Most Recent Arxiv Papers In Nonlinear Sciences | 2019-02-07
Adaptation And Self-Organizing Systems
Reconstructing bifurcation behavior of a nonlinear dynamical system by introducing weak noise (1810.05458v2)
Debraj Das, Sayan Roy, Shamik Gupta
2018-10-12
For a model nonlinear dynamical system, we show how one may obtain its bifurcation behavior by introducing noise into the dynamics and then studying the resulting Langevin dynamics in the weak-noise limit. A suitable quantity to capture the bifurcation behavior in the noisy dynamics is the conditional probability to observe a microscopic configuration at one time, conditioned on the observation of a given configuration at an earlier time. For our model system, this conditional probability is studied by using two complementary approaches, the Fokker-Planck and the path-integral approach. The latter has the advantage of yielding exact closed-form expressions for the conditional probability. All our predictions are in excellent agreement with direct numerical integration of the dynamical equations of motion.
Topological Convergence of Urban Infrastructure Networks (1902.01266v1)
Christopher Klinkhamer, Jonathan Zischg, Elisabeth Krueger, Soohyun Yang, Frank Blumensaat, Christian Urich, Thomas Kaeseberg, Kyungrock Paik, Dietrich Borchardt, Julian Reyes Silva, Robert Sitzenfrei, Wolfgang Rauch, Gavan McGrath, Peter Krebs, Satish Ukkusuri, P. S. C. Rao
2019-02-04
Urban infrastructure networks play a major role in providing reliable flows of multitude critical services demanded by citizens in modern cities. We analyzed here a database of 125 infrastructure networks, roads (RN); urban drainage networks (UDN); water distribution networks (WDN), in 52 global cities, serving populations ranging from 1,000 to 9,000,000. For all infrastructure networks, the node-degree distributions, p(k), derived using undirected, dual-mapped graphs, fit Pareto distributions. Variance around mean gamma reduces substantially as network size increases. Convergence of functional topology of these urban infrastructure networks suggests that their co-evolution results from similar generative mechanisms. Analysis of growing UDNs over non-concurrent 40 year periods in three cities suggests the likely generative process to be partial preferential attachment under geospatial constraints. This finding is supported by high-variance node-degree distributions as compared to that expected for a Poisson random graph. Directed cascading failures, from UDNs to RNs, are investigated. Correlation of node-degrees between spatially co-located networks are shown to be a major factor influencing network fragmentation by node removal. Our results hold major implications for the network design and maintenance, and for resilience of urban communities relying on multiplex infrastructure networks for mobility within the city, water supply, and wastewater collection and treatment.
Chimera patterns in three-dimensional locally coupled systems (1902.01036v1)
Srilena Kundu, Bidesh K. Bera, Dibakar Ghosh, M. Lakshmanan
2019-02-04
The coexistence of coherent and incoherent domains, namely the appearance of chimera states, is being studied extensively in many contexts of science and technology since the past decade, though the previous studies are mostly built on the framework of one-dimensional and two-dimensional interaction topologies. Recently, the emergence of such fascinating phenomena has been studied in three-dimensional (3D) grid formation while considering only the nonlocal interaction. Here we study the emergence and existence of chimera patterns in a three dimensional network of coupled Stuart-Landau limit cycle oscillators and Hindmarsh-Rose neuronal oscillators with local (nearest neighbour) interaction topology. The emergence of different types of spatiotemporal chimera patterns is investigated by taking two distinct nonlinear interaction functions. We provide appropriate analytical explanations in the 3D grid of network formation and the corresponding numerical justifications are given. We extend our analysis on the basis of Ott-Antonsen reduction approach in the case of Stuart-Landau oscillators containing infinite number of oscillators. Particularly, in Hindmarsh-Rose neuronal network the existence of non-stationary chimera states are characterized by instantaneous strength of incoherence and instantaneous local order parameter. Besides, the condition for achieving exact neuronal synchrony is obtained analytically through a linear stability analysis. The different types of collective dynamics together with chimera states are mapped over a wide range of various parameter spaces.
