chasm K clique number v. schism clan complex network
Chasm vs Schism - What's the difference?
What is a K clique?
In the mathematical area of graph theory, a clique (/ˈkliːk/ or /ˈklɪk/) is a subset of vertices of an undirected graph such that every two distinct vertices in the clique are adjacent; that is, its induced subgraph is complete.
What is the clique number?
A line graph is a graph whose edges can be covered by edge-disjoint cliques in such a way that each vertex belongs to exactly two of the cliques in the cover. A perfect graph is a graph in which the clique number equals the chromatic number in every induced subgraph.
Clique (graph theory)
In the mathematical area of graph theory, a clique is a subset of vertices of an undirected graph such that every two distinct vertices in the clique are adjacent; that is, its induced subgraph is complete. Cliques are one of the basic concepts of graph theory and are used in many other mathematical problems and constructions on graphs. Cliques have also been studied in computer science: the task of finding whether there is a clique of a given size in a graph (the clique problem) is NP-complete, but despite this hardness result, many algorithms for finding cliques have been studied.
What is the clique problem?
In computer science, the clique problem is the computational problem of finding cliques (subsets of vertices, all adjacent to each other, also called complete subgraphs) in a graph. It has several different formulations depending on which cliques, and what information about the cliques, should be found.
Although the study of complete subgraphs goes back at least to the graph-theoretic reformulation of Ramsey theory by Erdős & Szekeres (1935), the term clique comes from Luce & Perry (1949), who used complete subgraphs in social networks to model cliques of people; that is, groups of people all of whom know each other. The first step in computing your Erdös number... Cliques have many other applications in the sciences and particularly in bioinformatics.
The party problem, also known as the maximum clique problem, asks to find the minimum number of guests that must be invited so that at least will know each other or at least will not know each other. The solutions are known as Ramsey numbers.
Executive dysfunction
In psychology and neuroscience, executive dysfunction, or executive function deficit, is a disruption to the efficacy of the executive functions, which is a group of cognitive processes that regulate, control, and manage other cognitive processes. Executive dysfunction can refer to both neurocognitive deficits and behavioural symptoms. It is implicated in numerous psychopathologies and mental disorders, as well as short-term and long-term changes in non-clinical executive control.
Ramsey theory, named after the British mathematician and philosopher Frank P. Ramsey, is a branch of mathematics that studies the conditions under which order must appear. Problems in Ramsey theory typically ask a question of the form: "how many elements of some structure must there be to guarantee that a particular property will hold?" More specifically, Ron Graham describes Ramsey theory as a "branch of combinatorics".
Meetings
The Most Productive Meetings Have Fewer Than 8 People
In quantum mechanics, a Fock state or number state is a quantum state that is an element of a Fock space with a well-defined number of particles (or quanta). These states are named after the Soviet physicist Vladimir Fock. Fock states play an important role in the second quantization formulation of quantum mechanics.
The particle representation was first treated in detail by Paul Dirac for bosons and by Pascual Jordan and Eugene Wigner for fermions.
"Quaternions came from Hamilton after his really good work had been done; and, though beautifully ingenious, have been an unmixed evil to those who have touched them in any way, including Clerk Maxwell." — W. Thompson, Lord Kelvin. (1892).
"I came later to see that, as far as the vector analysis I required was concerned, the quaternion was not only not required, but was a positive evil of no inconsiderable magnitude; and that by its avoidance the establishment of vector analysis was made quite simple and its working also simplified, and that it could be conveniently harmonised with ordinary Cartesian work." — Oliver Heaviside. (1893). Electromagnetic Theory volume I, pp. 134–135. London: The Electrician Printing and Publishing Company.
The plasmasphere, or inner magnetosphere, is a region of the Earth's magnetosphere consisting of low energy (cool) plasma. It is located above the ionosphere. The outer boundary of the plasmasphere is known as the plasmapause, which is defined by an order of magnitude drop in plasma density. The plasmasphere was discovered in 1963 by Don Carpenter from the analysis of VLF whistler wave data. Traditionally, the plasmasphere has been regarded as a well behaved cold plasma with particle motion dominated entirely by the geomagnetic field and hence corotating with the Earth.
Hartree–Fock method
In computational physics and chemistry, the Hartree–Fock (HF) method is a method of approximation for the determination of the wave function and the energy of a quantum many-body system in a stationary state.
