IONChain. Facilitating an Internet of Things Economy.

Introduction
Nowadays it is known that the internet of things or IoT, is the main key to the new generation of information technology, and in this publication we will see how IONChain, solves a series of problems that this technology presents, in terms of security, transmission and sharing of data, using blockchain technology to create an ecosystem that will convert the IoT not only into a network of mining devices, but also into a new trend, where the value of information can be quantified, shared and transferred, thus expanding the IoT to the next level of development, both for the consumer and for business.

IOT: Internet of Things
Even though it is an abstract concept, the internet of things is an idea that has gained popularity in recent years and as the name implies, it is basically a series of everyday objects interconnected with the Internet.
The Internet of Things allows you to enhance objects that were previously connected by a closed circuit, such as cameras, sensors, communicators, allowing them to communicate through the network of networks or the Internet.
Not only objects now have new hardware that allows them to connect to the Internet, but also, these intelligent devices are able to be configured and programmed to fulfill and perform tasks sent remotely.
The internet of things is being applied in many other fields, such as the medical field (devices that allow patient monitoring), urban (traffic control, cctv), industrial (machinery, sensors, and robots). The internet of things, being an extension of the Internet, will eventually be combined with blockchain technology.
Weak points of the Internet of Things
Even though the demand for smart devices has increased both at the industrial level and at the consumer level, there are still problems that have not been solved, among them are:
No business model for the IoT industry. There is no defined business model for the industrial implementation of IoT. Generally, the model that is emerging is defined by the improvement of electronic components and artificial intelligence software, but there is a large gap in the application of a business scenario.
Lack of data security and privacy protection. IoT devices are constantly collecting information and data both industrially and individually, and all this data is stored by the companies in charge of these devices. Generally, users do not know or do not have control over the private data that is stored in these companies and unfortunately, these large information establishments are victims of attacks by hackers, who use or sell this information.
Lack of interoperability between platforms. As mentioned above, there is a great demand for IoT devices and many companies struggle to gain leadership in the manufacture of new devices. Creating new IoT data centers, isolated from each other, making it impossible to communicate with each other, not only because of fear of competition but also because of incompatibility between platforms.
The restrictions of cloud computing architecture. Cloud computing is the main medium of the IoT industry. However, it represents a medium that slows down interaction in real time, especially in applications such as VR, automotive devices, smart homes, etc.
IONChain presents a new technology called Edge computing, as an alternative to these problems.
Edge Computing
The Edge computing technology is an open platform that is presented as a solution for the existing problems in the IoT sector, in aspects of the real-time operation, data optimization, security and privacy, better connections, etc. The Edge computing technology represents an optimization of the cloud layer.
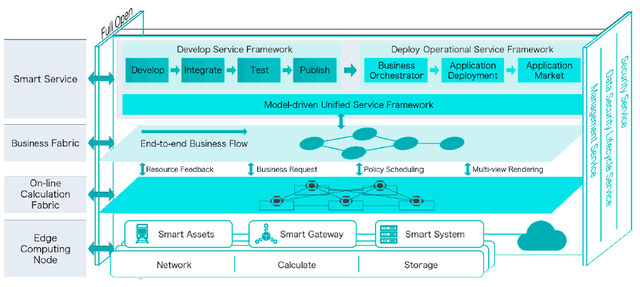
Source: White paper
Edge computing will not only solve the real-time response requests that IoT devices require, but also solve the privacy and data security protection problems presented by the traditional architecture of cloud computing technology.
Edge will allow users to have control of their data and allow defining the limits of access to the same, by third parties.
The main focus of the IONChain project is to ensure data security and facilitate circulation, sharing, and negotiation of data. For this, IONChain breaks the barriers of the platforms and establishes the connection between the nodes of the IoT network through the decentralized blockchain technology.
Thanks to Edge technology, IONChain introduces the concept in the IoT industry: each device is a mining machine. This means that each device connected to the IONChain network will be able to mine and receive remuneration through the "ionization algorithm". In this way, IONChain will encourage small and medium entrepreneurs to join in the development of IoT projects.
One Device, One Coin, One Code
The IONChain team creates the concept of "One Device, One Coin, One Code" from the premise of integrating all existing IoT infrastructures, as a single "device", controlled with blockchain technology, which will not only allow remuneration of "one currency", through the mining process, but also create a unique "code" for the IoT devices that are part of the IONChain network. In this way, the data generated by each IoT device can be stored in the ledger in a unique, reliable and traceable way.
IONChain will also make use of IPFS (Inter Planetary File System) to allow the massive information generated by IoT devices to be stored in an encrypted and distributed way, thus solving the problems of data block size and transaction speed and ensuring security. and data protection against theft or modification without authorization.