New combinational therapies for cancer using modern statistical mechanics (1902.00728v1)
Jorge A. González, M. Acanda, Z. Akhtar, D. Andrews, J. I. Azqueta, E. Bass, A. Bellorín, J. Couso, Mónica A. García-Ñustes, Y. Infante, S. Jiménez, L. Lester, L. Maldonado, Juan F. Marín, L. Pineda, I. Rodríguez, C. C. Tamayo, D. Valdes, L. Vázquez
2019-02-02
We investigate a new dynamical system that describes tumor-host interaction. The equation that describes the untreated tumor growth is based on non-extensive statistical mechanics. Recently, this model has been shown to fit successfully exponential, Gompertz, logistic, and power-law tumor growths. We have been able to include as many hallmarks of cancer as possible. We study also the dynamic response of cancer under therapy. Using our model, we can make predictions about the different outcomes when we change the parameters, and/or the initial conditions. We can determine the importance of different factors to influence tumor growth. We discover synergistic therapeutic effects of different treatments and drugs. Cancer is generally untreatable using conventional monotherapy. We consider conventional therapies, oncogene-targeted therapies, tumor-suppressors gene-targeted therapies, immunotherapies, anti-angiogenesis therapies, virotherapy, among others. We need therapies with the potential to target both tumor cells and the tumors' microenvironment. Drugs that target oncogenes and tumor-suppressor genes can be effective in the treatment of some cancers. However, most tumors do reoccur. We have found that the success of the new therapeutic agents can be seen when used in combination with other cancer-cell-killing therapies. Our results have allowed us to design a combinational therapy that can lead to the complete eradication of cancer.
Cardinality Leap for Open-Ended Evolution: Theoretical Consideration and Demonstration by "Hash Chemistry" (1806.06628v4)
Hiroki Sayama
2018-06-18
Open-ended evolution requires unbounded possibilities that evolving entities can explore. The cardinality of a set of those possibilities thus has a significant implication for the open-endedness of evolution. We propose that facilitating formation of higher-order entities is a generalizable, effective way to cause a "cardinality leap" in the set of possibilities that promotes open-endedness. We demonstrate this idea with a simple, proof-of-concept toy model called "Hash Chemistry" that uses a hash function as a fitness evaluator of evolving entities of any size/order. Simulation results showed that the cumulative number of unique replicating entities that appeared in evolution increased almost linearly along time without an apparent bound, demonstrating the effectiveness of the proposed cardinality leap. It was also observed that the number of individual entities involved in a single replication event gradually increased over time, indicating evolutionary appearance of higher-order entities. Moreover, these behaviors were not observed in control experiments in which fitness evaluators were replaced by random number generators. This strongly suggests that the dynamics observed in Hash Chemistry were indeed evolutionary behaviors driven by selection and adaptation taking place at multiple scales.
Chaotic Dynamics
Dynamical Component Analysis (DyCA) and its application on epileptic EEG (1902.01777v1)
Katharina Korn, Bastian Seifert, Christian Uhl
2019-02-05
Dynamical Component Analysis (DyCA) is a recently-proposed method to detect projection vectors to reduce the dimensionality of multi-variate deterministic datasets. It is based on the solution of a generalized eigenvalue problem and therefore straight forward to implement. DyCA is introduced and applied to EEG data of epileptic seizures. The obtained eigenvectors are used to project the signal and the corresponding trajectories in phase space are compared with PCA and ICA-projections. The eigenvalues of DyCA are utilized for seizure detection and the obtained results in terms of specificity, false discovery rate and miss rate are compared to other seizure detection algorithms.
Inclusion of Coulomb effects in laser-atom interactions (1902.01607v1)
Jonathan Dubois, Simon Berman, Cristel Chandre, Turgay Uzer
2019-02-05
We investigate the role of the Coulomb interaction in strong field processes. We find that the Coulomb field of the ion makes its presence known even in highly intense laser fields, in contrast to the assumptions of the strong field approximation. The dynamics of the electron after ionization is analyzed with four models for an arbitrary laser polarization: the Hamiltonian model in the dipole approximation, the strong field approximation, the Coulomb-corrected strong field approximation and the guiding center. These models illustrate clearly the Coulomb effects, in particular Coulomb focusing and Coulomb asymmetry. We show that the Coulomb-corrected strong field approximation and the guiding center are complementary, in the sense that the Coulomb-corrected strong field approximation describes well short time scale phenomena (shorter than a laser cycle) while the guiding center is well suited for describing long time scale phenomena (longer than a laser cycle) like Coulomb-driven recollisions and Rydberg state creation.
