Computer Ergonomics | How to Protect Yourself from Strain and Pain
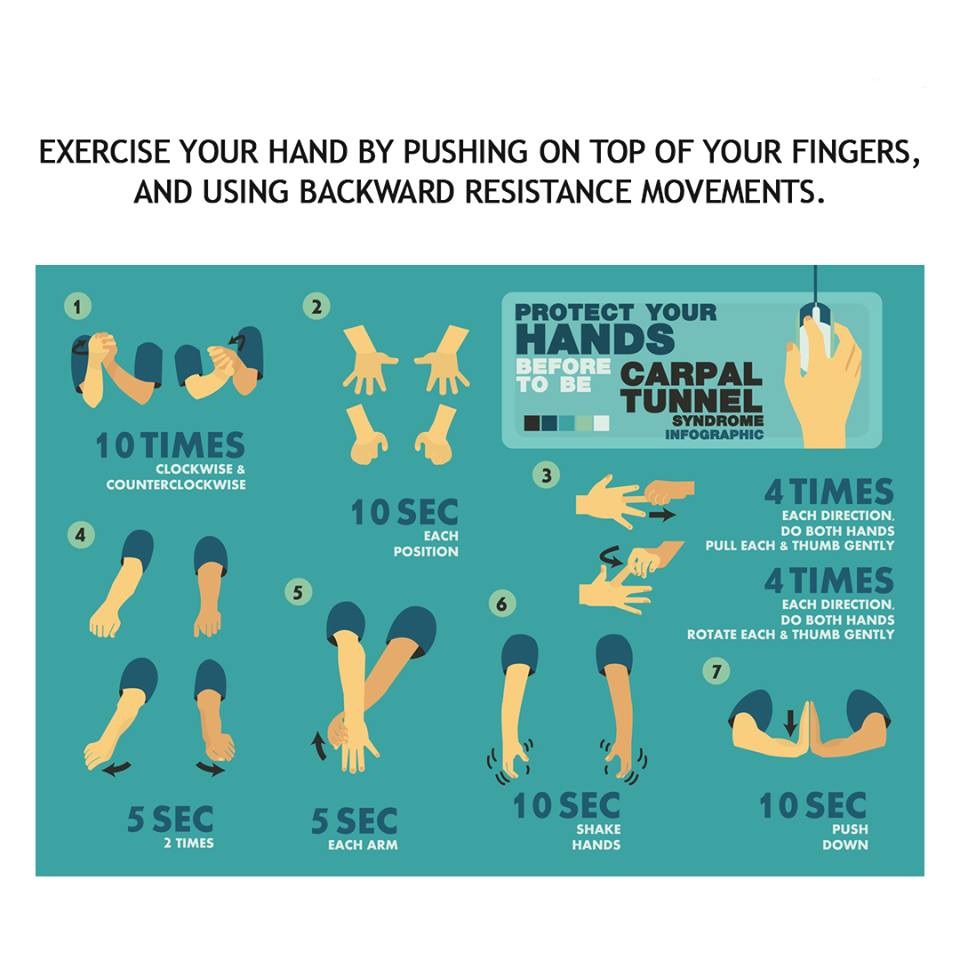
Take small breaks during your workday to release some of that muscle tension. Studies have shown that constant sitting is very damaging to your health. Try walking around for a couple minutes, standing and doing stretches—anything to break up a full day of sitting on your bottom is good for you!
Take short 1-2 minute stretch breaks every 20-30 minutes. After each hour of work, take a break or change tasks for at least 5-10 minutes. Always try to get away from your computer during lunch breaks.
Avoid eye fatigue by resting and refocusing your eyes periodically. Look away from the monitor and focus on something in the distance. Rest your eyes by covering them with your palms for 10-15 seconds. Use correct posture when working. Keep moving as much as possible.
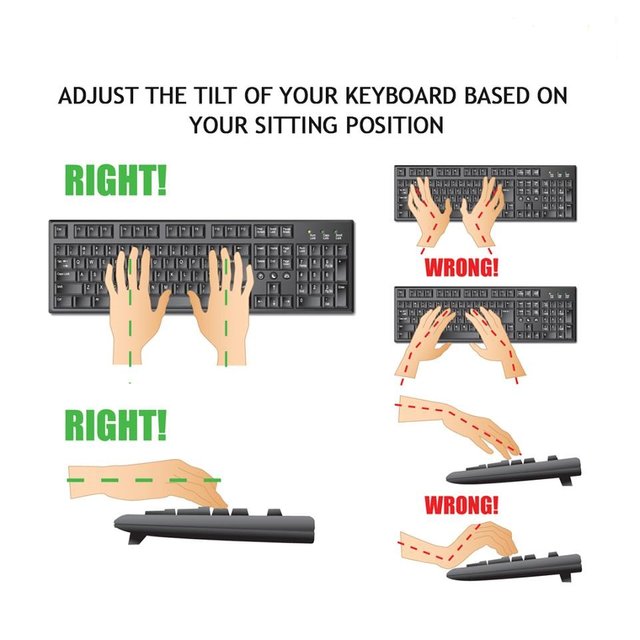
Adjust the tilt of your keyboard based on your sitting position. Use the keyboard tray mechanism or keyboard feet, to adjust the tilt. If you sit in a forward or upright position, try tilting your keyboard away from you, but if you are slightly reclined, then a slight forward tilt will help to maintain a straight wrist position.
Use wrist rests. They will help maintain neutral postures and pad hard surfaces. The wrist rest should only be used to rest the palms of the hands between keystrokes and not while typing. Place the mouse or trackball as close as possible to the keyboard.
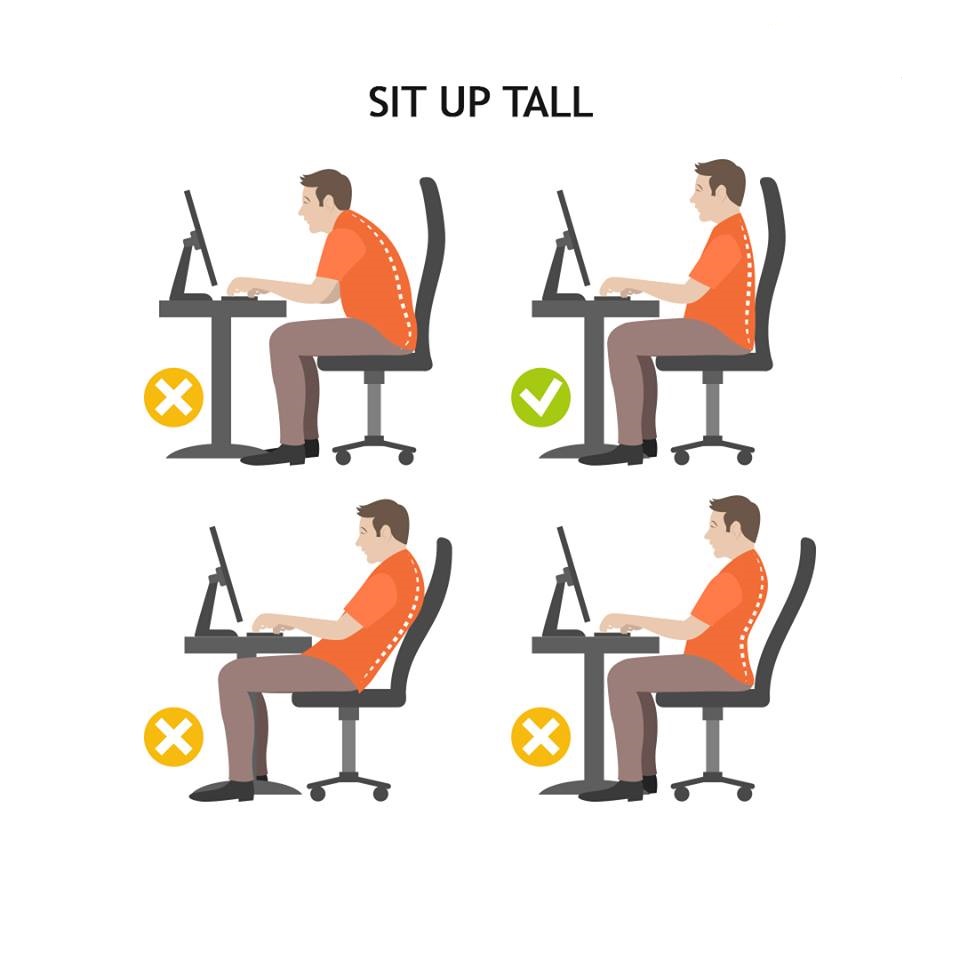