Technical Architecture
IONChain uses the Ionization Algorithm to separate the two main functions of the blockchain: the creation of value and the transfer of value. This algorithm is designed to make it possible for each IoT device to become a mining machine, allowing you to create value constantly; however, this value created depends on the type and function of the IoT device.
Thanks to the ionization algorithm, the value creation process is responsible for "translating" the values generated by the different IoT devices into a unified standard expressed in IONC tokens.
The value transfer layer will allow the sending and receiving of values created within the IONChain ecosystem.
A. Value Generation Process
The process of generating value consists of four layers, which are: creation, verification, evaluation, and confirmation of value.
A.1. Value creation
The value creation layer is the combination of the IoT devices connected to the IONChain network and Edge computing centers. Since the IoT devices lack the necessary computing capacity to calculate the created value, they load the information to the mining machines, which are responsible for calculating the value through the algorithms of Data Quality Proof and Time Lapse Proof. Once the value is generated, it passes to the verification layer.
A.2. Value verification
This process is similar to the consensus algorithms of the blockchains. Interested parties in the data provided by the IoT devices must cooperate to complete the value verification. Upon completion of the process, this value is transferred to the evaluation layer.
A.3. Value evaluation
This layer represents the second level of verification and fulfills the function of verifying the authenticity of the value. This layer allows the IONChain system to counteract the double-spending attacks.
A.4. Value confirmation
This layer is responsible for packaging the verified value and using it within the IONChain ecosystem as digital currency (IONC token), forming part of the transfer layer of the blockchain value.
B. Value Transfer
The part of the transfer of value within the IONChain ecosystem architecture is made up of six layers: application, service, IONChain protocol, smart contract, blockchain and data storage.
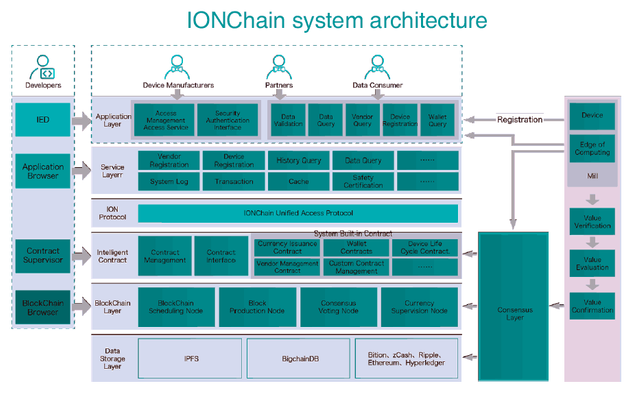
Source: White paper
B.1. Application layer
The application layer is the access layer to the IONChain interface. It consists of APIs based on the HTTP protocol. It provides the verification function of both the IoT devices and the vendors. The system includes services of data validation and query, vendor query, device registration, and wallet query.
B.2. Service layer
The service layer is only available for internal components. This layer adopts the gRPC protocol. The interface used by the layer is a program and is also responsible for providing authentication, flow control, bidirectional streaming, cancellations and timeouts.
B.3. Protocol layer
This layer provides a unified access protocol, which includes the consensus protocol, the network protocol, the monetary exchange protocol, among others. The IONChain protocol will be a common protocol for all third-party applications.
B.4. Smart contract layer
This layer represents the connection bridge between the blockchain layer and the application layer. The smart contract layer, in turn, is divided into two parts: contract administration and contract interface. The first is responsible for the installation, debugging, implementation and commissioning of the smart contract. The second is the interface for external systems.