Chaos-preserving reduction of the spin-flip model for VCSELs: failure of the adiabatic elimination of the spin-population difference (1902.00055v2)
Martin Virte, Francesco Ferranti
2019-01-31
When studying the dynamics of Vertical-Cavity Surface-Emitting Lasers, and their polarization properties, the spin-flip model appears to be the simplest model qualitatively reproducing all dynamical features that have been observed experimentally. Nonetheless, because of the fast time-scale of the spin-relaxation processes, the specific role and the importance of the spin-population difference - which is one of the specific feature of the spin-flip model - has been continuously questioned. In fact, the debate regarding the possible adiabatic elimination of the spin-population remains fully open. In this paper, our goal is to put a full stop to this debate by demonstrating that this variable is indeed essential to preserve the most complex dynamical features predicted by the spin-flip model, such as polarization chaos. To do so, we first perform a detailed analysis, focusing on the chaotic dynamics, to determine the minimal embedding dimension for the spin-flip model. As the latter confirms that a reduction of the model could be envisaged, we then consider the adiabatic elimination of the spin-population difference to highlight and explain its failure to reproduce essential dynamical features obtained in the original model. (c) 2019 IEEE. Personal use of this material is permitted. Permission from IEEE must be obtained for all other uses, in any current or future media, including reprinting/republishing this material for advertising or promotional purposes, creating new collective works, for resale or redistribution to servers or lists, or reuse of any copyrighted component of this work in other works.
Interaction between active particles and quantum vortices leading to Kelvin wave generation (1811.05342v2)
Umberto Giuriato, Giorgio Krstulovic
2018-11-13
One of the main features of superfluids is the presence of topological defects with quantised circulation. These objects are known as quantum vortices and exhibit a hydrodynamic behaviour. Nowadays, particles are the main experimental tool used to visualise quantum vortices and to study their dynamics. We use a self-consistent model based on the three-dimensional Gross-Pitaevskii (GP) equation to explore theoretically and numerically the attractive interaction between particles and quantised vortices at very low temperature. Particles are described as localised potentials depleting the superfluid and following Newtonian dynamics. We are able to derive analytically a reduced central-force model that only depends on the classical degrees of freedom of the particle. Such model is found to be consistent with the GP simulations. We then generalised the model to include deformations of the vortex filament. The resulting long-range mutual interaction qualitatively reproduces the observed generation of a cusp on the vortex filament during the particle approach. Moreover, we show that particles can excite Kelvin waves on the vortex filament through a resonance mechanism even if they are still far from it.
Edgeworth expansions for slow-fast systems with finite time scale separation (1708.06984v3)
Jeroen Wouters, Georg A. Gottwald
2017-08-23
We derive Edgeworth expansions that describe corrections to the Gaussian limiting behaviour of slow-fast systems. The Edgeworth expansion is achieved using a semi-group formalism for the transfer operator, where a Duhamel-Dyson series is used to asymptotically determine the corrections at any desired order of the time scale parameter
. The corrections involve integrals over higher-order auto-correlation functions. We develop a diagrammatic representation of the series to control the combinatorial wealth of the asymptotic expansion in
and provide explicit expressions for the first two orders. At a formal level, the expressions derived are valid in the case when the fast dynamics is stochastic as well as when the fast dynamics is entirely deterministic. We corroborate our analytical results with numerical simulations and show that our method provides an improvement on the classical homogenization limit which is restricted to the limit of infinite time scale separation.