Sit up tall. Push your hips as far back as they can go in the chair. Adjust the seat height so that your feet are flat on the floor and your knees equal to, or slightly lower than, your hips. Adjust the back of the chair to a 100°-110° reclined angle. Make sure that your upper and lower back are supported. If necessary, use inflatable cushions or small pillows. When your chair has an active back mechanism use it to make frequent position changes. Adjust the armrests so that your shoulders are relaxed, and remove them completely if you find that they are in your way.

Sit close to your keyboard. Position it so that it is directly in front of your body. Make sure that the keys are centered with your body.

Adjust the keyboard height. Make sure your shoulders are relaxed, your elbows are in a slightly open position, and your wrists and hands are straight.

Position your monitor properly. Adjust the monitor and any source or reference documents so that your neck is in a neutral, relaxed position. Center the monitor directly in front of you, above your keyboard. Position the top of the monitor approximately 2-3” above your seated eye level. If you wear bifocals, lower the monitor to a comfortable reading level.
Sit at least an arm's length away from the screen and adjust the distance for your vision. Reduce any glare by carefully positioning the screen, which you should be looking almost straight at, but partially looking down. Adjust any curtains or blinds as needed. Adjust the vertical screen angle and screen controls to minimize glare from overhead lights.
Position the source documents directly in front of you, and use an in-line copy stand. If there is insufficient space for that, place the documents on a document holder positioned adjacent to the monitor. Place your telephone within easy reach. Use headsets or a speaker phone to eliminate cradling the handset.