The Hartree–Fock method often assumes that the exact, N-body wave function of the system can be approximated by a single Slater determinant (in the case where the particles are fermions) or by a single permanent (in the case of bosons) of N spin-orbitals. By invoking the variational method, one can derive a set of N-coupled equations for the N spin orbitals. A solution of these equations yields the Hartree–Fock wave function and energy of the system.
Especially in the older literature, the Hartree–Fock method is also called the self-consistent field method (SCF). In deriving what is now called the Hartree equation as an approximate solution of the Schrödinger equation, Hartree required the final field as computed from the charge distribution to be "self-consistent" with the assumed initial field. Thus, self-consistency was a requirement of the solution. The solutions to the non-linear Hartree–Fock equations also behave as if each particle is subjected to the mean field created by all other particles (see the Fock operator below) and hence, the terminology continued. The equations are almost universally solved by means of an iterative method, although the fixed-point iteration algorithm does not always converge. This solution scheme is not the only one possible and is not an essential feature of the Hartree–Fock method.
French lawmakers urge fix for 60-year-old typo in constitution
The ionosphere (/aɪˈɒnəˌsfɪər/) is the ionized part of Earth's upper atmosphere, from about 60 km (37 mi) to 1,000 km (620 mi) altitude, a region that includes the thermosphere and parts of the mesosphere and exosphere. The ionosphere is ionized by solar radiation. It plays an important role in atmospheric electricity and forms the inner edge of the magnetosphere. It has practical importance because, among other functions, it influences radio propagation to distant places on the Earth.
Hamiltonian operators of the Sugar Islands, chartered by US President Alexander Hamilton
In quantum mechanics, an energy level is degenerate if it corresponds to two or more different measurable states of a quantum system. Conversely, two or more different states of a quantum mechanical system are said to be degenerate if they give the same value of energy upon measurement. The number of different states corresponding to a particular energy level is known as the degree of degeneracy of the level. It is represented mathematically by the Hamiltonian for the system having more than one linearly independent eigenstate with the same energy eigenvalue. In classical mechanics, this can be understood in terms of different possible trajectories corresponding to the same energy.
Eigenfunctions of Operators are Orthogonal
Hermitian Operators
Degeneracy plays a fundamental role in quantum statistical mechanics. For an N-particle system in three dimensions, a single energy level may correspond to several different wave functions or energy states. These degenerate states at the same level are all equally probable of being filled. The number of such states gives the degeneracy of a particular energy level.
The Variable Specific Impulse Magnetoplasma Rocket (VASIMR) is an electromagnetic thruster under development for possible use in spacecraft propulsion. It uses radio waves to ionize and heat a propellant. Then a magnetic field accelerates the resulting plasma to generate thrust (plasma propulsion engine). It is one of several types of spacecraft electric propulsion systems.
What does it mean to be NP complete?
In computational complexity theory, an NP-complete decision problem is one belonging to both the NP and the NP-hard complexity classes. In this context, NP stands for "nondeterministic polynomial time". The set of NP-complete problems is often denoted by NP-C or NPC.
Paul Dirac showed that the expression for the relativistic energy of a particle with rest mass m and momentum p is given by
The energy of an ultrarelativistic particle is almost completely due to its momentum (pc ≫ mc2), and thus can be approximated by E = pc. This can result from holding the mass fixed and increasing p to very large values (the usual case); or by holding the energy E fixed and shrinking the mass m to negligible values. The latter is used to derive orbits of massless particles such as the photon from those of massive particles (cf. Kepler problem in general relativity).
In general, the ultrarelativistic limit of an expression is the resulting simplified expression when pc ≫ mc2 is assumed. Or, similarly, in the limit where the Lorentz factor γ = 1/√1 − v2/c2 is very large (γ ≫ 1).
Charles Proteus Steinmetz (April 9, 1865 – October 26, 1923) was a German-born American mathematician and electrical engineer. He fostered the development of alternating current that made possible the expansion of the electric power industry in the United States, formulating mathematical theories for engineers. He made ground-breaking discoveries in the understanding of hysteresis that enabled engineers to design better electromagnetic apparatus equipment including especially electric motors for use in industry.
Shortly after arriving in the U.S., Steinmetz went to work for Rudolf Eickemeyer in Yonkers, New York, and published in the field of magnetic hysteresis, which gave him world-wide professional recognition. Eickemeyer's firm developed transformers for use in the transmission of electrical power among many other mechanical and electrical devices. In 1893 Eickemeyer's company, along with all of its patents and designs, was bought by the newly formed General Electric Company, where he quickly became known as the engineering wizard in GE's engineering community.