Cellular Automata And Lattice Gases
Ergodicity versus non-ergodicity for Probabilistic Cellular Automata on rooted trees (1710.00084v2)
Bruno Kimura, Wioletta Ruszel, Cristian Spitoni
2017-09-29
In this article we study a class of shift-invariant and positive rate probabilistic cellular automata (PCA) on rooted d-regular trees
. In a first result we extend the results of [10] on trees, namely we prove that to every stationary measure
of the PCA we can associate a space-time Gibbs measure
on
. Under certain assumptions on the dynamics the converse is also true. A second result concerns proving sufficient conditions for ergodicity and non-ergodicity of our PCA on d-ary trees for
and characterizing the invariant product Bernoulli measures.
Throughput reduction by the simultaneous effect of two traveling routes equipped with parking sites in a two-dimensional stochastic lattice model (1901.10390v1)
Satori Tsuzuki, Daichi Yanagisawa, Katsuhiro Nishinari
2019-01-29
This paper proposes a two-dimensional stochastic lattice model that comprises a junction of two traveling routes: the domestic route and the international route, each of which has parking sites. In our model, the system distributes the arrived particles to either of the two routes and selects one of the parking sites in the route for each particle, which stops at the parking site once during its travel. Because each particle has antennas in the back and front directions to detect other approaching particles, the effect of the volume exclusion of each particle extends in the moving direction. The system displays interesting behavior; remarkably, the dependence of the throughput on the distribution ratio of particles to the domestic route reduces after reaching the maximum parking capacity of the domestic route. Our simulations and analysis with the queueing model describe this phenomenon and suggest the following fact: As the distribution ratio of particles to the international route decreases, the throughput of the international route reduces, and simultaneously, that of the domestic route saturates. The simultaneous effect of the decrease and saturation causes reduction in the throughput of the entire system.
Dissipation of traffic congestion using agent-based car-following model with modified optimal velocity (1901.06058v1)
Manit Klawtanong, Surachate Limkumnerd
2019-01-18
We investigate dynamical properties of traffic flow using the stochastic car-following model with modified optimal velocity on circular road. The safety distance following the two-second rule and autonomous vehicles, acting as agents, obeying simple requirements are incorporated into the model. The dynamic safety distance increases in a light traffic condition where the average driving velocity is high, while decreases in a dense traffic condition in anticipation of slower traffic motion. The results show that the presence of the agents can enhance overall velocity and traffic current of the system, and postpone the traffic congestion. In a particular phase region, imposing a speed limit enables the system to leave the congested flow phase. The density-dependent speed limit in agent-free condition is obtained to achieve the optimal traffic flow.
Search Space Reduction of Asynchrony Immune Cellular Automata by Center Permutivity (1901.01534v1)
Luca Mariot, Luca Manzoni, Alberto Dennunzio
2019-01-06
We continue the study of asynchrony immunity in cellular automata (CA), which can be considered as a weaker version of correlation immunity in the context of vectorial Boolean functions. The property could have applications as a countermeasure for side-channel attacks in CA-based cryptographic primitives, such as S-boxes and pseudorandom number generators. We first give some theoretical results on the necessary conditions that a CA rule must satisfy in order to meet asynchrony immunity, the most important one being center permutivity. Next, we perform an exhaustive search of all asynchrony immune CA rules of neighborhood size up to
, leveraging on the discovered theoretical properties to greatly reduce the size of the search space.
Exact large deviation statistics and trajectory phase transition of a deterministic boundary driven cellular automaton (1901.00845v1)
Berislav Buča, Juan P. Garrahan, Tomaž Prosen, Matthieu Vanicat
2019-01-03
We study the statistical properties of the long-time dynamics of the rule 54 reversible cellular automaton (CA), driven stochastically at its boundaries. This CA can be considered as a discrete-time and deterministic version of the Fredrickson-Andersen kinetically constrained model (KCM). By means of a matrix product ansatz, we compute the exact large deviation cumulant generating functions for a wide range of time-extensive observables of the dynamics, together with their associated rate functions and conditioned long-time distributions over configurations. We show that for all instances of boundary driving the CA dynamics occurs at the point of phase coexistence between competing active and inactive dynamical phases, similar to what happens in more standard KCMs. We also find the exact finite size scaling behaviour of these trajectory transitions, and provide the explicit "Doob-transformed" dynamics that optimally realises rare dynamical events.
