IAGON: Changing The Clouds
INTRODUCTION
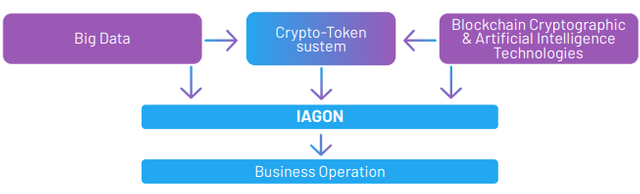
The recent development in Artifcial Intelligence (AI) and Big Data technologies and the dramatic increase
in adoption of these technologies signify an ongoing and exponentially growing demand to both storage
capacity and for computational processing power vis-à-vis the broader adoption of these technologies.
Big Data technologies such as the Hadoop framework (notably its MongoDB , HDFS and Spark databases)
require vast amounts of storage capacity, either in a centralized or a distributed manner, for processing
and managing Big Data fles. To a large extent, Big Data technologies support the exponential growth of
data in any type of organization , within web based services and social networks and their implementation
is essential to support the proper operation and processing of these vast amounts of data (see Fig. 1).
Machine learning and deep learning processes (notably Google’s TensorFlow, Caffe and Theano; see also:
Dean et al., 2012, Ray, 2017) carry out advanced computational pattern recognition, image recognition and
predictive analytics that require high volume of computations . The scenario of an exponentially growing
demand for both Big Data and AI capabilities is solid and highly tangible , given that both technological
areas are the basis to support IoT and Industry 4.0 systems . Additionally, though Big Data and AI
technologies are only at their infant stages of implementation, most of the corporates and public institutes
have begun examining their application to improve many aspects of their operations.
Introducing IAGON VIDEO
MARKET OUTLOOKOFCLOUDSTORAGESERVICES
Cloud data storage is based on the delivery of fles from local computers and servers into the remote
servers and storage facilities that are obscure to the user, but can be accessed and managed at any time.
Thereby, the reliability of cloud storage services and the privacy of users (i.e. protecting the fles from being
accessed by any party other than their owner) are paramount to subscribing to and implementing any cloud
services.
The market of cloud storage services is composed by a large number of companies that operate and offer
data storage programs, from small data centers who cater to the needs of individuals and SMEs to large
storage facilities of companies (such as Amazon, Google and Microsoft), aiming at managing their own
gigantic volumes of data, but also offered to external customers. However, since the frst days of cloud
storage services and until recently concerns over the protection of data, the reliability of centralized data
centers, the liability of cloud storage companies in cases of lost or incorrectly stored fles and the privacy of
users are often expressed by experts (see for example Hu et al., 2010; Dai et al., 2017).
Faults associated with technical performance of the cloud emerge from its servers, from retrieval systems
(Content Distribution Networks, or CDNs) and from clients. Some are faults are defned as crash faults while
others are performance-degrading faults. Crash faults are the most common category, categorized by
service “blackouts”, whereas services that are temporarily disabled or exhibit lower degrees of performance
are performance-degrading faults. For example, an incident in which fle that were uploaded to the cloud
are not accessible due to writing errors to a folder is a crash fault, while CPU leaks that cause lower performance
of a server (and therefore slower retrieval of a fle) are performance-degrading faults (Wang, 2017).
When data and fles are managed through a centralized data centers (or through a series of them), a wide
scale fault, and in particular a crash fault that terminates the access of users to their stored fles, can cause
the termination of operations of companies, organizations and individuals as long as the outage persists.
For example, AWS’ recent outage in March 2017 continued for several hours, causing damages that are estimated
by more than 300 million USD (Sverdlik, 2017).
IAGON’S AI-BASEDCOMPUTATIONALPROCESSES
Just like a human brain, AI and machine learning algorithms require inputs of data to deduce an inference.
Data mining is the computing process of discovering patterns in large data sets and helps reduce large sets
of data structures to allow machine learning algorithms to make decisions and inferences. Consequently, as
organizations and companies accumulate large datasets as a part of their day-to-day operations virtually on
every aspect of their performance , suppliers and clients , they seek new ways to apply AI and machine
learning methods to derive new managerial insights from the data on a continuous basis.
Nonetheless , AI and machine learning tools for analyzing vast amounts of data require large volumes of
computational power that organizations often lack, hence requiring them to subscribe to a commercial cloud
service and uploading their sensitive data fles into another company ’s servers . Due to the confdential
nature of data and its commercial value , many companies avoid doing so, hence not beneftting from the
potential value of analyzing their databases with advanced AI methods.
The Blockchain technology provides a unique and fully secure solution towards processing, storing and
distributing data and maintaining their consistency and integrity that can be used for use cases like
decentralized processing . The Blockchain is simply blocks of data hashed together and chained
using previous hashes and its current block to maintain consistency across the chain (Viayan , 2017 ).