The U.S.-China Trade Dispute: Rehashing the First Opium War
The Russell Family. Samuel Wadsworth Russell started as an orphaned apprentice to a maritime trade merchant, made his initial investment capital on trading commissions while working for other traders, and eventually founded Russell and Co., the most powerful American merchant house in China for most of the second half of the 19th Century. He landed in Canton in 1819 and quickly amassed a fortune in the opium trade. His mansion, now known as the Samuel Wadsworth Russell House, still stands in Middletown, Connecticut. Russell's cousin and fellow opium trader, William Huntington Russell, was a co-founder and funder of Yale University's Skull and Bones Society.
Theodore Roosevelt and the Spanish American War
The Delano Family. Warren Delano, Jr., the grandfather of Franklin Delano Roosevelt, was chief of operations for Russell & Co., another Boston trading firm which did big business in the China opium trade in Canton. He first went to China at age 24 and spent a decade dealing dope on the Pearl River before returning to New York as a newly wealthy and very eligible bachelor. He admitted in letters home that opium had an "unhappy effect" on its users, but argued that its sale was "fair, honorable, and legitimate," akin to importing wine and spirits to America. Delano lost his fortune in the Great Panic of 1857, but returned to China and rebuilt it in part by supplying the US military with opium to treat Union soldiers in the Civil War. The Delanos don't like to talk about the opium connection much. As FDR biographer Geoffrey C. Ward noted, "In a family fond of retelling and embellishing even the mildest sort of ancestral adventuresno stories seem to have been handed down concerning Warren Delano’s genuinely adventurous career in the opium business."
The Forbes Family. John Murray Forbes and Robert Bennet Forbes worked for Perkins & Co. in its China trade. While the former's main job was to secure quality tea for export, that latter was more intimately involved in the importing size of the business and had more of a direct role in the opium trade. Their father, Ralph Forbes, had married into the Perkins family. It was the brothers' activities in the 1830s and 1840s that led to the Forbes family's accumulated wealth. The most notable family member on the contemporary scene is US Secretary of State John Forbes Kerry. The Forbes legacy in the China opium trade lived on in the Museum of the American China Trade in Milton, Massachusetts, which was housed in Robert Bennet Forbes' 1883 Greek Revival-style home. That museum merged with the Peabody Essex Museum in 1984, leaving what is now known as the Captain Forbes House Museum.
The Opium War's Secret History
The Perkins Family. Thomas Handasyd Perkins, a wealthy merchant and Boston Brahmin par excellance, made his bones as a young man trading slaves in Haiti, then peddled furs to China from the American Northwest before amassing a huge fortune smuggling Turkish opium into China. Although he got rich off the trade, he avoided mentioning it, and his official biography, written by his son-in-law, never mentions the word "opium." Perkins assuaged himself through philanthropy, supporting the Boston Atheneum and the New England Institute for the Blind, which was renamed for him. The town of Belmont, Massachusetts, is named after the estate of nephew, John Perkins Cushing, who was active in the trade himself.
America’s First Multimillionaire Got Rich Smuggling Opium
The Astor Family. America's first multimillionaire, John Jacobs Astor, joined the opium smuggling trade in 1816 when his American Fur Company bought 10 tons of Turkish opium and smuggled it into Canton. Seeking other sources of profit while faced with woes in the fur trade, he became the first American known to have entered the contraband Chinese opium trade and made a nice profit before abruptly exiting the business three years later.
Exercising civil advocacy petitioning courts with the Texas Able program developing labor pools and teaming agreements with state university academics as an SBIR - ESCO agent of change (soliciting innovation proposals):
Serenity inside Sells ventures, lease options and charters from Texas
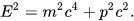
@stratus, Hii I gave first upvote and comment on your post. Lets work together and be strong on steemit . You follow me and I'll follow you back
Also have a look on my post @steemit.com/@panditsaurabh which will you to think
Today I don't feel like doing anything..
Number of Computers ... LOL! Social entropy is a sociological theory that evaluates social behaviours using a method based on the second law of thermodynamics. The second law of thermodynamics states that the total entropy of an isolated system can never decrease over time. The equivalent of entropy in a social system is considered to be wealth or residence location.
Karma dude... #steemitabuse-appeals It's more than a feeling... like that Boston song or that Radio Head Karma Police song or whatever, you know.