the need for expensive resources to deploy.
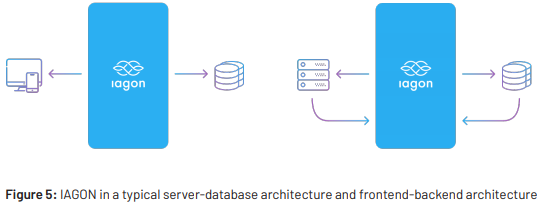
backend in existing IT infrastructure. IAGON can work with both SQL and NoSQL database structures
that are commonly used today without the need for expensive migration processes or specialized resources
to implement and deploy. IAGON provides a security layer because it identifes specifc digital fngerprints
associated with the request going through the server to identify if a request is an honest node.
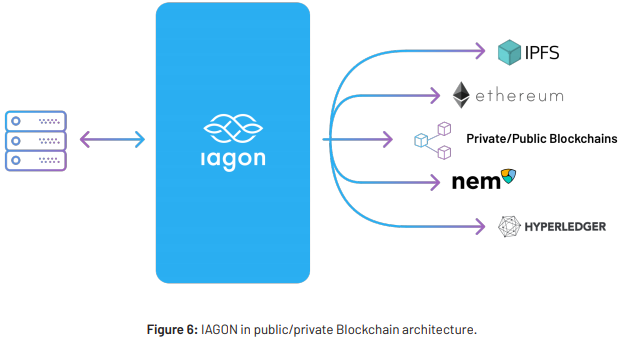
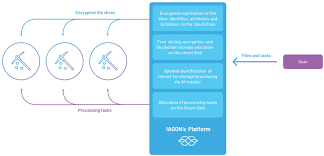
Figure 6 provides an overview of IAGON in a private and public Blockchain network. It serves as a layer
to allow data to be securely stored within both private and public blockchains. Using machine learning
algorithms and encryption/decryption protocols, IAGON is able to provide a secure method in storing
data across platforms.
IAGON can be configured to serve not only as a secure platform to integrate with existing blockchains but
also utilize its data mining feature to process data. IAGON scales by distributing processing load across a
decentralized network and securely stores data the across different decentralized platforms. This is done
through IAGON machine learning algorithm that works to distribute the data based on the task it is required
to undertake.
ARCHITECTURE:
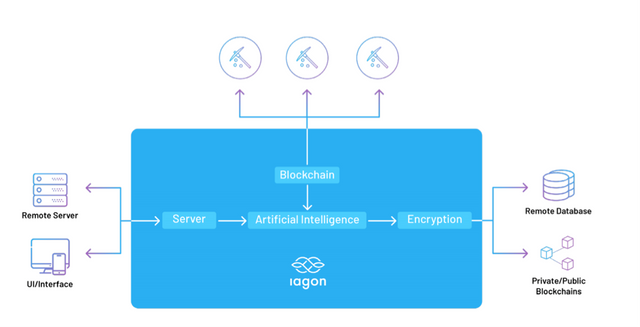
The architecture of IAGON ’s Open Source platform can be broken down into three unique sections. The
sections are the machine learning algorithm , the Blockchain and miners , and the encryption/decryption
protocol . When a request is sent to IAGON, the machine learning algorithm sends blocks of data over to the
miners to process and fnd for matching signatures . These blocks of data are then sent back to be validated
over the blockchain along with an output which the machine learning algorithm will use to identify a node.
It will be impossible to identify a node without processing the data in multiple blocks and to identify
a correlation thus this provides a level of anonymity and privacy to the users utilizing IAGON’s platform.
Individual miners will not beable to identify a certain request or node unless they have access to enough blocks .
Blocks are distributed evenly to miners by utilizing proof of variance and does not store any
of the data within their local systems . This allows data to be process anonymously
without being able to identify any single node individually except through the machine learning
a l g o r i t h m . I n a d d i t i o n, M i n e r s a r e i n c e n t i v i z e d to p r o c e ss t h e d a t a q u i c k l y to e a r n
rewards , as such it would not be ideal for miners to actually spend time , energy and money to try to store or
process the data.