Blockchains use the SHA 256 algorithm to create a hash. The unique nature of the hash makes its
resource intensive to crack as the SHA 256 hash can only be broken today through brute force with
computational power that is not avail- able yet in the commercial hardware market (Viayan, 2017).
Distributed data mining of large datasets was introduced by the SETI Institute through its BOINC program
(Estrada et al., 2009). The introduction of ‘Bitcoin’ and the proof of work mechanism allowed a framework
for providing incentives to data miners for work and energy to accomplish a large series of computations
expanded to process data over a decentralized network (Nakamoto, 2008).
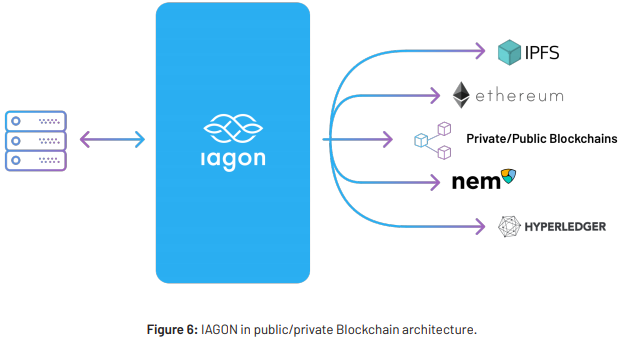
There are many projects ongoing in terms of providing secure storage over a decentralized network.
A decentralized storage network is defned as a cloud platform where nodes either store a part of the data or fle
or the entire chain of data in a blockchain. Some of the more well-known names in this space are FileCoin,
IPFS, SiaCoin, Storj, NextCloud, and NEM’s Miin project (see e.g. Protocol Labs, 2017). Reliability and privacy
on a decentralized network can be a major issue. Most decentralized networks are not equipped to recover
lost data in the event the hosting node experiences hardware crashes or nodes with malicious intent confgure
fles in order to hack the fle recipient (a common problem that plagues torrent).
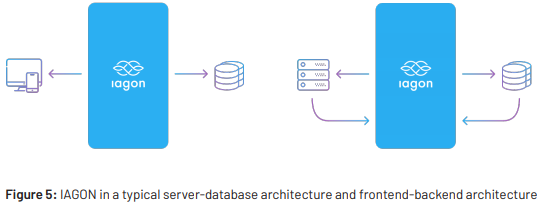
IAGON was built not only to serve the decentralized network but also work with current data storage facilities
like SQL and NoSQL databases . The approach taken with IAGON is unique to the point that IAGON
utilizes is machine learning algorithm to distribute load across a decentralized network for processing and
then encrypts/decrypts data which fows through its system.
There are many use cases that IAGON can serve. IAGON can provide secure storage over centralized, clustered
or decentralized networks, distribute data processing load across its network of data miners for data
analytics, provide a secure solution for creating smart contracts over the Blockchain, or serve to identify
honest and attacking nodes within a system.
IAGON Presentation at the Blockchain pre-Accelerator Bootcamp in Switzerland Video
IAGON’S SMARTCOMPUTINGGRIDPLATFORM
AND AI-TRACKERTECHNOLOGY
The increasing demand for processing power is evident for example by the growing sales of NVIDIA systems for
Machine Learning and Deep Learning operations , as well as other advanced operations of Artifcial Intelligence
that require vast volumes of computing and processing capabilities . The technology domain of AI based
innovations that require large capacities of processing power (mostly supplied by batteries of servers with large
amount of CPUs and GPUs ) include face recognition , video processing , voice analysis , text analysis, pattern
recognition in Big Data databases and digital document repositories , autonomous cars, IoT based decision
support systems and many more. AI technologies and applications are expected to exponentially grow over the
next years , thereby increasing the demand for processing power to support both research and their day-to-day
operations.
IAGON’s Smart Computing Grid is equivalent to any other power grid (such as solar production of electricity):
• It connects multiple producers to customers
• Smart Computing Grid fulfls the demand for the necessary resource
• It transfers unused resources to customers in need (CPU and GPU processing power and
storage space), and
• It benefts the miners providing processing power and storage space to the grid without
requiring efforts when their servers and computers are not used by them.
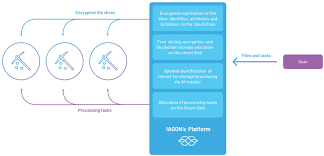
The Smart Computing Grid is based on advanced Artifcial Intelligence components that include more than 100
Machine Learning algorithms , methods and techniques that integrate to form our AI-Tracker system. AI-Tracker
is the “brain ” behind IAGON ’s Smart Computing Grid . It optimally allocates encrypted fle slices to the miners ’
free storage spaces and computational tasks to the miners ’ free (idle) CPUs and GPUs that compose the Smart
Computing Grid.