Pattern Formation And Solitons
Structured light in self-organized laser output patterns and nonlocal maps (1901.09274v2)
A. Yu. Okulov
2019-01-26
Spatial chaos as a phenomenon of ultimate complexity requires the efficient numerical algorithms. For this purpose iterative low-dimensional maps have demonstrated high efficiency. Natural generalization of Feigenbaum and Ikeda maps may include convolution integrals with kernel in a form of Green function of a relevant linear physical system. It is shown that such iterative
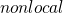
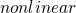
are equivalent to ubiquitous class of nonlinear partial differential equations of Ginzburg-Landau type. With a Green functions relevant to generic optical resonators these
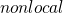
emulate the basic spatiotemporal phenomena as spatial solitons, vortex eigenmodes breathing via relaxation oscillations mediated by noise, vortex-vortex and vortex-antivortex lattices with well defined periodic location of vortex cores.
Controlled Generation of Chimera States in SQUID Metasurfaces using DC Flux Gradients (1902.01711v1)
N. Lazarides, J. Hizanidis, G. P. Tsironis
2019-02-05
SQUID (Superconducting QUantum Interference Device) metamaterials, subject to a time-independent (dc) flux gradient and driven by a sinusoidal (ac) flux field, support chimera states that can be generated with zero initial conditions. The dc flux gradient and the amplitude of the ac flux can control the number of desynchronized clusters of such a generated chimera state (i.e., its `heads') as well as their location and size. The combination of three measures, i.e., the synchronization parameter averaged over the period of the driving flux, the incoherence index, and the chimera index, is used to predict the generation of a chimera state and its multiplicity on the parameter plane of the dc flux gradient and the ac flux amplitude. Moreover, the full-width half-maximum of the distribution of the values of the synchronization parameter averaged over the period of the ac driving flux, allows to distinguish chimera states from non-chimera, partially synchronized states.
Wavenumber Selection in Pattern Forming Systems (1902.01245v1)
S. Saxena, J. M. Kosterlitz
2019-02-04
Wavenumber selection in pattern forming systems remains a long standing puzzle in physics. Previous studies have shown that external noise is a possible mechanism for wavenumber selection. We conduct an extensive numerical study of the noisy stabilized Kuramoto Sivashinsky equation. We use a fast spectral method of integration, which enables us to investigate long time behavior for large system sizes that could not be investigated by earlier work. We find that a state with a unique wavenumber has the highest probability of occurring at very long times. We also find that this state is independent of the strength of the noise and initial conditions, thus making a convincing case for the role of noise as a mechanism of state selection.
Modelling chemotaxis of microswimmers: from individual to collective behavior (1802.07933v2)
B. Liebchen, H. Löwen
2018-02-22
We discuss recent progress in the theoretical description of chemotaxis by coupling the diffusion equation of a chemical species to equations describing the motion of sensing microorganisms. In particular, we discuss models for autochemotaxis of a single microorganism which senses its own secretion leading to phenomena such as self-localization and self-avoidance. For two heterogeneous particles, chemotactic coupling can lead to predator-prey behavior including chase and escape phenomena, and to the formation of active molecules, where motility spontaneously emerges when the particles approach each other. We close this review with some remarks on the collective behavior of many particles where chemotactic coupling induces patterns involving clusters, spirals or traveling waves.
Lateral inhibition provides a unifying framework for spatiotemporal pattern formation in media comprising relaxation oscillators (1902.01163v1)
R. Janaki, Shakti N. Menon, Rajeev Singh, Sitabhra Sinha
2019-02-04
The collective dynamics seen in a wide variety of chemical, biological and ecological systems involve interactions between relaxation oscillators that typically involve fast activation process coupled with a slower inactivation. In this paper, we show that systems of such oscillators having distinct kinetics governing local dynamical behavior and whose interactions are described by different connection topologies, can exhibit strikingly similar spatiotemporal patterns when diffusively coupled via their inactivation component. We explain the apparent universality of this global behavior by showing that relaxation oscillators interacting via lateral inhibition will generally yield two basic classes of patterns, viz., one comprising one or more clusters of synchronized oscillators while the other is a time-invariant spatially inhomogeneous state resulting from oscillation death. All observed collective states can be interpreted either as specific instances of these fundamental patterns or as resulting from their competition.