The Blockchain allows data to be broken down into blocks and sent across nodes. The hashing algorithm
utilizes SHA 256 and hashes each block with its previous hash to create a chain . When data is received
back from an individual node, the data output will be matched against the hash of its corresponding block
and validated against its header to determine if the output data is valid. This way of processing provides a
unique method towards distributed processing as it provides a layer of integrity to the data being
processed and to determine if the output has been tempered in any way. In the event any of the miners
have manipulated the data in anyway, the returning block will be rejected and the block will be sent over
to a different node to be reprocessed . Miners receive incentives based upon the number of processes
they perform – in simple speak, the more data they process the bigger the incentives.
The encryption and decryption protocol allows for secure storage of data within any external or internal
platforms. This provides a unique approach towards decentralization as any external platform with an API
can simply be integrated to IAGON’s platform to utilize its services. What makes IAGON unique is the fact that
IAGON is able to integrate seamlessly with current database architecture including SQL, NoSQL, Big data
databases, private Blockchain, hyperledger, or any public Blockchain or decentralized network.
REINFORCEMENT LEARNING:
IAGON is an AI that learns over time. To achieve this, IAGON learns through a method known as reinforcement
learning. Reinforcement learning is the science of decision making to handle a dynamic environment. This
means IAGON undergoes an active learning process to optimize its decision making process
to determine its course of action. This creates and unparalleled paradigm towards how IAGON handles its
input. Using a method known as Markov Decision Process that is based on probability theory, IAGON tries to
determine an optimized form of reward system that improvises its actions to maximize its reward system
over time.
The Markov Decision Process can be describe using the following algorithm:
• S, a set of states of the world
• A, a set of actions
• R, the expected reward from a state and action
• , expected reward for transition from where some action is taken
• Rules to describe the observation the agent makes
The end goal is pick actions that maximizes future rewards
Markov state is unique in its approach because it bases decision making of the future independent of the
past given the present (David Silver). This is represented by the information state (a.k.a Markov state) if and
only if:
P[ st+1 st ] = P[ st+1 s1………,st ]
The information state proves that if the present state of a system is known, then the historical actions need
not be considered as the results of the future will be independent to the historical state.
BLOCKCHAIN:
.png)
IAGON leverages the Blockchain technology to maintain honesty of nodes across IAGON distributed data
mining algorithm. The Blockchain uses SHA256 algorithm of previous blocks to maintain a chain link to its
historical state (in this case data).This allows IAGON to incentivize miners on its platform to process data
honestly and to guard against deliberate manipulation of the data output. Using the Blockchain, IAGON ’s
machine learning algorithm can quickly identify if a data output mined from a block is actually a valid part of
the block. This can be achieve within the framework of a simple Blockchain similar to that used by «Bitcoin» by
hashing the inputs with the hash of the previous block. Genesis block are created internally within the
private blockchain. The Blockchain presents a unique approach towards sharing data across a
decentralized network. The data can be stored, processed and validated by a network of nodes or it can be
stored and validated within an internal facility where the processing is outsourced to a decentralized
network of nodes . The Blockchain allows consistency to be maintained throughout the entire data structure.
One of the major reason the Blockchain is maintained privately is to compete with big data databases in
the market in terms of volume , variety and velocity . A private Blockchain allows for the research,
development and facility cost to be borne by IAGON’s team with input from various stakeholders as oppose
to getting multiple parties to reach a large enough consensus before making big development changes to
improve the system . In order to keep up with massive read and write operations within its private
Blockchain , IAGON might in the future scale to introduced multiple private Blockchains to reduce the
potential of a single point of failure which can bring the down whole system by using a masterless architecture.
