What is a Computational Process?
Full blown ideas are as a result of simple broken down ideas coming together to form a complex one.
Two complex ideas can come together ultimately to form an even bigger idea.
A simple idea might be the only the only required addition to an already complex idea while trying to make the complex idea more functional.
The three principles described above when summed up are the basis of a computational process.
A computational process is an ideal instance of abstraction wherein several factors are put together in order to perform calculations and give precise solutions devoid of errors.
The result of a computational process is set to be as accurate as possible.
Bigger computers are being built everyday which gives a rise in the need to improve on the old processes in terms of accuracy, precision, execution speed among other factors.
Processes operate on data using programs to direct the data at every point and through every stage until the process is completed.
Since there's absolutely no pre-designed format for solving computing problems, the development of problem solving procedures are usually a result experimental tryouts based on research and hypotheses.
The entire process of providing a solution can be broken down into three sequential procedures which are
Problem Formulation
Solution Expression
Solution execution and evaluation
Computational processes are a simulation of the real time processes required to produce solutions to certain problems and the inception of these processes are usually brought about by computational thinking which is the art of solving scalar problems using algorithms.
Algorithms
Software is a program used to map a problem onto a computer for the computer to find a solution.
All software contains an underlying problem solving framework wherein data is manipulated by algorithms to produce results.
Algorithms are the engines of all computational processes. Algorithms can be said to be a layout of the procedure data has to undergo in order to give a complete precise output.
One algorithm can be able to directly manipulate a group of alike data that's sharing the same behavioral patterns.
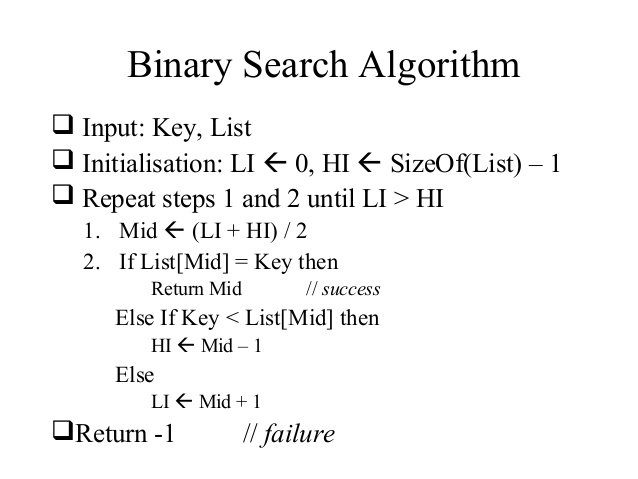
An ideal example of such is the binary search algorithm.
Sometimes we might have to search through voluminous data to retrieve simple information, such a case that conducting a linear search would be highly tasking.
In this case a binary search can be put to use by applying its algorithm.
The completion of the algorithm to give an output based on the input data is a computational process.
The aim of the entire process is to solve the problem of locating the occurence of a value that exists in the data.
To solve this a system has to come into play that facilitates looking for a target value within a sorted array.
During a binary search the target value's compared with the element in the middle of the array, if both values are not the same the array is divided into two equal parts.
After division the part most likely to contain the desired result is then searched through by comparing the target value with the value appearing in the middle.
Again if the desired result is not reached the process repeats itself and arrays keep getting divided into two until the target value is located.
The code that executes the process described above is known as an algorithm.
In order to be able perform their functions algorithms need a vital ingredient to fire up, that ingredient is data.
Data
Algorithms need to be fed with data for them to work on. Without data to work on algorithms are just frameworks, data provides the specific parameters that will determine the final output of the process.
Data is a collection of facts from which conclusions can be drawn.
There are different forms of data.
Data can exist in written form as numbers or texts and they can also exist in digital form as bits and bytes.
Computational processes can be designed in a way which they either accept only one type of data or they can take multiple types of data.
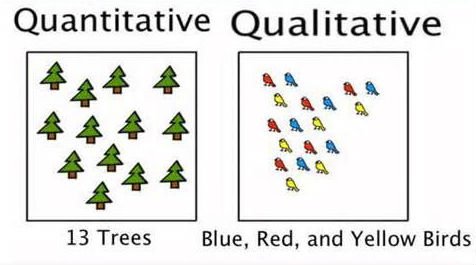
Data can also exist as qualitative and quantitative data where the former is also known as descriptive data and the latter can alternatively be called numerical data.
Quantitative data can be further sub-divided into
Discrete quantitative data which only allows a specified data type for inclusion in a data set.
For example a data set
Xcontaining only the first five prime numbers is a discrete since it can only allow numerical values.Continuous quantitative data which can allow the addition of any type of value in its data set.