The smart contract layer already contains a series of system contracts defined to perform specific operations within the system, such as: Currency issuance contract, which is the core of the IONChain and is responsible, as the name implies, for the monetary issue. Wallet contract is used to manage the user's wallet. IoT device lifecycle contract defines the life cycle of the IoT device, includes the loading of information to the chain, activation, and elimination, among other actions. Manufacturer management contract, like the previous one, this contract is used to maintain the information of the manufacturer of the equipment, including the loading of the information to the chain, circulation of information, etc. And, finally, Custom Contracts Manager tool, which allows the user to develop and manage their own contracts.
IONChain provides an intelligent contract engine, which allows all kinds of operations through intelligent contracts. The management of the contract depends on the IPOS consensus algorithm (own of IONChain) and the intelligent contract of the system have greater authority than the user contracts, and that these require a multi-authorization to execute.
B.5. Blockchain layer
This layer represents the core of IONChain and the consensus algorithm is the most important part of the layer. IONChain creates the IPOS consensus algorithm, such as an improved version of PoW and PoS, which is better suited for the requirements of IoT devices. The IPOS algorithm is divided into two parts: the party that chooses the block producer group and the production schedule. The algorithm ensures that the control of the election is in charge of the stakeholders, who are the ones who have more to lose if the network does not operate as it should.
IPOS is robust in the face of any conceivable situation that could damage the operation of the network, even in the face of corruption problems. Unlike other algorithms, IPOS can continue to work when most producers fail. During this period, the community can vote to replace the producers of damaged blocks. IPOS uses a voting approval process that ensures that someone with 50% voting power can not select any of their own block producers. In addition, the algorithm is designed to optimize the performance of honest node participation by 100%. What gives you the power to confirm a transaction with a 99.9% certainty.
B.6. Data storage layer
IONChain provides two ways to store data in the blockchain: IPFS and BigChainDB.
IPFS allows you to store all types of information, regardless of its size and prevents it from affecting the speed of the transaction, allowing only the hash of its contents to be stored within the blockchain. In this way, the files whose names are derived from the hash can be recalculated to guarantee that they have not been modified.
Due to the data storage requirement requested by the IoT devices, IONChain chooses the IPFS system as the storage system.
IPFS can store smart contract data, transaction records, and other data; However, IONChain will need to store business data in the future and for this, it will use the BigChanDB system, as a data storage engine to support data research requirements. BigChanDB has advantages similar to those of the blockchain, such as decentralization, immutability, and asset registration and transfer.

