Do you know there are different types of Blockchain?
Blockchain is a shared immutable ledger for recording the history of transactions. Mainly there are two types of ledger:
Public Ledger: Decentralized, anycome can read and send tranasctions. e.g. Bitcoin, Ethereum
Private Ledger: Centralized under one organization which controls the right to view and sens transactions. e.g. Bankchain, multichain
Based on permissions blockchain maily of two types:
Permissionless Blockchain: Every node in the network participate in consensus procedure, e.g. Bitcoin Blockchain (Proof of Work)
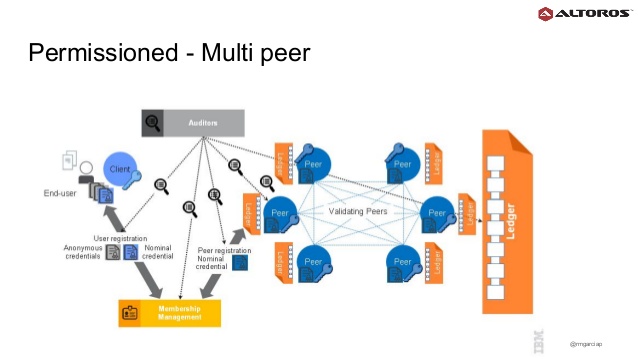
Permissioned Blockchain: Only Selected nodes(validators, e.g. Government or trusted nodes) participate in consensus procedure e.g. Hyperledger Blockchain
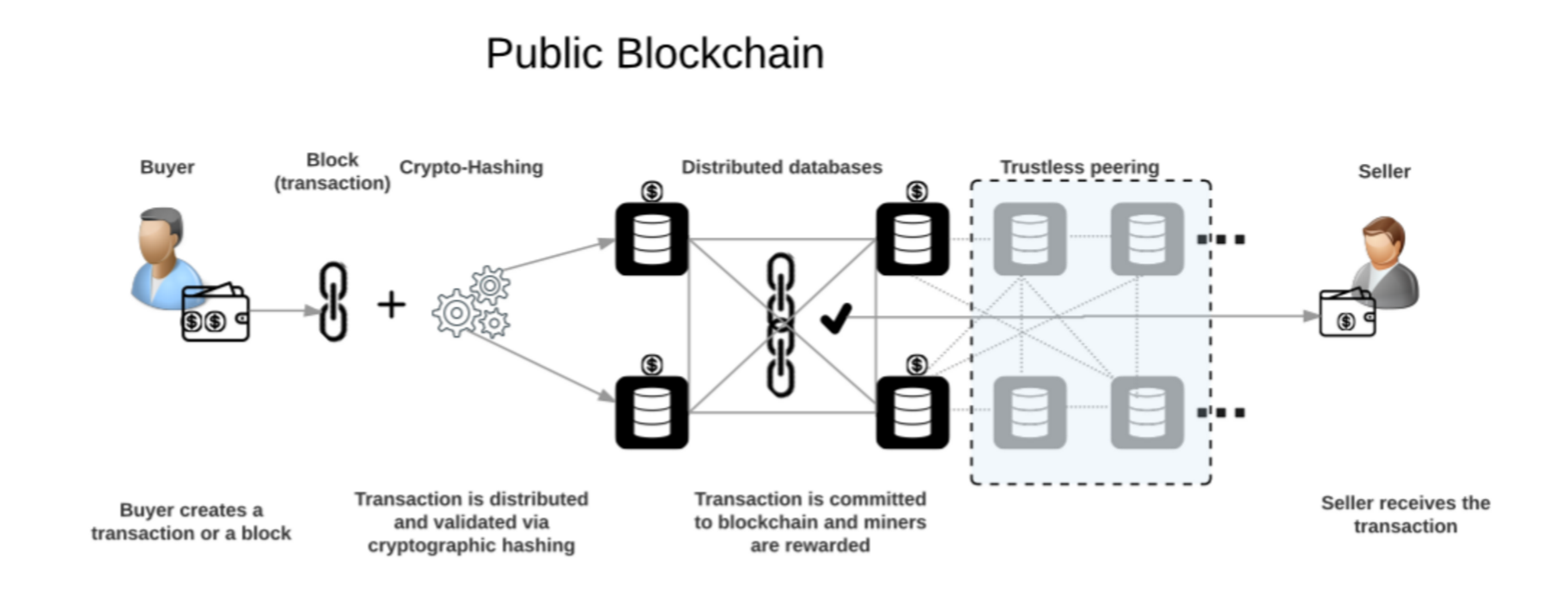
Public Blockchain: Anyone in the world can download the data and read the data. Anyone can participate in the consensus process to write the data or block into the public Blockchain. There are numerous public blockchains. Bitcoin which is a peer to peer currency exchange was the first public Blockchain followed by Ethereum which allows anyone to build smart contracts and decentralized apps on it. Some other examples are Dash and Lisk. It is highly secured using cryptography and consensus protocol.
Examples – Bitcoin, Ethereum, Dash, Lisk, Factom and Blockstream
Consortium Blockchain:
Consortium Blockchain as the name suggests is controlled by a consortium of members. It has pre- defined set of nodes, the users with access to write the data or block. For example in the case of Trade Finance use case, the consortium may be participating banks, importer, exporter, ports of sending and receiving countries, custom officials etc. Some of these participants will have write access and some or all will have read access. It is not fully decentralized as public blockchain.
Examples – Ripple and R3
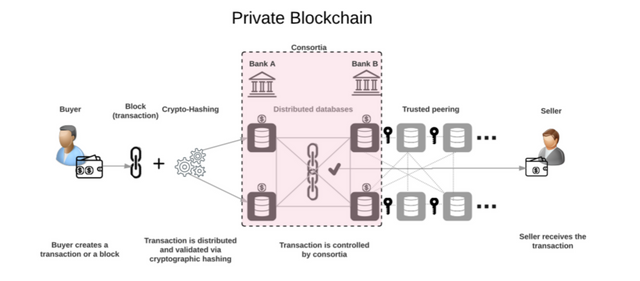
Private Blockchain:
In Private Blockchain, all permissions are kept centralized to an organization. Companies who wanted to create own currencies started using this type of Blockchain. One major criticism of Private Blockchain is that since it is not decentralized, it’s just a distributed database. There are some points in favor of this approach. One it allows some organizations who have compliance and privacy requirements to implement Blockchain. Second, it adds the values like cryptographic auditing and known identities to the internal processes. But with private Blockchain, the central idea and beauty of decentralization and open protocols gets lost.
Examples – Multichain, Blockstack
Stay tuned for more updates!