AI-Tracker is a dynamically learning system that continuously analyzes past and current data streams that
refect the availability of storage space and processing capacities of miners. AI- Tracker carries out the tasks of
optimally allocating and transmitting encrypted fle slices to designated storage spaces, allocation for
processing tasks for rapid , optimal performance of the grid and identifcation of rogue nodes that should be
blocked and removed from the grid and continuously fne tuning the grid ’s attributes to optimize its
performance at any time.
.png)
CASE STUDY
IAGON intends to bring decentralization into mainstream businesses and consumer markets. In order to
achieve this, IAGON was designed and built to integrate seamlessly into existing IT infrastructure without
the need for expensive resources to deploy.
IAGON intends to bring decentralization into mainstream businesses and consumer markets. In order to
achieve this, IAGON was designed and built to integrate seamlessly into existing IT infrastructure without
the need for expensive resources to deploy.
DATA MINING
IAGON takes a very different approach towards data mining. IAGON does this by utilizing a private
Blockchain with public network protocols over API networks. A miner does not need to store any of the data
in order to mine, the miner’s sole duty is to honestly process the data and send the output back to IAGON’s
machine learning algorithm for analysis.
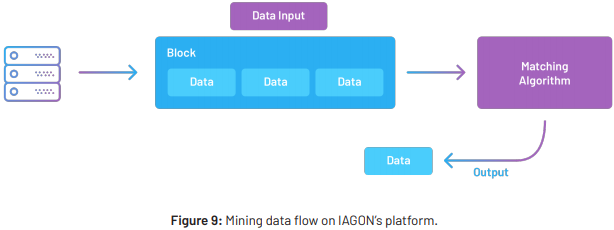
Data mining on IAGON ’s platform does not have the need to perform complex algorithm to solve an
equation. Instead, IAGON uses the decentralized computing network to distribute load and increase speed
for mundane data processing tasks . Block tasks are distributed to miners using the proof of variance
method . Miners will need to match the data signature from the data input and fnd its corresponding data
object in the block and return the data output. The miners do not need to store any of the data it processes,
and once the data has been validated to belong to the specifc block, the miner is considered to have mined
the block. The miner receives rewards based on the number of data points it mines, and if no data is found
within the block the miner does not receive any reward. This will incentivize miners to complete mining the
entire block and to increase the number of blocks they mine. The incentive mechanism discourages miners
from just mining a block until the frst data output is achieved because of the speed limitations associated
with network connections will prove to be uneconomical , as such miners will be encouraged for their own
beneft to completely mine the entire block to fnd all possible data points that matches the data input.
Blocks are generated at a bounded rate and there are no communication between miner’s clients.
The server connecting the miners to IAGON’s platform uses a multithreaded server to distribute and receive
results. Blocks are sent over HTTP-based protocols so that clients inside frewalls can connect to it. There
are two methods currently to approach block storage and removal from miner’s unit. The option would be to
process purely in memory provided by the random -access memory unit in a computer or introducing a
garbage collector program that effectively removes the block from disk. The mining client architecture
should allow it to run as a background process or a GUI application. To support different architectures , the
best approach would be to create multiple threads , where one thread does communication and data
processing while the other thread handle GUI interactions (Anderson, 2002). Proof of variance allows IAGON
to identify the typical speed at which miners take to process a block . In the event a miner is disconnect ,
goes ofine or does not complete computation on its block , the block is resent to other nodes in the network.
IAGON Storage Services
Cloud storage services allow users and companies to store data outside of their local machines. The purpose of cloud computing is to off-load the burden of maintaining local storage services.
For example, if an individual wants to run a website, there is no need for them to buy and assemble a server machine as well as run a dedicated internet service to maintain up-time. They can simply purchase cloud storage services and run their website from some kind of hosting service.
IAGON's storage services will ensure a high level of security by utilizing the slicing of data and military layer file encryption (SHA256). By splicing data and distributing smaller encrypted components of the whole, it is ensured that no single miner has access to an entire file.
The issue in the current market is that these cloud storage services are dominated by a few large players such as "Amazon, Google and Microsoft"[WhitePaper page 6].
IAGON will allow users to share their unused space in exchange for IAG tokens! Miners receive incentives based upon the number of processes they perform. In other words, the more data they process the bigger the incentives.
Assign the IAGON project a "Stable +” rating
The IAGON project is a modern decentralized cloud platform that supports both cloud storage services and cloud computing. Decentralization helps create a secure operation; this is still an issue for many potential customers when choosing from the large centralized platforms. The main stated innovation of the IAGON platform is its complete use of AI for more efficient grid management, which is an important step forward for the industry.