Economic model
IONC is the official token of the IONChain ecosystem. The coin was initially launched as an ERC20 token. The maximum supply is 800 million and will be released during the next 20 years.
From the ecosystem point of view, the IONC token is the only authorized cryptocurrency and all IONChain ecosystem participants will be allowed to take part in the creation of value within the system. The mechanisms of reward through mining will increase the participation of users in the ecosystem, encouraging the use of many IoT devices.
IONChain will distribute rewards with IONC tokens to all users that generate and upload data from their IoT devices. The data and the privacy of the users will be based on encryption and anonymity algorithms.
From the business point of view, with the increase of data from IoT devices loaded to IONChain, the value of the ecosystem will be increased through the analysis of data and use cases related to AI. The companies will be willing to buy IONC tokens in order to pay for the services of analysis, search, and statistics of data stored in the chain.
Apart from this, there will be other situations that involve the use of IONC token, such as: as fuel to run DAPP in IONChain, payment commissions for IONC token transfers between system users, payment to developers, etc.

IONC token distribution
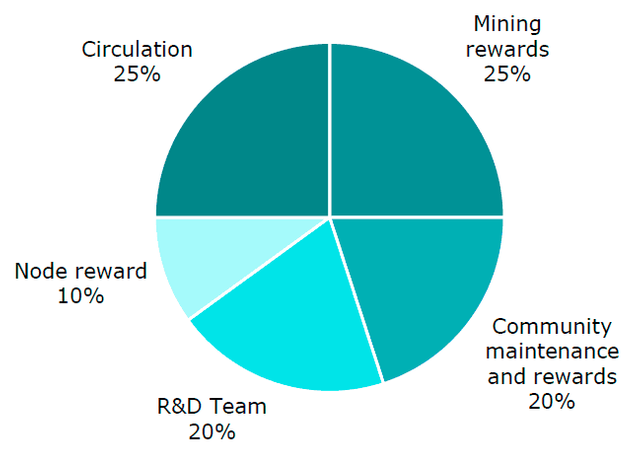
Source: White paper
Circulation. IONChain will give away IONC tokens as a community promotion, up to 25% of the total tokens issued.

Use-Cases: Application scenarios of IONChain
IONChain can be adapted to any field where the IoT device network works
Source: White paper
UC.1. Data security and privacy protection
IONChain uses decentralized and distributed storage methods together with encryption algorithms to ensure privacy and data security, to avoid external attacks or catastrophes.
Case 1: It is well known that there are cases where the activities and behavior of users when using smartphones or smart devices, are hidden from the network to be used and exploited by companies or other malicious entities. There are cardiology patients who need to charge devices that measure and record cardiac information for a certain time, to be analyzed by doctors. In the future, these devices could be part of the network of IoT devices of the IONChain ecosystem, which could transmit this information with the help of smartphones to the IONChain storage system in a safe way and with the authorization of the user, the medical staff could have access to said information to analyze the patient's health. Such information could also be sold within the ecosystem for researchers and pharmacists to measure the effectiveness of a medication on the health of the individual in general; benefiting all the participants of the IONChain ecosystem
UC.2. Exchange and circulation of IoT data
The processing of information and data in the traditional network of IoT devices is limited to its own value or platform. The exchange and circulation of data between different platforms become almost impossible, due to the different IoT device development platforms. IONChain will break this barrier, allowing the exchange and circulation of information as well as allowing the process to be monetized.
Case 2. B2B data exchange. The pharmaceutical company Vargas, makes use of the IONChain platform to access the information of the IoT devices from the transport network of the company MRW, to take control and monitoring of the chain of products exported by the branches of the pharmaceutical company to the dealers. The data transaction is carried out automatically through the smart contracts, thus the information will be delivered after the transfer of the funds is confirmed. Each of the packages contains an intelligent IoT device that has IONChain identification, which allows uploading information on the location of the same throughout its journey, including extra information on temperature, altitude, pressure, etc. Both companies benefit through the IONChain ecosystem.
Case 3. C2B data exchange. Small companies selling appliance spare parts need to acquire information on the performance of smart appliances. These data are monopolized by the manufacturers. However, through the incentive model of IONChain, users of household appliances will be able to exchange the data of their experiences when using them in exchange for compensation, automatically transferred to their wallets through smart contracts. Not only these small companies can obtain the data, but also data analysis that allows predicting the most relevant spare parts to keep them in their stocks and not invest in spare parts that could stay frozen in their inventories.
UC.3. Smart contract facilitates the sharing economy
IONChain not only supports data exchange but also allows the smart contract to be configured to automate certain operations in certain scenarios that allow the interaction and transfer of values between IoT devices.
Case 4. A small company that offers laundry service has recently acquired a new model of smart washing machines. With the help of IONChain, they can set up smart contracts to allow users to rent the washing machine services and pay for them automatically, using IONC tokens without the intervention of staff to collect the fees for use of the washing machine and without the need to involve any other type of currency or banking activity.
UC.4. Edge computing optimizing IoT user experience
Thanks to the technology called edge computing, typical of IONChain, certain applications of IoT that require response or interaction in real time can be realized.
Case 5. The security company WatchTower has decided to create a series of intelligent IoT devices that allow its users to transmit a signal of danger in case intruders enter their homes, in addition to these devices, they include a DAPP for smartphones that allows transmitting a distress signal to be taken care of in the surroundings of their homes. Given the success of the application and the growing demand of users in need of a security system has incremented the amount of security devices, these devices require real-time responses, however, the cloud system is not sufficient given its level of latency. Fortunately, the security company decides to be part of the IONChain ecosystem and use its edge technology, which improves the response times of the devices, in addition to allowing the automatic payment of the service through smart contracts.