MINING ALGORITHM:
IAGON does not use the Blockchain like other cryptocurrencies. Even its use case approaches data processing
in a more conventional method hence using a POW (proof of work) or POS (proof of stake) mechanism
to reward a particular miner for discovering a particular block is not a viable solution. Hence IAGON uses its
own mechanism for determining miners’ contribution and processing speed using a method know as proof
of variance . Proof of variance classifes each miner based on their contribution into a pool. Miners within
the same pool then compete which each other. Miners from lower pools get upgraded or downgraded based
on several factors but the two main factors are speed and amount of data miners are able to fnd. Proof of
variance uses a combination of algebraic theory and probability functions to compute a miner ’s
contribution and which pool the miner can be classifed under. This allows for newer miners to proft from
mining data and increase their processing assets exponentially while miners investing more into their
assets can obtain an immediate return on their investment. The probability theory utilizes both discrete and
continuous functions and results of mining change over time.
Block Imaging: Block imaging is the method in which certain subset of the Blockchain is imaged or copied
to be randomly distributed across the node. An image of the block sent to nodes will mean the Blockchain
does not undergo any sort of permutation and remains immutable . Theoretically , randomly selected
blocks are branched and distributed to nodes for processing . The imaging algorithm is a suitable method
that is scalable to solve arbitrarily large problems by using distributed nodes. To create the algorithm for
block imaging, we assume that and are block separable:
IAGON #ICO
TOKEN SALE AND OPERATIONS:
The IAGON Pre-sale begins on May 27th, 16:00 CEST and lasts for 30 days. Pre-sale will be done
through IAGON website - https://iagon.com.
The Pre-sale offers 20% of the tokens at a price of:
• 0.06 USD per IAG token - for contribution > 25 ETH;
• 0.07 USD per IAG token - for contribution > 10 ETH;
• 0.08 USD per IAG token - for contribution > 5 ETH;
• 0.09 USD per IAG token - for contribution > 0.1 ETH;
The ETH price is the equivalent of 1,000 USD.
Individuals who participated in the Dragonchain pre-sale will have the right to buy according to their DSS
score, which will be locked according to when the previous contribution was made and pegged ETH price.
Otherwise, they can take advantage of the new prices. Purchases can be made in ETH.
The IAGON crowdsale (Token Sale ) begins on July 7th . Token sale lasts for 30-60 days, depending on sale.
In addition to the Pre-sale, the crowdsale offers 50% of the IAGON tokens to the public (offering in total
500,000,000 tokens).
Purchases can be made via all ETH according to the following rates:
• 0.12 USD per IAG token fo all 500 million tokens
Total amount of IAG tokens for two phases: 700,000,000 tokens.
Other 30% of the tokens (max. 300,000,000 tokens) will be dedicated to: 10% for IAGON’s team
10% for advisors and bounty hunters; 10% for development.
Team tokens are allocated by the following:
• First taking out the performance related tokens for team members.
• Then remaining tokens will be distributed to co-founders: Dr. Navjit Dhaliwal (65%),
Dr. Elad Harison (25%), Dr. Claudio Lima (10%)
• 70% of team tokens are locked until mainnet launch (Q1 2019)
• CEO's (Dr. Navjit Dhaliwal) tokens are locked in following way: 30% for one year and 70% for two years.
ROAD MAP:

IAGON Partners:
.png)
THE IAGONTEAM:



for more information
• https://www.iagon.com/
• https://www.reddit.com/r/iagon/
• https://www.linkedin.com/company/iagon/
• https://steemit.com/@official.iagon
• https://medium.com/iagon-official
• https://t.me/Iagon_official
• https://bitcointalk.org/index.php?topic=2945888.0
Twitter link:
https://mobile.twitter.com/jeniferEva2/status/1020951800373919744?p=v
IAGON 2018
This post has been submitted for the @OriginalWorks Sponsored Writing Contest!
You can also follow @contestbot to be notified of future contests!