The IAGON project is presented by a strong team with undeniable competence. The project is headed by strong professionals with extensive experience in the technical sector. It is notable that the project is supported by a large number of advisors, and we hope that their expertise will help create a better service.
IAGON has positive feedback from the community arising from a balanced marketing campaign. The information presented in the documentation corresponds to best corporate practices. IAGON has an extensive financial plan that is fully published. The project team discloses a five-year P & L (with a monthly breakdown in the first year), a revenue structure, cash flows, a breakeven analysis, etc. Such a range of quantitative information is very useful for investors, as it enables increased transparency for the project and the team’s strategy.
The main risk for the IAGON platform is its powerful competitive environment. A major portion of the market is already divided between online giants, led by Amazon. At the same time, the market remains flexible enough and may be quickly restructured to meet the needs of customers.
In addition to the leaders in the centralized market, competition is also evident amongst blockchain start-ups. There are several well-known names the community has high expectations of, and IAGON still needs to position itself in the industry.
In such a dense competitive environment as has developed in the cloud services market, the time factor will play a decisive role, and quality and convenience will help retain customers on a specific platform.
IAGON is a open source cloud platform with an ecosystem connecting buyers and sellers of computer power. In fact, IAGON is a cloud platform for storing and calculating data. As an analogy, we can give an example of the well-known Google Cloud, Amazon Web Services, etc. The key differences of this project from such services are its p2p nature, decentralization and extensive application of AI.
Standard platforms provide their own capacities but recently the trend for a sharing economy involving the use of crowd computer resources has become relevant. The task of the IAGON platform is to bring buyers and sellers of these resources together. The platform is developed on a decentralized basis as a DApp; its architecture uses advanced AI technologies and machine learning, and the core is the Alexandria Protocol, an intelligent system that manages the entire data flow process.
The IAGON ecosystem also runs on the public Ethereum blockchain and the IAG token, creating IAGON's token economy. It is an autonomous system based on a smart device, server and data center owners, operating on the basis of virtual tokens.
The project is conducted by IAGON AS, incorporated in Norway. IAGON AS has the following ownership structure: Dr. Navjit Dhaliwal and Bogna Kaczmarek-Dhaliwal own 65% of company shares, Dr. Elad Harison has 25% and others own 10%. In the documentation, the emphasis is on the legal aspects and a description of the current structure of the company. The organizational structure is also presented:
At the seed stage of investment, the company was financed to the amount of 190,000 Euros by its founders, and $2.6 million was attracted within the framework of private funding.
The project’s ICO is taking place in two stages - a public pre-sale and a crowdsale. All token sale parameters are standard, except for the fact that unsold tokens will be distributed to token holders. The situation with the hard cap is unclear; this is declared as $50 million, but it exceeds $70 million by calculation. The ICO’s parameters could be changed at any point before the start date.
Presale
Start date: May 27, 2018
End date: June 26, 2018
Price:
0.06 USD per IAG token - for contributions > 25 ETH.
0.07 USD per IAG token - for contributions > 10 ETH.
0.08 USD per IAG token - for contributions > 5 ETH.
0.09 USD per IAG token - for contributions > 0.1 ETH.
Minimum investment: $1000
ICO
Start date: July 7, 2018
End date: After 30-60 days
Soft cap: $5,000,000
Hard Cap: $50,000,000
Price: 0.12 USD = 1 IAG
Token: IAG, standard ERC-20
Accepted currency: ETH
Total emission: 1,000,000,000 IAG
50% - crowdsale
20% - presale
10% - team
10% - advisors and bounty program
10% - development
On sale: 700,000,000 IAG
Freezing periods for tokens not distributed at the main sale are not announced
70% of team tokens are locked until mainnet launch (Q1 2019)
The CEO's (Dr. Navjit Dhaliwal) tokens are locked in the following way: 30% for one year and 70% for two years. The CEO owns 65% of team tokens.
The IAGON project is based on the provision of cloud services: computing resources and virtual storage, i.e. the IAGON platform is limited to these two services.
Despite a fairly simple idea, the architecture of the project is complex and based on advanced digital technologies and AI systems. Separately, it is worth mentioning the project’s blockchain. In addition to the progressive idea in terms of centralized technologies (AI, neural networks, etc.), distributed networks of different natures are used so much so that the team announces the IAGON platform as fully decentralized, with the use of public and private blockchains.
More Information & Resources:
• https://www.iagon.com/
• https://www.reddit.com/r/iagon/
• https://www.linkedin.com/company/iagon/
• https://steemit.com/@official.iagon
• https://medium.com/iagon-official
• https://t.me/Iagon_official
• https://bitcointalk.org/index.php?topic=2945888.0
iagon2018


.png)




This post has been submitted for the @OriginalWorks Sponsored Writing Contest!
You can also follow @contestbot to be notified of future contests!