Conclusion
It is inevitable that the blockchain technology and the internet of things combine to help manage the vast information that these intelligent devices generate on a daily basis. It is evident that IONChain is making this fact a reality, by creating an ecosystem that will help improve the internet of things network, taking it to a new level of development when combined with the blockchain. With its disruptive edge computing technology and its IPOS consensus algorithm, it will allow the creation of dAPPs, smart contracts, giving it a decentralized nature that will not only facilitate the transfer of information in a secure and transparent way between the different devices, but will also give it a value monetary intrinsic to the data through its IONC currency.

Annexes
* * * * * MY VIDEO PRESENTATION * * * * *
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *
Roadmap
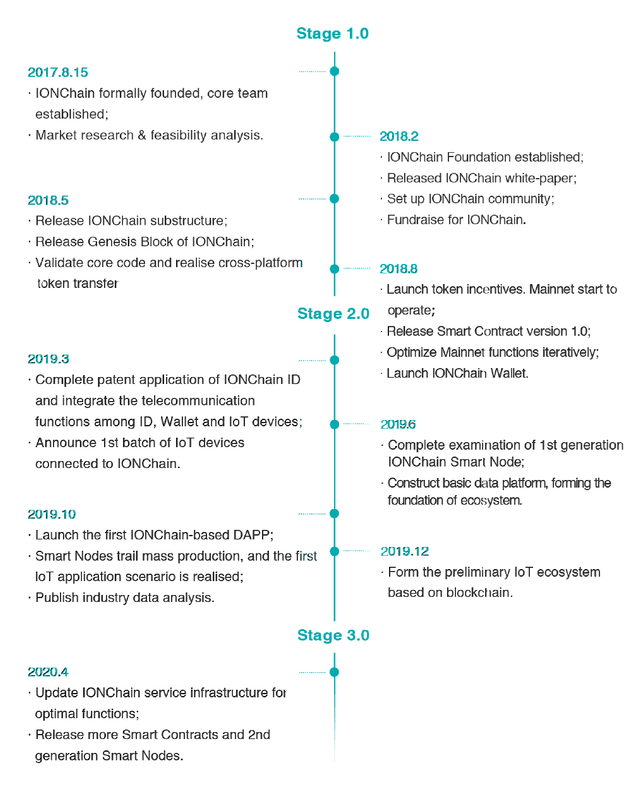
Source: White paper
Team





Consultants



Partners

More Information & Resources:
- IONChain Website
- IONChain Bitcointalk Explanation
- IONChain WhitePaper
- IONChain YouTube
- IONChain Twitter
- IONChain Medium
- IONChain LinkedIn
- IONChain GitHub
- IONChain Steemit
- IONChain Telegram
My Twitter Link

https://twitter.com/jadams2kx/status/1059936264345055237


If you want to participate in this contest, go to:
https://steemit.com/crypto/@originalworks/1300-steem-sponsored-writing-contest-ionchain-org
ionchain2018





This post has been submitted for the @OriginalWorks Sponsored Writing Contest!
You can also follow @contestbot to be notified of future contests!
You really did a good job.
Congratulation friend
Thanks, mate. You too!