Cryptocurrency basics - 3 key characteristics and why they matter

In order to believe in the crypto revolution, it's important to understand the fundamental aspects of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology that makes it so revolutionary. The 3 key characteristics of cryptocurrencies are that they are trustless, immutable, and decentralized.
Bitcoin: our first and most prominent example
Bitcoin is a cryptographically secure currency that was created to be used universally for payments, similar to cash. It was also created with the replacement of all forms of fiat currency in mind.
3Because the Bitcoin code is open source, people have been creating their own versions of Bitcoin, a.k.a. "Alt-coins" for the past few years, and the vision of Bitcoin replacing all fiat currency is becoming less realistic, with bitcoin's current dominance at 45% (less than half) of the total cryptocurrency market. 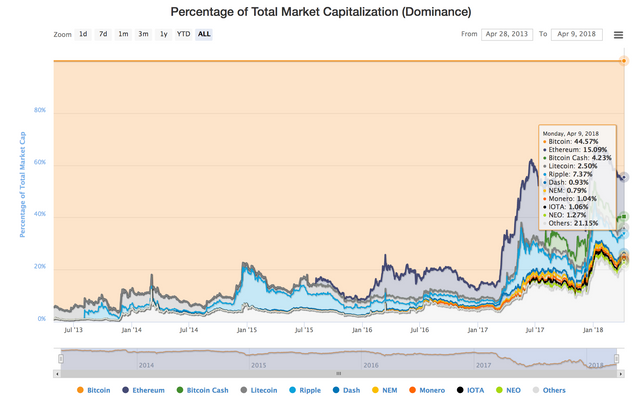
However, bitcoin and altcoins share very similar blockchain technology and the 3 key characteristics also apply across the board (in most cases).
These 3 characteristics we will discuss are the answers to the questions you might often hear from skeptics such as: "what makes cryptocurrencies so special?" and "How are cryptocurrencies any different that fiat currencies?"
1) Trustless
Bitcoin is trustless because it was designed in a way that nobody has to trust anybody else in order for the network to function. The consensus algorithm, known as proof-of-work
Every form of currency before bitcoin required a central authority that you had to trust in order to use it. In all cases, that central authority becomes the central weakness that leads to the demise of the currency.
With bitcoin, each part of the ecosystem validates what the other parts are telling it without needing to trust anybody. If you broadcast a bitcoin transaction, all nodes receive it and verify that the signatures are valid. If the signatures are not valid, they discard the transaction.
Everyone on the network has a copy of the ledger so we no longer need to trust a single entity/organization/third-party because there is no need to trust when you can just verify against this ledger because you have a copy of it. The decentralized ledger is known as the blockchain.
ncentivization of individual network actors though the proof-of-work (PoW) consensus algorithm is one of the most groundbreaking ideas in modern economics.
The incentive may help encourage nodes to stay honest. If a greedy attacker is able to assemble more CPU proof-of-worker than all the honest nodes, he would have to choose between using it to defraud people by stealing back his payments, or using it to generate new coins.He ought to find it more profitable to play by the rules, such rules that favor him with more new coins than everyone else combined, than to undermine the system and the validity of his own wealth.
— Satoshi Nakamoto
Although we are still figuring out exactly how we use cryptocurrencies and and what for, they are here to stay. Aside from the other major benefits of cryptocurrencies and blockchain tech, solving the centralized trust issue alone is a big enough innovation to give crypto staying power.
2) Immutable
"Immutable", in its simplest sense, means "cannot be undone."Immutability in regards to blockchain and cryptocurrency should follow 3 principles:
When we want to check how money has been spent from our bank accounts, we check our transaction history with the bank. We trust our banks not to fabricate transactions or manipulate our money as we trust them to deliver our transactions to recipients. If there are fraudulent transactions, the bank also needs to be trusted to change them and fix the situation.
- It should be highly improbable or highly difficult to undo a state change (i.e. rewrite history)
- It should be impossible for anyone but the owner of a private key to move funds they own (subject to the above).
- All state changes are recorded on the blockchain (to guarantee the above principles are true).
As we have already seen that the elements of centralization and trust are removed from cryptocurrency, there is no longer a third part for us to trust to do these things. Therefore, transaction records are made public and unchangeable (immutable).
The cryptographic security of cryptocurrency makes it so that although it isn't impossible to change the transaction ledger, it is extremely difficult and would require you to compromise the entire network of cryptocurrency users.
3) Decentralized
With "decentralization" no doubt being one of the top buzzwords in the cryptocurrency and blockchaincommunity, it's important to define it well; as it can take on different meanings."Blockchains are politically decentralized (no one controls them) and architecturally decentralized (no infrastructural central point of failure) but they are logically centralized (there is one commonly agreed state and the system behaves like a single computer)." - Vitalik ButerinSo, why is decentralization useful in the first place?
With central banks and governments, the supply and creation of money through mints and interest rates are at their sole discretion. Users of fiat currencies are at the mercy of the central banks' money-printing whims.
- Fault tolerance: decentralized systems are less likely to fail accidentally because they rely on many separate components that are not likely.
- Attack resistance: decentralized systems are more expensive to attack and destroy or manipulate because they lack vulnerable central points that can be attacked at much lower cost than the economic size of the surrounding system.
- Collusion resistance : it is much harder for participants in decentralized systems to collude to act in ways that benefit them at the expense of other participants. On the other hand, corporations and governments collude in ways that benefit themselves but others all the time.
The problem in this world is to avoid concentration of power — we must have a dispersion of power .— Milton FriedmanIf you are not yet outraged by the central banking money-printing scam, it is helpful to think of it as a hidden tax when they print and destroy the wealth you have stored in those fiat currencies.With cryptocurrency however, no individual or consortium is able to affect the supply of currency or exert significant influence over it without the approval of the majority.
Maximum Supply & Infinite Supply with pre-defined production
Many top cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin, Litecoin, and Dash have a maximum supply, making them deflationary by nature. Any increase in the demand or adoption of the cryptocurrency will cause a corresponding increase in the price.Most of the other major cryptocurrencies such as ethereum, monero etc., that have infinite supply have pre-defined rules for how many coins will be produced each year. Therefore they are predictable in nature. If these currencies are successful in the long-term, it's highly unlikely that the rate of production of more currency will result in any sort of inflation.
The increasing demand, adoption, and destruction of coins in the form of lost private keys will likely offset any moderate increase in supply due to PoW/PoS mining rewards.
Conclusion
So there you have it. Next time anyone asks you those pesky questions like "what's so special about crypto?" or "what makes them any different", you can take them to school on the 3 key characteristics: trustlessness, immutability, and decentralization.Hold On for Dear Life
Posted from my blog with SteemPress : https://hodlcrypto.co/2018/04/09/cryptocurrency-basics-3-key-characteristics-and-why-they-matter/
