PLATON; THE BLOCKCHAIN OF BLOCKCHAINS

Blockchain Technology is considered as a community-oriented open source initiative where each member of the decentralised network has the power, in place of a central authority.
With the Blockchain, it is possible today to transfer money from any part of the world without third party interference such as banks or any other centralized financial institution. This in turn eliminates unnecessary transaction charges which can be very expensive and in some cases unaffordable. Blockchain breaks trust barriers and offers seamless opportunity for executing transactions across national borders.
One outstanding feature of the blockchain is that it is decentralized and designed to resist any form of data modification. Therefore, it cannot be controlled or manipulated by an individual, organization or government.
Blockchain technology brings greater transparency, enhanced security, improved traceability, increased efficiency, and speed.

The blockchain is driven by a collaborative computing model where trust is shifted to the computers and eliminates the need to have trust an individual in executing transactions. The model also allows the integrity of the computer to be verified without the assistance of an intermediary.
The emergence of the blockchain has led to the success of the Bitcoin , Ethereum ( run on tge Ethereum smart contract). Blockchain is run and maintained by miners who in turn get paid for using their hash rates in verifying transactions and using computational power to solve difficult mathematical problems. These can take a lot of time and consume a lot of energy (electricity) thereby producing lots of heat.

When someone makes a purchase or sale using bitcoin, we call that a “transaction.” Transactions made in-store and online are documented by banks, point-of-sale systems, and physical receipts. Bitcoin miners achieve the same effect without these institutions by clumping transactions together in “blocks” and adding them to a public record called the “blockchain.”
Scalability has also remained a huge problem that has hindered the global blockchain space from growing and becoming truly decentralized. Various blockchains cannot easily interact and exchange data or execute transactions because they operate on different consensus.

Some attempts have been made to try solving this issue in the industry by separating the computing tasks from the consensus layer and operating a migrated offchain. This strategy of solving the issue is called the offchain strategy which allows trustless entities collaborate and design a verifiable computing minfrastructure.
The PlatON team has created a real world solution that can handle major issues bothering the blockchain industry like the scalability issue. PlatON works using a Verifiable Computation algorithm which does not rely on an external setup (unlike previous attempts made at solving the problem). This helps to ensure that the proof size is shortened to a large extent and a super fast proof generation and verification process is enabled.
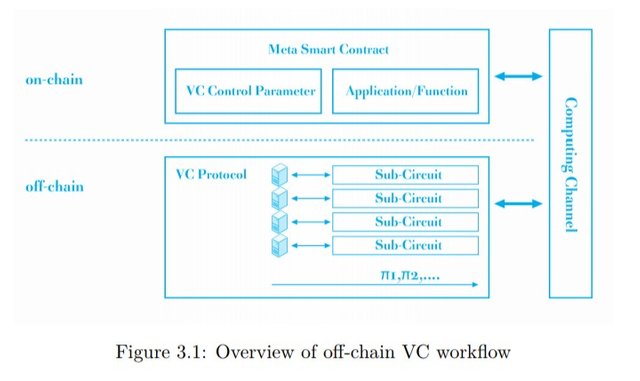
PlatON uses a high efficiency verifiable computing algorithm built on a homophobic encryption and a safe multiparty computation. It offers an all round solution for trustless computing and also ensures client's data and computing logic remain private.
In some cases trusted computing usually depends on what is obtained from trustless hardware as offered by the third party intermediary for computing integrity. PlatON is different as it depends on falsifiable cryptographic assumptions alone, this guarantees absolute security of private data for a very long time with no trust limit.
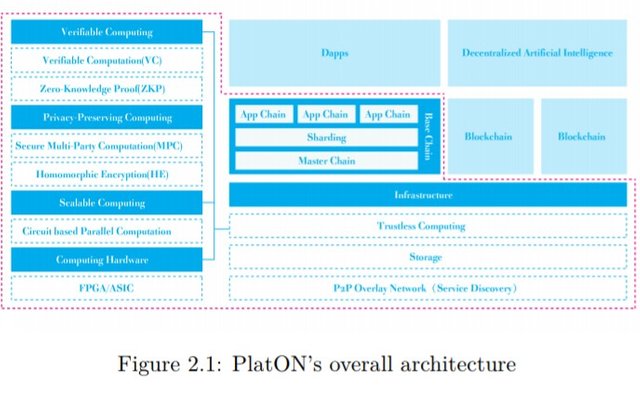
The onchain consensus on PlatON is independent of the computation, hence it does not suffer from the scalability, decentralization and safety issues encountered on the blockchain. Basic computation is handled by multiple computing nodes which ensure quick verification and in turn speeds up the whole process. Computing nodes here are simply the providers of computing services for the Platon network and are responsible for executing various computing tasks.
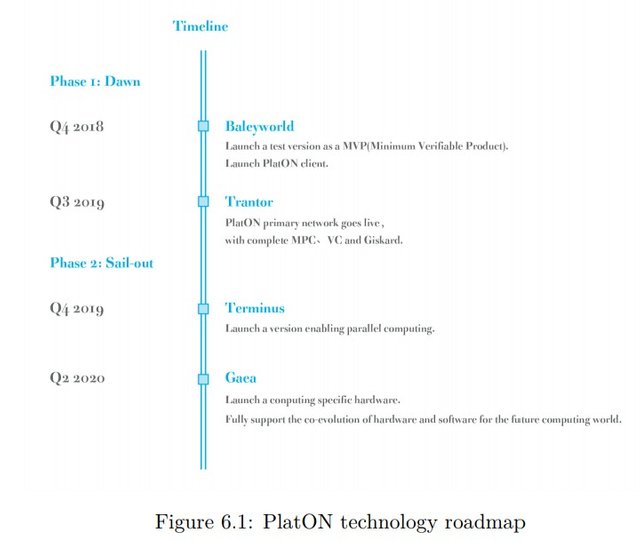
PlatON offers an absolute trustless computing architecture which can be deployed for creating Decentralized Applications or improving blockchains. PlatON blockchain infrastructure serves as the primary blockchain which rewards computing nodes and proofs, it will also be an unchangeable database for preserving states and proofs.
You can check out the PlatON network and be a part of the project through the links below.
Web: https://www.platon.network/
Twitter: https://twitter.com/PlatON_Network
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/PlatONNetwork/
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/platonnetwork/
Telegram: https://t.me/PlatONHK
White paper: https://platon.network/static/pdf/en/PlatON_A_High-Efficiency_Trustless_Computing_Network_Whitepaper_EN.pdf
Bounty0x Username: Donrep09
