How blockchain works
Blockchain is the technology the underpins digital currency (Bitcoin, Litecoin, Ethereum, and the like). The tech allows digital information to be distributed, but not copied. That means each individual piece of data can only have one owner.
You may hear it described as a “digital ledger” stored in a distributed network. Blockgeeks has a good analogy to help understand how Blockchain works:
“Picture a spreadsheet that is duplicated thousands of times across a network of computers. Then imagine that this network is designed to regularly update this spreadsheet and you have a basic understanding of the blockchain.”
The information is constantly reconciled into the database, which is stored in multiple locations and updated instantly. That means the records are public and verifiable. Since there’s no central location, it harder to hack since the info exists simultaneously in millions of places.
Blockchain technology was invented in 2008, but only came into the public conversation when Bitcoin launched.
Why Is It Called Blockchain?
A block is record of a new transactions. When a block is completed, it’s added to the chain. Bitcoin owners have the private password (a complex key) to an address on the chain, which is where their ownership is recorded. Crypto-currency proponents like the distributed storage without a middle man — you don’t need a bank to verify the transfer of money or take a cut of the transaction.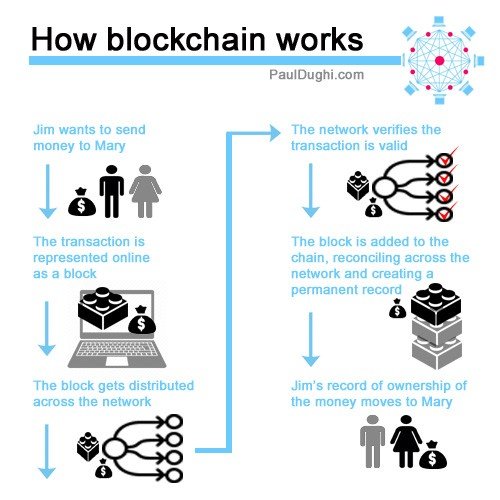
✅ Enjoy the vote! For more amazing content, please follow @themadcurator for a chance to receive more free votes!
Congratulations @impankaj14! You have completed the following achievement on the Steem blockchain and have been rewarded with new badge(s) :
Click here to view your Board
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOP