Polkadot ICO Report
The information contained in this report is not legal or financial advice and is for informational purposes only. The projects included in cyber•Fund reports vary significantly in terms of investment risks. Before considering any investment, make sure you read the report below carefully and take time to do your own due diligence.
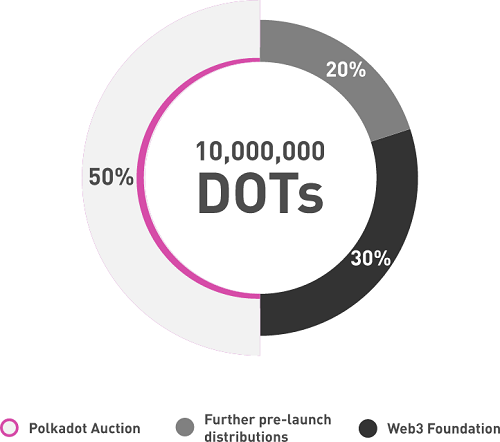
Polkadot project develops the network protocol that connects independent blockchains and allows independent blockchains to exchange information. The project’s goal is to create the network of blockchains with the data and user identity independent from any central authority. The network is being developed by the Parity Technologies, the blockchain consulting company founded by Dr. Gavin Wood, co-founder of Ethereum. The Polkadot’s protocol will be the open source one. The team’s technical vision of this product and the code of its core components are available on GitHub: WASM backend, Bridge, Light client proofs, Secret store and Singer, Consensus. The ICO smart contract has also been presented. Expectedly, a genesis block launch of Polkadot will be in Q3/ 2019 with 10,000,000 DOT token supply, out of which 50% will be distributed among ICO participants whose contributions are accepted since October 15th, 2017. 30% goes to the Web3 Foundation and 20% is allocated for further pre-launch distributions.

About
The Polkadot is a multi-chain technology. It is being built to connect both public and private chains, oracles and new emerging technological tools that can enrich the Web3 (the decentralised web) ecosystem. It creates a cross-chain environment where independent blockchains can exchange information and trust-free transactions using the Polkadot’s inter-chain system providing the benefits of scalability, governance and interoperability. Polkadot’s protocol is designed as an inter-chain blockchain protocol that brings order and validity to the messages that transit between the chains. The scalability effect results from creating a common environment for multiple chains with different consensus mechanisms and inner security options. The project is in development since the end of 2016, and the Polkadot’s first genesis block is expected in Q3/2019.
Platform use-cases
- Collators maintain parachains (see Technology section below) by pooling transactions from users and produce new candidate blocks for validators. Collators submit blocks ensuring proof-of-validity. Collators collect all fees related to transactions they maintain; in this kind their roles resemble the roles of miners in present-day blockchains
- Validators
- verify information contained in a particular set of parachain blocks, thus validating proofs from Collators by staking DOT tokens issued by Polkadot
- participate in the consensus mechanism to produce the relay-chain blocks based on validity statements from other validators
In other words, they add new blocks to the relay-chain with further move to all parachains making it possible for the parties to complete cross-chain transactions via the relay-chain (see Technology section below). Validators are “bonded” that means they put a “security deposit” which can be lost in case of the validator’s misbehavior: any non-compliance with the consensus algorithms: improper execution of functions described in the whitepaper (page 16, par. 6.7). Good performance, in return, will be rewarded: they will receive transaction fees in the form of DOT tokens.
- Nominators secure the relay-chain by selecting good validators (executing the validation process in accordance to Polkadot’s rules) and staking DOT tokens; they are not expected to participate in transaction validation. Their role is to nominate validators and contribute to the security bond of their nominated validators. Bonding DOT tokens to a validator requires nominators to perform constant analysis in order to select the validators that are the most likely to behave according to the Polkadot protocol rules. Nominators’ DOT holding increases or decreases correspondingly to the growth or reduction of the “security bond” to which their DOT tokens were contributed
- Fishermen monitor Polkadot network activities on misbehavior of validators, on any breach of the Polkadot’s governing rules. Fishermen are not supposed to participate in the process of validating transactions in the same way as validators or nominators, but rather serve as a constraining mechanism to deter bad actors. Fishermen will be required to deposit fewer DOT tokens via “security bond” in order to participate in the process, but will receive a larger portion of DOT tokens as a reward (comparing to rewards received by validators and nominators in proportion to the size of their “security bond”) when demonstrating a proof of a particular breach
- The Polkadot users won’t be involved in the blockchain facilitating process, but they will be interested in the Polkadot protocol for the following purposes:
- Inter-chain transfer of data/value
- Triggering smart contracts hosted by other chains
- Linking private to public chains
- Using it for migration to newer/better chains.
Market
The number of blockchains is increasing with a need to process mutual transactions. The Polkadot will serve well when a user will need to create its own state transition engine, specific to a particular industry and meeting the necessary industry requirements, for example: healthcare, legal, insurance, transportation & logistics, IoT, etc. These specific blockchains will need to be compatible with a wider range of developing chains, and the Polkadot will ensure compatibility and “common security” for all interacting blockchains: private and public, irrespectively to their inner features. For example, if the Ethereum smart contract triggering the payment by the SWIFT system proofs its viability, it won’t be necessary to develop a similar solution for other types of blockchains. This smart contract can be called successfully from other chains powered by the Polkadot protocol.Thus, blockchain developers can focus on tailoring specific solutions leaving to Polkadot a work on common functions and integration.
Competitors
The Polkadot is not considered to be a competitor to Ethereum, Bitcoin, or any other chain. Also, the Polkadot is not intended to compete with other inter-chain solutions such as Cosmos (even though their goals can look similar to some extent), Hyperledger and many others which have also promised scalability and privacy as part of their consensus. By its concept, the Polkadot will rather cooperate with existing and emerging chains. It would be prudent to look at the Polkadot as “a blockchain platform”, meaning a platform for developing, experimenting with, deploying and maintaining other blockchains. Comparing to other inter-chain solutions, the Polkadot will have distinct advantages by its design, such as scalability, compatibility with other chains maintained and shared security.
Technology
- An open source project being shaped as a heterogeneous multi‑chain technology that provides solution to the blockchain scalability and interoperability problem through creating the common inter-chain environment compatible with blockchains run with different consensus models and pooling their inner security features, so creating the “common security” mechanism. The Polkadot “as it is” won’t provide any application functionality, and this makes it different from other blockchain implementations trying to reach some degree of generality. In return, the Polkadot builds the secure common home for a large number of validatable and becoming globally-compatible data structures
- Consensus: PoS; according to the Polkadot’s whitepaper, the nominated PoS consensus (NPoS). It will be necessary to elect validators (whose role described above); the DOT tokens will play a role of a “stake” for each account
- Scalability: Polkadot is designed to provide a possibility to run several inner chains called “parachains”, each processing multiple transactions in parallel, which allows networks to obtain great scalability
- Security: Polkadot maintains security within the network, which means that individual chains can leverage collective security
- Interoperability: Polkadot is designed to enable applications and smart contracts on one blockchain to seamlessly transact with data and assets on other chains.The Polkadot’s whitepaper (page 7, paragraph 5.4.) provides an example of how an inter-chain transaction can be processed
Polkadot Components:
- Relay-chain coordinates consensus and transaction delivery between chains; the Byzantine fault tolerant “BFT” algorithm (described in the Tendermint) is employed to achieve low-level consensus for a set of commonly approved valid blocks in the relay-chain
- Parachains are designed as extensible elements that can be plugged into the relay chain similar to the concept of sharding in Ethereum. Creating parachain will not require building a consensus mechanism from a scratch, and all parachains will be capable to interact with each other
- Bridges link to blockchains with their own consensus such as Ethereum; no details found concerning inter-chain consensus compatibility
Economics and token
- Polkadot has its own token DOT
- The DOT will have a fixed supply of 10,000,000 DOT at a genesis block. The DOT will have uncapped supply and predetermined inflation mechanism; however, no detailed info concerning the inflation rate found so far
- Token utility:
- to facilitate participation by holders of DOT tokens in the protocol governance
- to facilitate participation by holders of DOT tokens in the relay-chain’s Proof of Stake consensus mechanism
- to serve as a value metrics: the rewards for Polkadot’s validators for their active participation in the network will be denominated in DOT tokens, with higher value contributions being rewarded with a higher number of DOT tokens
- Being designed to serve limited functions facilitating the Polkadot protocol, the DOT tokens will lack liquidity at the beginning
Company
The Polkadot is developed by the Web3 Foundation. Parity Technologies will be contracted by the Web3 Foundation to build the Polkadot network. Parity Technologies is a technology company incorporated in England and Wales. Dr. Gavin Wood, the member of the Web3 Foundation council, holds a major share stake in Parity Technologies; other Web3 Foundation council members also hold shares or other equity interests. There is, however, no direct group relationship reported between the Web3 Foundation and Parity Technologies.
