@CateredContents Writing Contest : Harmony, the Revolutionary Blockchain Solution
The Blockchain Revolution
Still unsatisfied at the scalability problem that persisted, several blockchain proposed the replacement of Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus by Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus. However, some blockchains like the EOS make use of Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS), which allows for the election of block proposers by voting rather than subjecting it to a non-chain algorithmic process. Irrespective of the several trials, blockchains that came close to achieving a highly scalable network were projects like the IOTA which replaced chain-of-blocks data structure with the Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) data structure, thereby breaking away from limitation in sequential processing of transactions but sacrificing security and decentralization which renders it an inefficient solution. With the emergence of sharding concept, later blockchain solution such as Zilliqa were able to tackle scalability problem but however was deemed “inefficient” because of its inability to fully handle decentralization and security. Capitalizing on strengths and building on weaknesses in previous blockchain solutions consequentially brought about the Harmony blockchain network that adopts the sharding concept which enables it to create multiple groups of validators used in processing a large number of transactions concurrently.
What is Harmony?

Harmony is a next generation sharding based blockchain capable of providing a highly scalable, secure and energy efficient network.
What makes Harmony better?
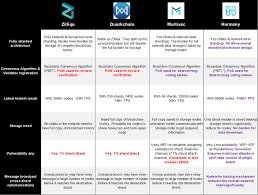
Harmony is better because it addresses the problems and flaws of existing blockchains by combining the best research results and engineering practices in an optimally tuned system. Harmony is a PoS blockchain capable of linear scaling, enabling unprecedented transactions per second, also with the ability to scale easily as the network becomes heavily utilized. As opposed to other sharding network, Harmony scales decentralization to a completely new level. Harmony is as a result of persistent need for an improved and efficient blockchain network. Harmony will enable applications which were not previously feasible on blockchain, and it includes; high-volume decentralized exchanges, interactive fair games, Visa-scale payment systems, and Internet-of-Things (IoT) transactions.
Benefits of using Harmony as an underlying Infrastructure
Harmony as an Underlying Structure will provide projects with;
- Scalability: Due to the efficient utilization of shards by the Harmony network, it proves to be the most scalable solution not just in transaction validation and network interactions, but also in the state of the network. Sharding of the blockchain state reduces the restrictive nature of storage requirements to the minimum.
- Secure Sharding: Unlike the sharding deficiencies in Zilliqa network, Harmony network sharding process has proven secure all due to adoption of the Distribute Randomness Generation (DRG) process which makes all interactions and transactions unpredictable, unbiased, verifiable and even more scalable.
- Efficient and Fast Consensus: Other sharding based blockchain solution makes use of Proof-of-Work (PoW) which requires selection of validators and it also consumes more energy. However, Harmony adopts a Proof-of-Stake concept which utilizes the right amount of energy to bring about an efficient network. Hence, Harmony proves more energy efficient than other PoW alternative solutions. Harmony also maintain a fast consensus by adopting a scalable linear Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT) algorithm that’s 100 times faster than the Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT).
- Adaptive Threshold PoS: Threshold of stakes is of adjustable nature and based on the total staking volume so as to curtail the probable influence and concentration of malicious stakers on single shard, and also the staking threshold is so low to accommodate the participation of small stakers in the network.
- Scalable Network Infrastructure: The RaptorQ fountain code in conjunction with the Adaptive Information Dispersal Algorithm provides Harmony with a scalable network infrastructure by fostering ease of block propagation within and across shard or network. Harmony also adopts the Kademlia Routing to achieve cross-shard transactions that scale logarithmically with number of shards. Unlike other previously existing solution with transactions of 5, 10, 15 etc., each new Harmony shard generates 1, 10, 100 more transaction.
- Consistent Cross-Shard Transactions: Harmony supports cross-shard transactions of shards in direct communication with each other. Also utilizes the Anatomic locking mechanism which ensures the consistency of cross-shard transactions.
Implication of having a resource efficient and linear scale network
Harmony’s network is resource efficient and able to scale linearly, thereby capable of providing necessary support for the growing needs of industries while also ensuring that those industries are not bottlenecked by their infrastructures.
How does sharding on multiple layers improve security and efficiency?
Sharding on multiple layers improves security and efficiency by dividing the database’s computational responsibilities into smaller segments or layers (called shards) which individually carry out their tasks, making the total burden of computation smaller i.e. instead of tackling large computational tasks, they are broken into smaller chunks which are easier to process. Harmony developed an adaptive threshold system to guarantee the security of the network.
Potential Use Case1
Charles Dickson is a successful crypto trader with lots of digital asset in holdings. What he does most of the time is to hold certain cryptocurrencies until they experience a price pump. Charles’s previous experience with other blockchain solution wasn’t totally satisfactory, as he’s had to wait a couple of times than necessary just to conclude an already initiated transaction. At the beginning, some of the blockchain he was opportune to transact on was secure and decentralized but scalability issue remains at large. He’s had to spend valuable portion of his time waiting on transactions he initiated, however, he knows delay isn’t good for business and he tried other available options. Other alternatives provided him with a scalable network but security and decentralization was the price he’s had to pay, and sometimes he’d incur losses in his crypto trading business because of that. Mike Deen, a fellow crypto trader learnt of Charles troubles and offered to help. He introduced him to the Harmony network, and even though Charles’s account was split into multiple balances at different shards i.e 6,000 tokens at Shard A, 500 tokens at Shard B and 800 tokens at Shard C, he’s still able to move his balance between shards with ease by issuing a cross-shard transaction. However, multiple shards in Charles’s transactions help make the total burden of computation smaller, easier, and faster to process. Splitting shards into multiple shards helps to reduce system complexity that exists. Harmony network provided Charles with the best decentralization exchange experience and also a secure haven for his funds.
Potential Use Case2
Ned Forbes is a gamer, he’s always had to participate in leagues, and in most cases won gaming token which can be exchanged for real-time value. Ned has been on the gaming network for long and in appreciation of the values he’s gathered, he decided to give back to the community by hosting one of such leagues. Ned was somehow troubled when he thought about his past experience with malicious stakers which had once brought about loss in a good percentage of his funds stored on the network. Ned’s brother- Greg, suggested that he should give Harmony a try. Harmony was able to meet Ned’s transactional expectations. He was able to transact with ease on the network, sending gaming tokens to the necessary party without incurring lost time incident.
Additional Resources
- Harmony Website
- Harmony OnePager
- Harmony WhitePaper
- Harmony Medium Blog
- Harmony Telegram Group
- Harmony Twitter
- Harmony LinkedIn
- Harmony Instagram
https://blog.ethereum.org/2014/07/05/stake/
https://searchoracle.techtarget.com/definition/sharding
Team Harmony
