Coco Framework a game changer in Blockchain technology (Throughput of around 1600 transactions per second)
Blockchain technology is getting lots of attention from enterprises but almost all existing blockchain standards are not able to meet the requirements of an enterprise level solution. Some of the initial requirements of a blockchain solution required by enterprise are high transaction throughput & latency, effective governanace, confidentiality and computational efficiency.
In most of the existing blockchains solutions participants are untrusted. These untrusted participants submit transactions, create blocks and add new blocks in the blockchain using the consensus.
Coco framework is trying to simplifying consensus and reducing duplicative validation by creating a trusted network on nodes, where participants identities are known and controlled. Coco framework is compatible with any blockchain protocol, intially starting with Hyperledger Sawtooth, Ethereum, Corda, and Quorum. Coco framwork will provide following advantages for creating enterprise ready solutions:
- Throughput and latency approaching database speeds
- Richer, more flexible, business-specific confifentiality models.
- Network policy management through distributed governance.
- Support for non-deterministic transactions
- Reduced energy consumption
These are achieved in Coco framework by the use of Trusted Execution Environments also known as TEEs. Intel’s SGX and Windows VSM will be used for the creation of trusted execution environment.

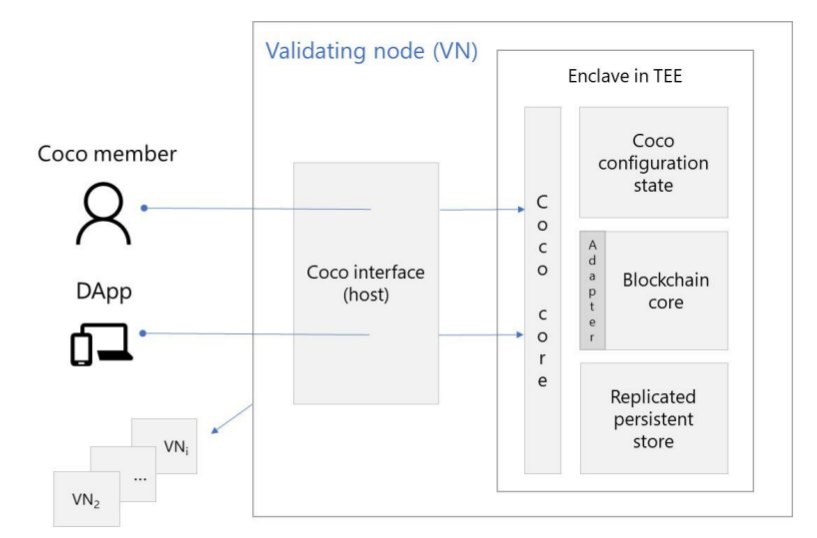
Lets explore the Coco architecture:
Validating Nodes: Distributed network of trusted nodes, running Coco framework & blockchain protocol. Used to verify the identity of participanting nodes in the network and validate the code using TEE at runtime.
Coco interface: A gateway for the end user to interact with VNs.
Coco cores: An interface between the end user and all other functionality within the VNs.
Persistent store: Ledger state is stored here
Coco configuration state: Used to create network constitution
Blockchain core and adapter: All transactions or smart contract are executed here, blockchain protocol are integrated in Coco system using this.
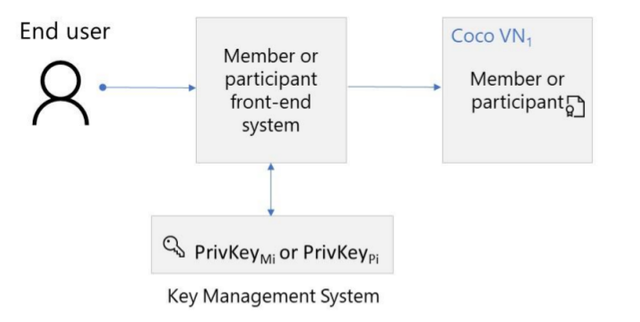
There are two types of actors in the Coco network. Both use a private/public key pair and identified using X.509 certificate within the Coco network.
Members: Members are the governing bodies of a consortium and defines the set of rules for the Coco ecosystem. Members run VNs and define initial configuration of a Coco network. Any chances in the network like modifying underlying rules, adding new memebers will be done by a vote caste by existing members.
Participants: They have no operational control on the network and can be added by the members by voting process. Participants can transact on the network and run their own VNs.
Coco network includes a membership list(list of all approved actors), VN list (list of all approved validating nodes in the network), code manifest (specifications of Coco framework versions, blockchain protocols, all approved code that can run within the Coco network.), TEE manifest (specification of all approved execution environments) and voting policies.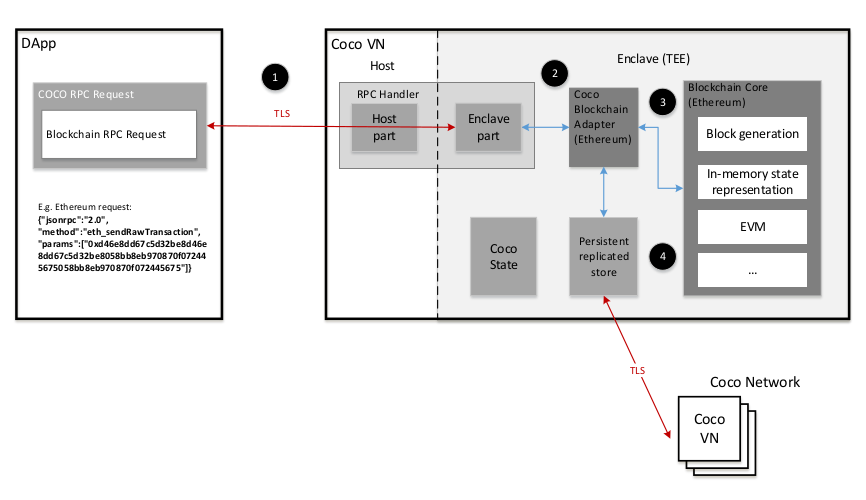
The Coco Framework is designed to support pluggable consensus algorithms — with plans to initially integrate Paxos-like consensus algorithms and Caesar consensus, an algorithm from Microsoft Research.
Microsoft selected 2000 transactions from the public Ethereum network to feed through the prototype. In general, transaction rates were roughly 100 times faster than for a non-Coco-enabled protocol.
This shows that Coco framework will be a game changer for enterprise blockchain solutions as it have the high throughput and latency.
In this article i have tried to cover the important part of Coco framework by using the Coco white paper as reference. It is supposed to release this year. I will update you with implementation details when it becomes available for public use.
Hi! I will upvote and resteem your post to my 35,000+ followers if you reply to this comment.
👍🏻 a-0-0