WHAT IS CRYPTOCURRENCY ?
1)cryptocurrency is a digital currency built with cryptographic protocols that make transactions secure and difficult to fake.
2)The most important feature of a cryptocurrency is that it is not controlled by any central authority: the decentralized nature of blockchain makes cryptocurrency theoretically immune to the old ways of government control and interference.
3)Cryptocurrencies make it easier to conduct any transactions, for transfers are simplified through use of public and private keys for security and privacy purposes. These transfers can be done with minimal processing fees, allowing users to avoid the steep fees charged by traditional financial institutions.
In 2016, you‘ll have a hard time finding a major bank, a big accounting firm, a prominent software company or a government that did not research cryptocurrencies, publish a paper about it or start a so-called blockchain-project
Announcing the first release of Bitcoin, a new electronic cash system that uses a peer-to-peer network to prevent double-spending. It’s completely decentralized with no server or central authority. – Satoshi Nakamoto, 09 January 2009, announcing Bitcoin on SourceForge.
after more than a decade of failed Trusted Third Party based systems (Digicash, etc), they see it as a lost cause. I hope they can make the distinction, that this is the first time I know of that we’re trying a non-trust based system. – Satoshi Nakamoto in an E-Mail to Dustin Trammell
What Are Cryptocurrencies Really?
If you take away all the noise around cryptocurrencies and reduce it to a simple definition, you find it to be just limited entries in a database no one can change without fulfilling specific conditions. This may seem ordinary, but, believe it or not: this is exactly how you can define a currency.
Take the money on your bank account: What is it more than entries in a database that can only be changed under specific conditions? You can even take physical coins and notes: What are they else than limited entries in a public physical database that can only be changed if you match the condition than you physically own the coins and notes? Money is all about a verified entry in some kind of database of accounts, balances, and transactions.
How miners create coins and confirm transactions
Let‘s have a look at the mechanism ruling the databases of cryptocurrencies. A cryptocurrency like Bitcoin consists of a network of peers. Every peer has a record of the complete history of all transactions and thus of the balance of every account.
A transaction is a file that says, “Bob gives X Bitcoin to Alice“ and is signed by Bob‘s private key. It‘s basic public key cryptography, nothing special at all. After signed, a transaction is broadcasted in the network, sent from one peer to every other peer. This is basic p2p-technology. Nothing special at all, again.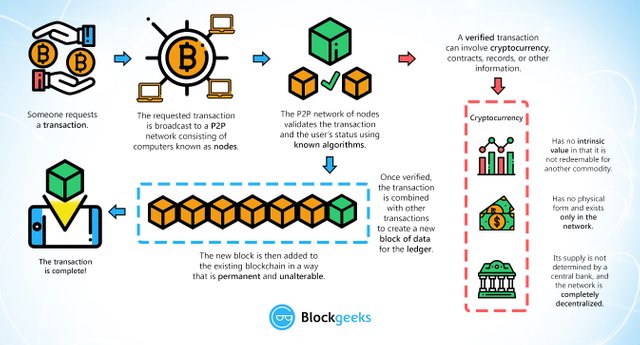
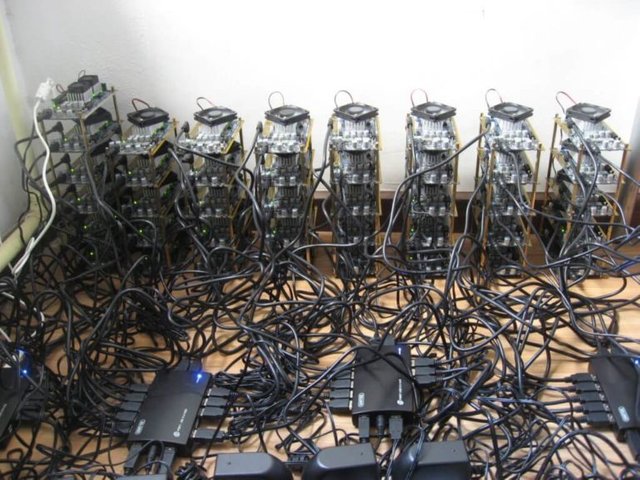

What Are Miners Doing?
Principally everybody can be a miner. Since a decentralized network has no authority to delegate this task, a cryptocurrency needs some kind of mechanism to prevent one ruling party from abusing it. Imagine someone creates thousands of peers and spreads forged transactions. The system would break immediately.
So, Satoshi set the rule that the miners need to invest some work of their computers to qualify for this task. In fact, they have to find a hash – a product of a cryptographic function – that connects the new block with its predecessor. This is called the Proof-of-Work. In Bitcoin, it is based on the SHA 256 Hash algorithm.