Data set
Y = { a, 1, ab4 }is continuous because of its acceptance of diverse data types.
Simply defined , we can say that discrete data is counted while continuous data is measured.
Program
Data contributes to the final output whenever an algorithm is run.
The other factor that contributes to the successful execution of an algorithm is the program written on the algorithm.
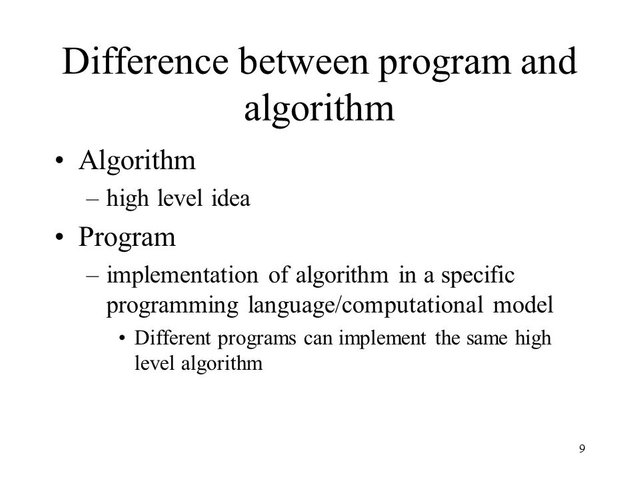
Algorithm and programs can be said to be alike save for one major difference, algorithms are blueprints that will help solve a problem while programs are specific instructions as to how that problem should be solved.
Algorithms can be written in plain language like English or a programming language like C, as long as it leads to a solution a particular problem it will be accepted as an algorithm.
Programs on the other hand requires it to be written in a programming language before it can be acknowledged as a program.
The successful execution of a program automatically means the algorithm the program is based on has completed a computational process.
Programs are snippets of code used to communicate with a computer and instruct it to perform functions.
These snippets of code are written using a programming language.
Programming Language
Just like English language serves as a medium for communicating with others so does a programming language serve as an avenue to communicate with the computer.
Programs are written by following rules defined for the language they are being written in.
These defined rules are known as the syntax.
Syntax is a set of rules that determines how code is written in a language.
The syntax is akin to the alphabet in any spoken language.
The same way words and letters have to stringed together to form understandable sentences so it is for programming languages.
Programs use a combination of functions, variables, dictionaries, lists, arrays and other form of data types to perform calculations on a given problem.
Programming languages are used to write problem solving programs.
In order to understand the levels of programming languages we have to first of all talk about the evolution of programming languages.
The earliest computers were programmed using machine language.
Machine language is the language used for the set of instructions that are executed directly from the CPU.
Machine Languages are also known as first generation programming languages.
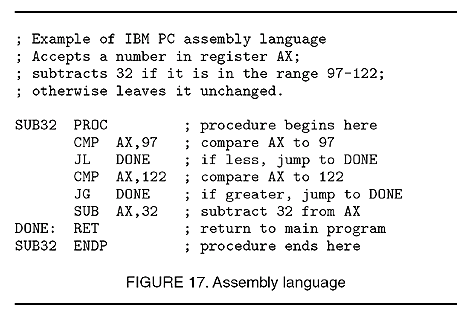
A little after second generation programming languages came on, these set are known as assembly languages and unlike machine language which is just raw binary hard-to-read code the assembly languages were more easy to read.
Presently, we have the third generation programming languages also known as high level programming languages.
All common programming languages of the present age are all third generation. Examples include JavaScript, Python, Java e.t.c
All high level languages will eventually be converted to machine language in the process of executing the code. Converting a high level language to machine language requires the use of a compiler or interpreter.
Bugs
A bug or software bug is an error in a computer program that causes the program to produce the wrong output or worse still stall the entire process such that no output is created.
Bugs can arise for a number of reasons including
- Mistakes in the source code
- Faulty design
- Incompatibility and glitches between component programs and operating system.
The process of troubleshooting bugs in a program and correcting them to produce the desired result is known as debugging.
Some common side effects bugs are
- Freezing of the computer screen
- Slowing down of PC processing speed
- Creating access for a hacker to exploit
- Crashing the computer
Bugs causes a computational process to be unproductive and no matter how little the bug is it can cause the entire program not to run.



It almost blown my head's processor(?) by reading this piece! Ha-ha
Your Post Has Been Featured on @Resteemable!
Feature any Steemit post using resteemit.com!
How It Works:
1. Take Any Steemit URL
2. Erase
https://3. Type
reGet Featured Instantly – Featured Posts are voted every 2.4hrs
Join the Curation Team Here