Exactly Solvable And Integrable Systems
Coalescence Model of Rock-Paper-Scissors Particles (1808.02386v3)
Yoshiaki Itoh
2018-08-06
The rock-paper-scissors game, commonly played in East Asia, gives a simple model to understand physical, biological, psychological and other problems. The interacting rock-paper-scissors particle system is a point of contact between the kinetic theory of gases by Maxwell and Boltzmann ( collision model) and the coagulation theory by Smoluchowski ( coalescence model). A
types extended rock-paper-scissors collision model naturally introduces a nonlinear integrable system. The time evolution of the
types extended rock-paper-scissors coalescence model is obtained from the logarithmic time change of the nonlinear integrable system. We also discuss the behavior of a discrete rock-paper-scissors coalescence model.
Matrix product solutions to the reflection equation from three dimensional integrability (1802.09164v3)
Atsuo Kuniba, Vincent Pasquier
2018-02-26
We formulate a quantized reflection equation in which
-boson valued
and
matrices satisfy the reflection equation up to conjugation by a solution to the Isaev-Kulish 3D reflection equation. By forming its
-concatenation along the
-boson Fock space followed by suitable reductions, we construct families of solutions to the reflection equation in a matrix product form connected to the 3D integrability. They involve the quantum
matrices of the antisymmetric tensor representations of
and the spin representations of
,
and
.
Extended Z-invariance for integrable vector and face models and multi-component integrable quad equations (1812.10893v2)
Andrew P. Kels
2018-12-28
In a previous paper, the author has established an extension of the Z-invariance property for integrable edge-interaction models of statistical mechanics, that satisfy the star-triangle relation (STR) form of the Yang-Baxter equation (YBE). In the present paper, an analogous extended Z-invariance property is shown to also hold for integrable vector models and interaction-round-a-face (IRF) models of statistical mechanics respectively. As for the previous case of the STR, the Z-invariance property is shown through the use of local cubic-type deformations of a 2-dimensional surface associated to the models, which allow an extension of the models onto a subset of next nearest neighbour vertices of
, while leaving the partition functions invariant. These deformations are permitted as a consequence of the respective YBE's satisfied by the models. The quasi-classical limit is also considered, and it is shown that an analogous Z-invariance property holds for the variational formulation of classical discrete Laplace equations which arise in this limit. From this limit, new integrable 3D-consistent multi-component quad equations are proposed, which are constructed from a degeneration of the equations of motion for IRF Boltzmann weights.
Resilience of constituent solitons in multisoliton scattering off barriers (1501.00075v3)
Vanja Dunjko, Maxim Olshanii
2014-12-31
We introduce ``superheated integrability,'' which produces characteristic staircase transmission plots for barrier collisions of breathers of the nonlinear Schr"odinger equation. The effect makes tangible the inverse scattering transform, which treats the velocities and norms of the constituent solitons as the real and imaginary parts of the eigenvalues of the Lax operator. If all the norms are much greater than the velocities, an integrability-breaking potential may nonperturbatively change the velocities while having no measurable effect on the norms. This could be used to improve atomic interferometers.
Exact solution of an integrable anisotropic  spin chain model (1902.00688v1)
spin chain model (1902.00688v1)
Yi Qiao, Pei Sun, Zhirong Xin, Junpeng Cao, Wen-Li Yang
2019-02-02
An integrable anisotropic Heisenberg spin chain with nearest-neighbour couplings, next-nearest-neighbour couplings and scalar chirality terms is constructed. After proving the integrability, we obtain the exact solution of the system. The ground state and the elementary excitations are also studied. It is shown that the spinon excitation of the present model possesses a novel triple arched structure. The elementary excitation is gapless if the anisotropic parameter
is real while the elementary excitation has an enhanced gap by the next-nearest-neighbour and chiral three-spin interactions if the anisotropic parameter
is imaginary. The method of this paper provides a general way to construct new integrable models with next-nearest-neighbour interactions.

Don't forget to Follow and Resteem. @complexcity
Keeping everyone inform.
✅ Enjoy the vote! For more amazing content, please follow @themadcurator for a chance to receive more free votes!