Team
The Polkadot is developed by the Parity Technologies team. The core team consists of 30 developers with expertise in systems programming, cryptography, and distributed systems.
ICO
- The ICO started on October 15th, 2017 with 454,268 ETH already raised (as of October 23st, 2017, 1 AM (GMT)
- ICO is organized in the form of the Dutch auction (without the pre-ICO stage): the price of the tokens would decline over the course of the sale. The exchange DOT/ETH rate starts very high and decreases over time until all tokens are exchanged. All participants will get the same final exchange rate which is determined at the end of the auction
- The amount of tokens offered: 5,000,000 DOT tokens (50% of the total genesis supply)
- Token offered for sale: the DOT token
- Contributions accepted in ETH
- Early birds bonus announced: 15% for the “first hour” contributors
- A mandatory registration to participate in ICO is needed using Parity's PICOPS as KYC service
- Distribution date: The DOT will be issued with the Polkadot’s genesis block in Q3/2019; the token (or its ownership right) is not transferable until this moment
- ICO webpage: https://sale.polkadot.network
- Terms of Sale: https://polkadot.network/memorandum
- DOT token smart contract code can be found here, its audit is here
Token distribution
- Token genesis supply: 10,000,000 DOT, not fixed
- 50% (5,000,000 DOT) - to ICO participants (with 15% discount for the first hour contributors)
- 2,000,000 DOT will be reserved for participants in one or more later sales, or otherwise distributed to the public in a fashion to be determined by the Web3 Foundation
- 3,000,000 DOT will be allocated to the Web3 Foundation to be retained or distributed at its sole discretion
Use of proceeds
The Web3 Foundation intends to use funds raised through the sale of DOT tokens to finance the development of Web 3.0 Technologies, including Polkadot. The Foundation plans entering the software development agreement with Parity Technologies under which Parity Technologies will conduct research and develop the Polkadot protocol with further deployment of the Polkadot genesis block.
Summary
- The Polkadot provides an innovative concept of multi-chain environment enabling value and data transfer between blockchains of a different type (private/public), consensus patterns and security options
- The core value of the concept proposed is in resolving the crucial problems of blockchains scalability, compatibility and “shared security” irrespectively to the chains’ inner features. This will allow developers to focus on creating tailored and industry-specific applications on blockchains of their choice when common tasks, such as the chain compatibility and even security, will be ensured by the Polkadot solution
- The Polkadot is not intended to be a competitor of Bitcoin, Ethereum or others (even those promising the benefits of scalability, such as Hyperledger). The Polkadot functions are similar to Cosmos in terms of allowing inter-chain value transfers, but it creates additional options, such as data transfer between the chains: an interaction between smart contracts hosted by different blockchains. Another important advantage of the Polkadot is that it is supposed to cooperate well with both the established and emerging blockchains
- The Polkadot’s genesis block is expected in the Q3/2019. The technical specifications provided in the whitepaper describe the concept “as it intended to be”; thus, a high degree of uncertainty remains concerning the way of how the concept will be executed and its final properties
- The DOT tokens will be issued at genesis block. The ICO contributors won’t be able to transfer their right of DOT ownership before this time. There is no mechanism of exchanging the DOT for the underlying value of fiat currency provided or supported by the issuer; from this point of view, the DOT can hardly be considered as any form of a virtual currency, though such a consideration is possible under the laws of certain jurisdictions
- The main DOT function is to empower the holders to exercise certain rights related to managing processes of the Polkadot, including determination of fee structures, the addition or removal of parachains and proposed changes to the protocol operational process. Delegation of rights is not expressed in any legal form (or a binding agreement), but rather predetermined by the algorithm of the underlying code of Polkadot protocol
- Holding the DOT, as explained on the Polkadot.network, “...doesn’t confer any ownership or voting right or interest in the Foundation, nor will a holder of DOT tokens be entitled to any share of the income of the Foundation or any other party. Further, a holder of DOT tokens will not be entitled to any proceeds raised in connection with the sale of DOT tokens, nor will a person have any right against the Foundation or any other person in respect of any funds provided in connection with the sale of DOT tokens.”
Useful links
For more details on the project check the project’s website, Whitepaper or join their Riot.im.
You can also check Polkadot’s profile on cyber•Fund website or improve Polkadot’s page on Github
Done by @cyberanalytics — the team of the cyber•Fund company that conducts the analysis in fields of crypto-economics and blockchain industry
You can also read this article on Medium
